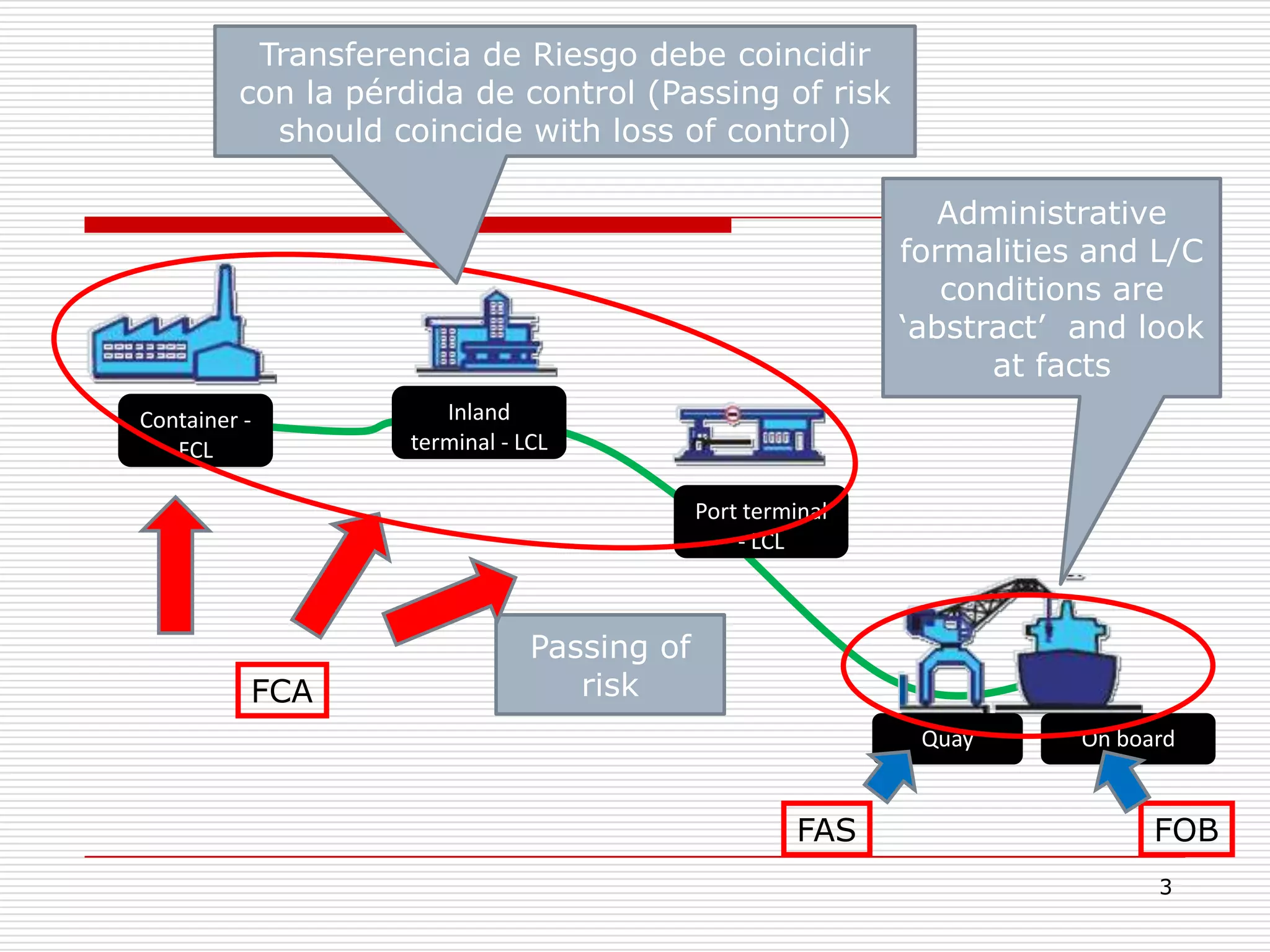
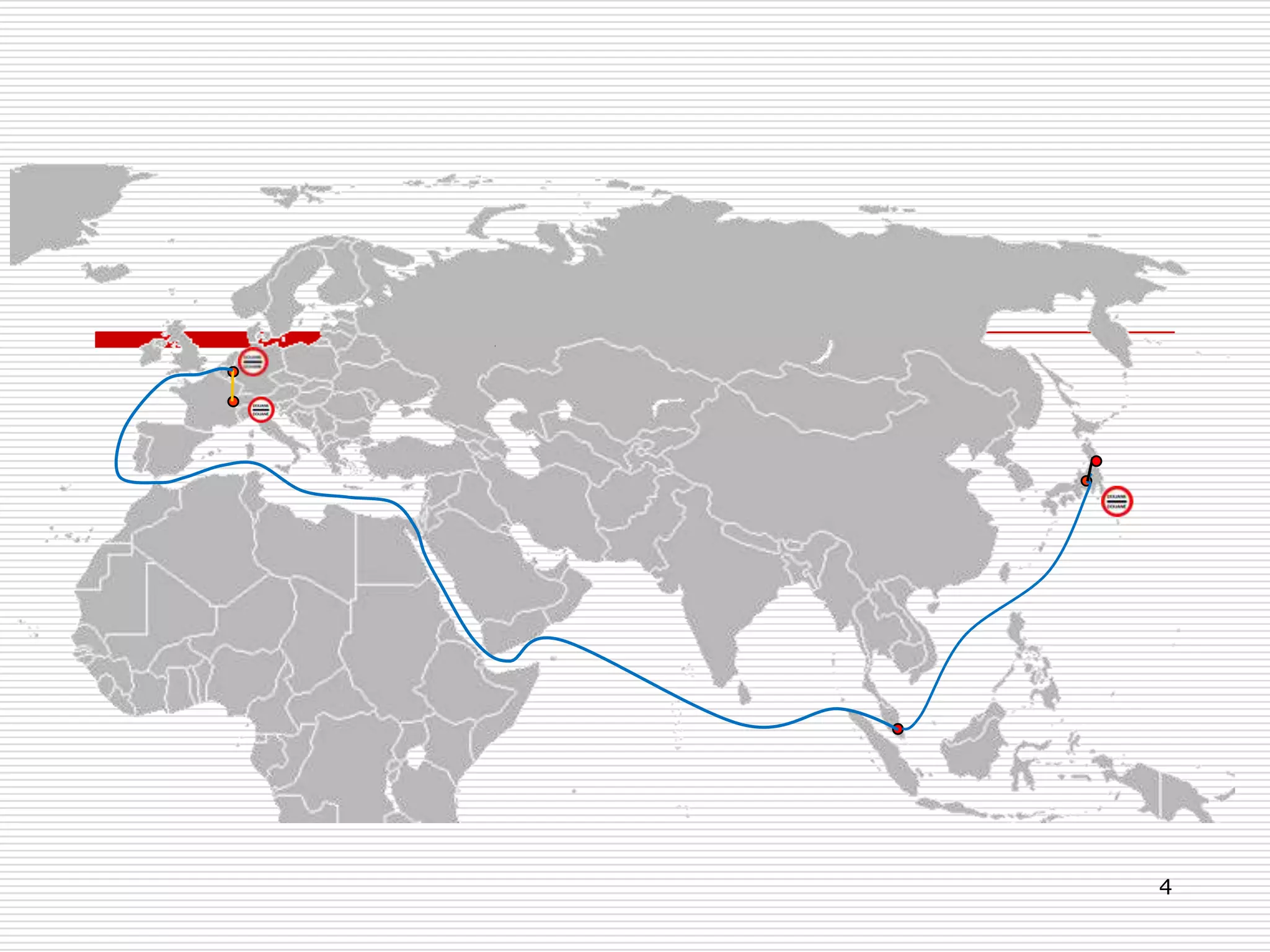
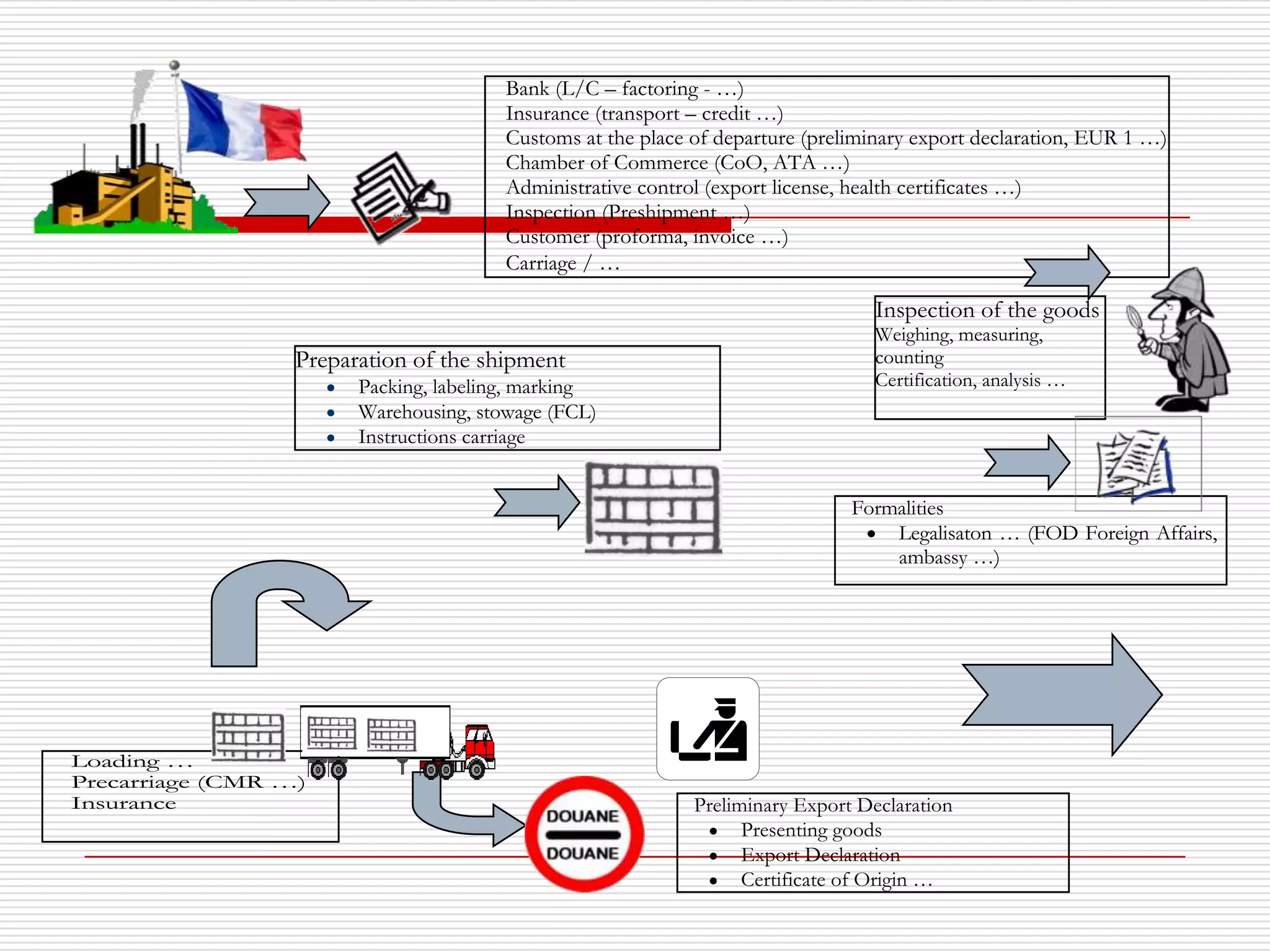
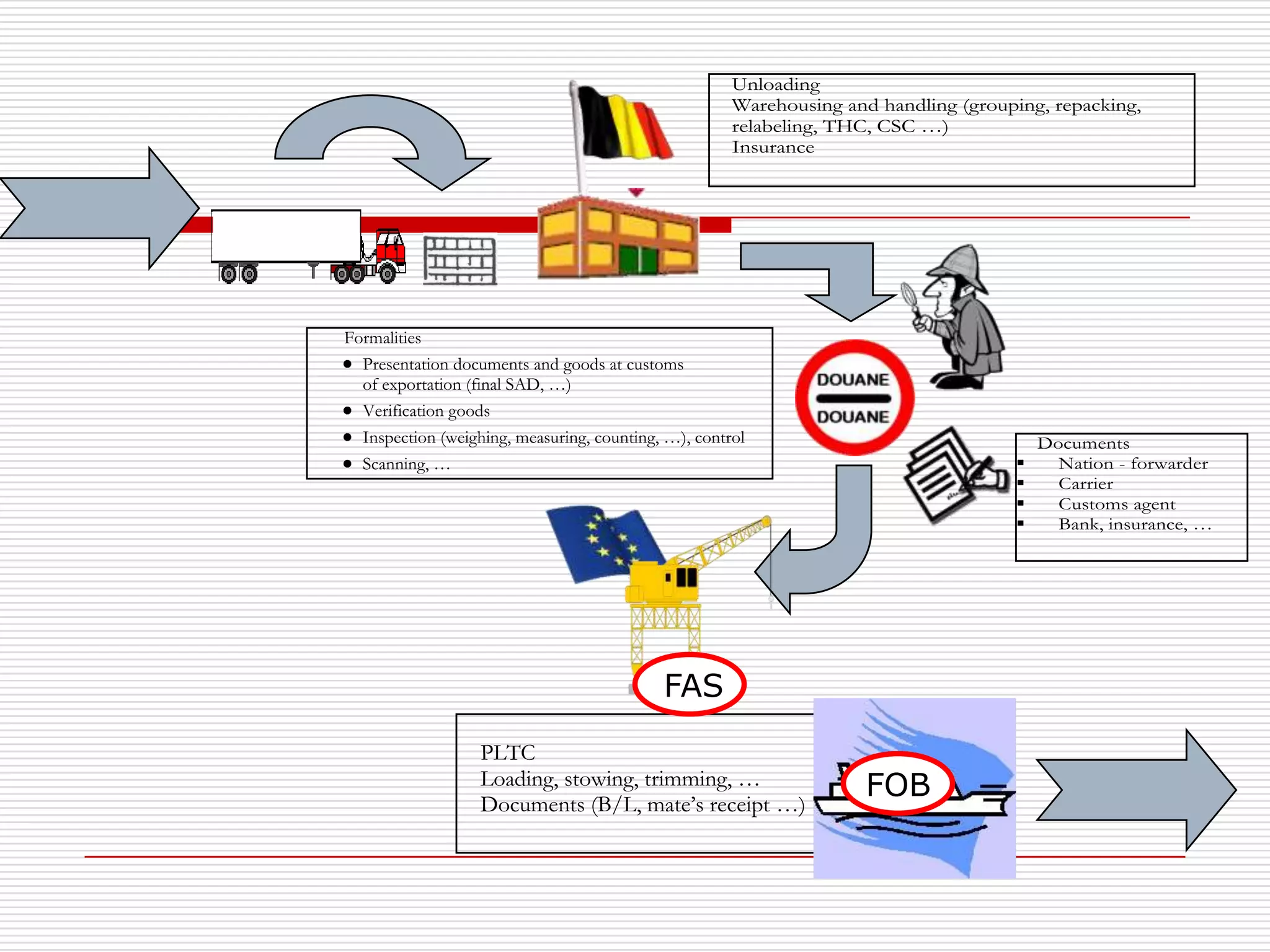
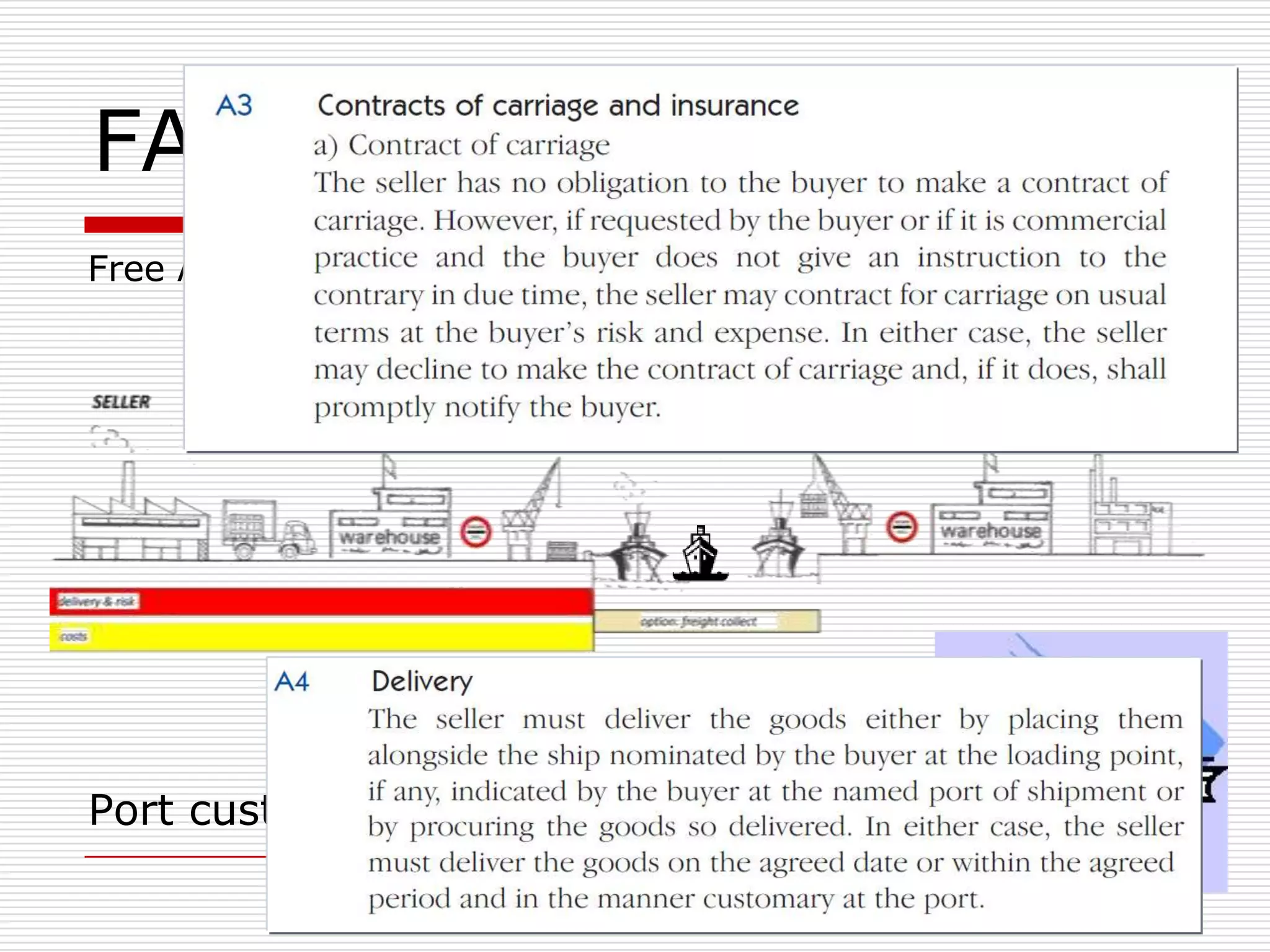
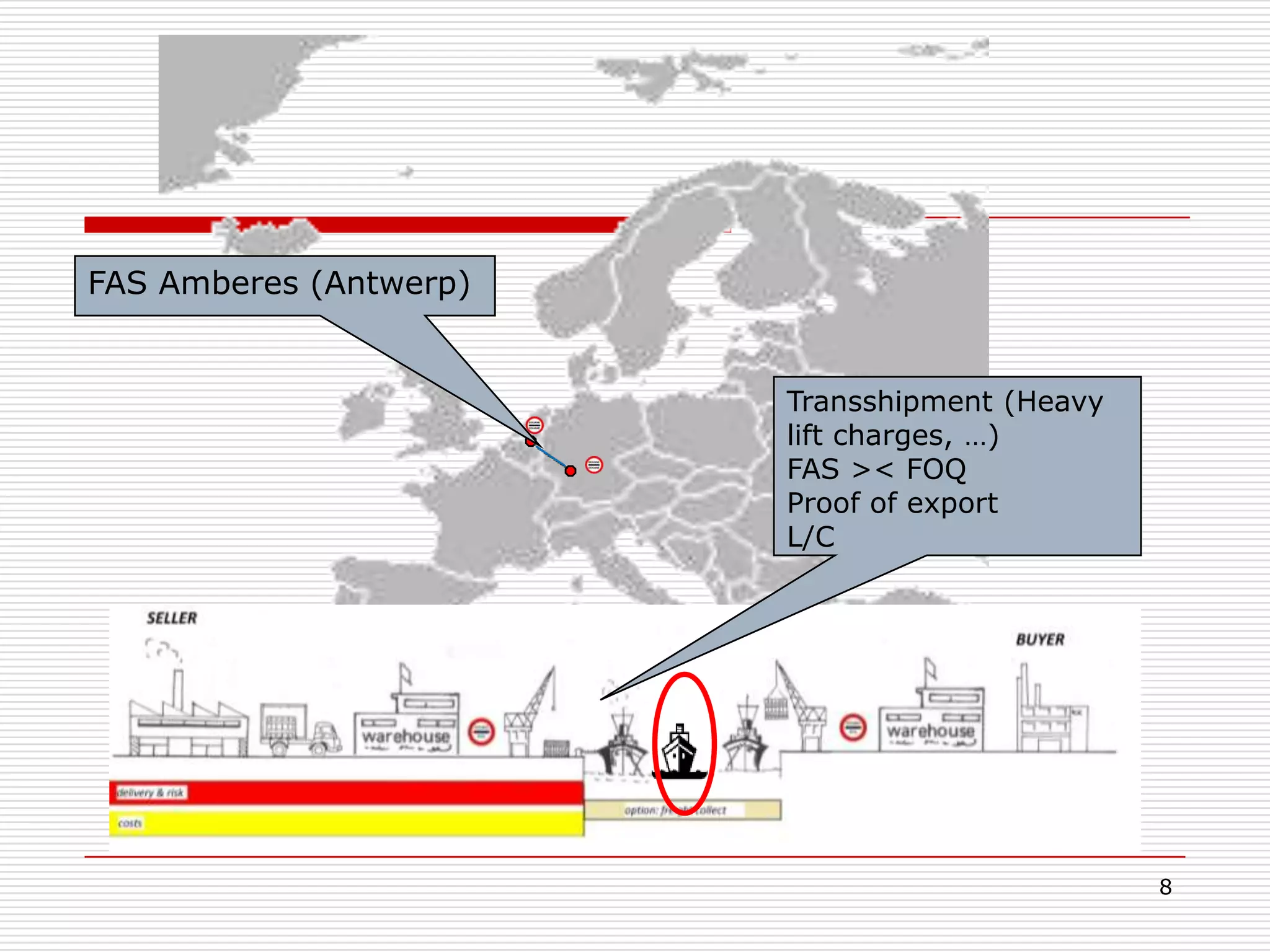
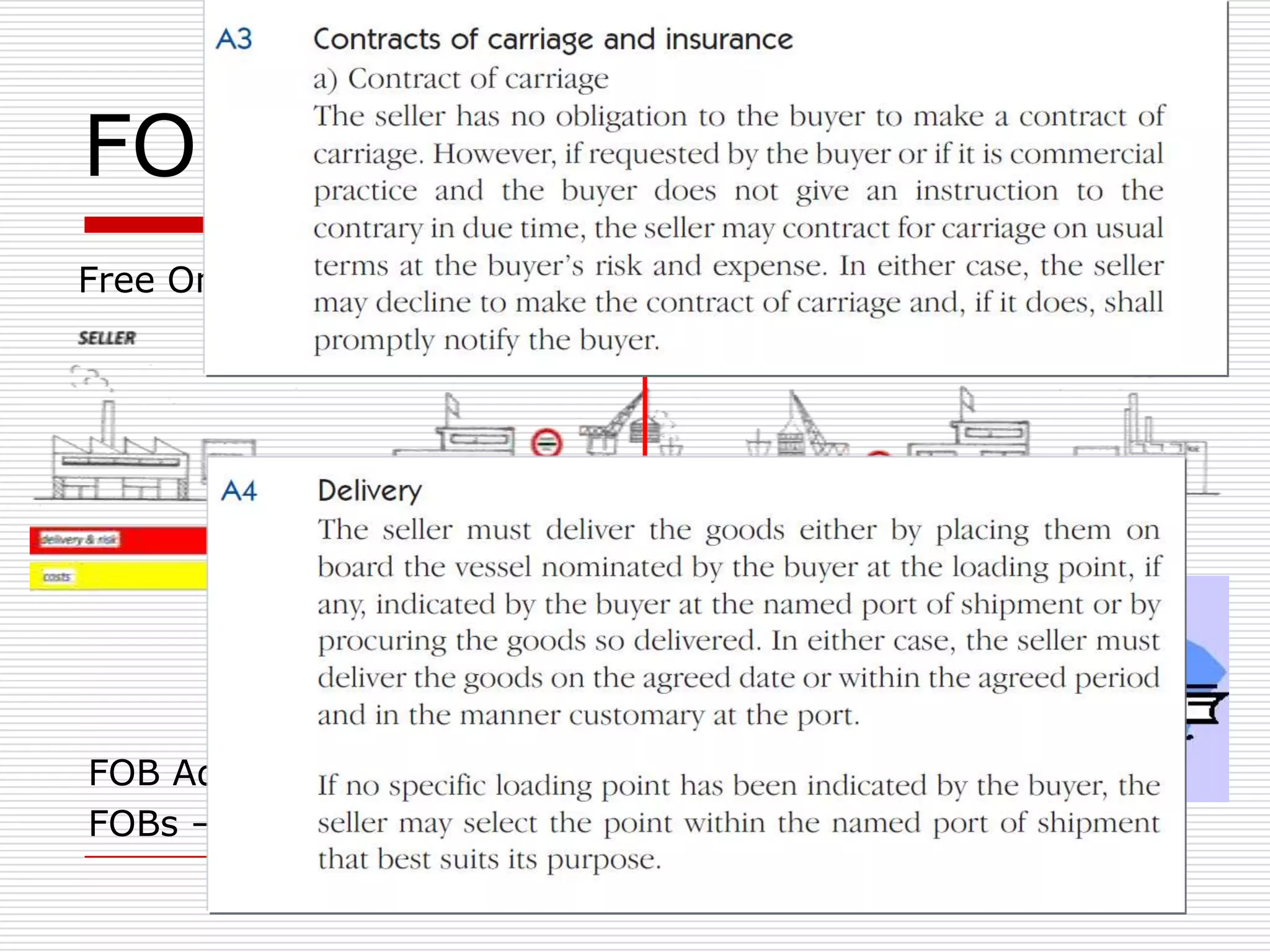
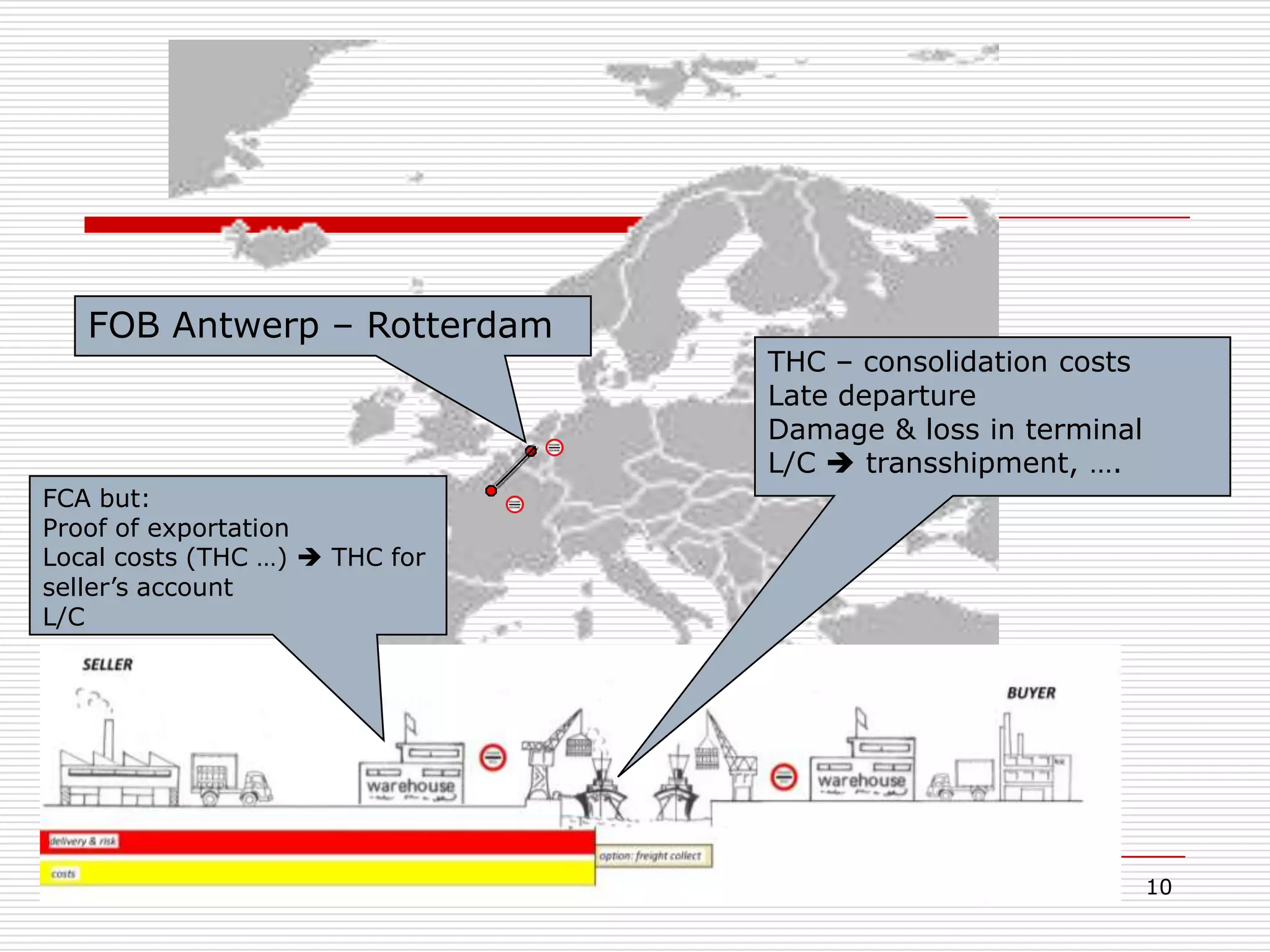
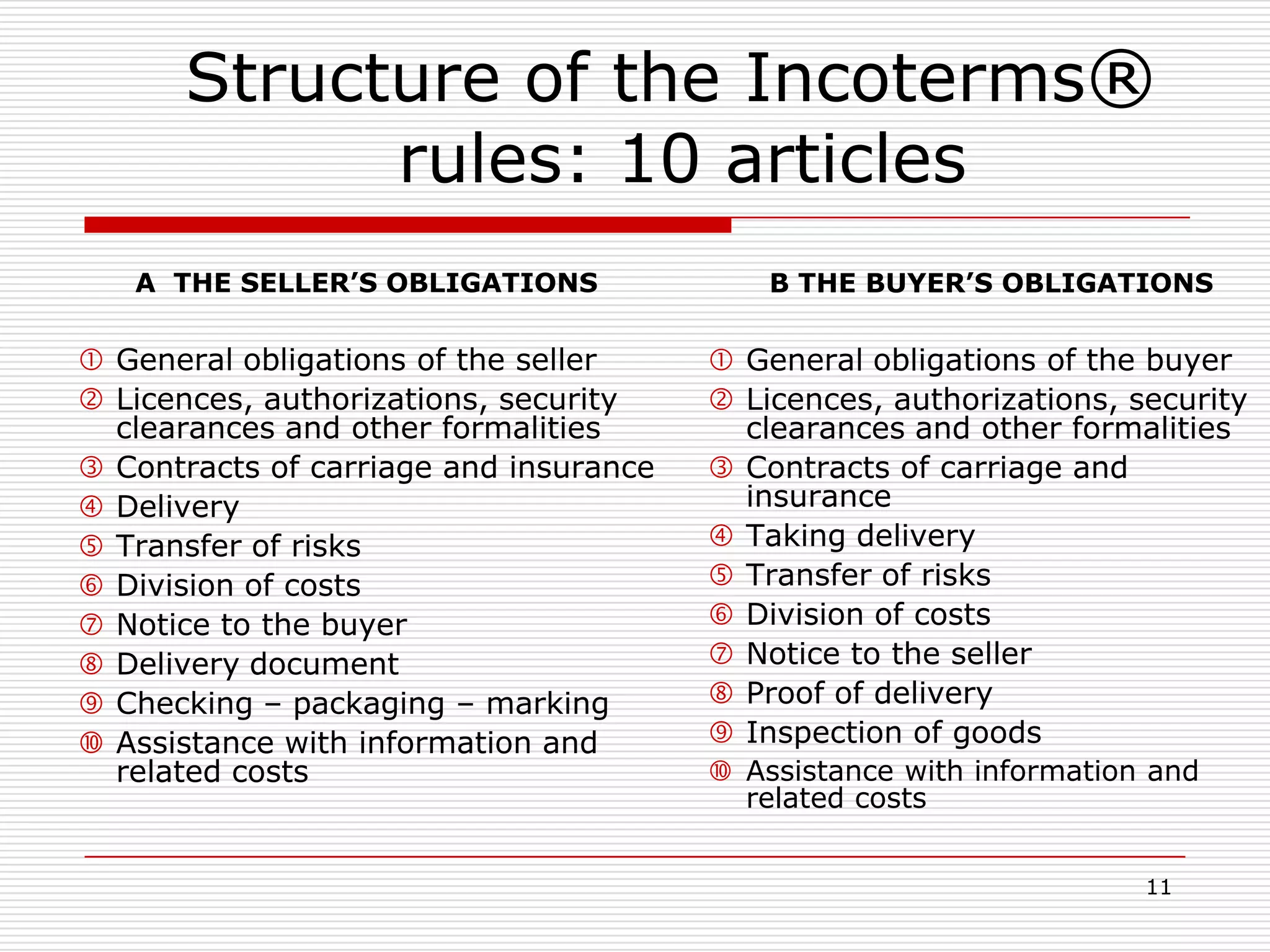
The document discusses Incoterms 2010 rules, which govern international commercial terms. It is structured in two main sections (A and B) that define the obligations of the seller and buyer. Section A covers topics for the seller like delivery, transfer of risks, costs, and notices. Section B covers the buyer's obligations regarding taking delivery, proof of delivery, and inspection of goods. The document also discusses how Incoterms rules define delivery but not legal ownership, and how passage of title and risk are important for accounting, customs, and VAT purposes.



![Incoterms and
transfer of title
Delivery vs. legal ownership
Delivery Incoterms ® Rules
Legal ownership contract national law
Legal title – economic ownership (title –
property – ownership)
B/L’s
Leasing - retention of title – consignment
stock
Contract – Accounting – Customs – VAT
- …
Product sales will be recorded as revenue upon passage of title of
goods from the company to a third party customer. All sales should be
made on shipping terms of "FOB shipping point". Accordingly,
passage of title is deemed to occur upon physical delivery of goods to
a common carrier. All invoices should specify in the conditions of sale
that title to the goods shall pass to the buyer upon delivery to the
carrier (i.e., shipping terms are FOB shipping point). In international
markets, the terms utilized to convey "FOB shipping point" may be
different (e.g. CIF, EXW, FCA). We should not sell products on terms
that are legally considered to be "FOB destination point."
VAT art. 14.1 Directive 2006/112/EC.
"Supply of goods" shall mean the transfer of the right to dispose
of tangible property as owner.
IAS 18.14:
Revenue arising from the sale of goods should be recognised when
all of the following criteria have been satisfied: [IAS 18.14]
1. the seller has transferred to the buyer the significant risks and
rewards of ownership
2. the seller retains neither continuing managerial involvement to
the degree usually associated with ownership nor effective
control over the goods sold
3. the amount of revenue can be measured reliably
4. it is probable that the economic benefits associated with the
transaction will flow to the seller, and
5. the costs incurred or to be incurred in respect of the transaction
can be measured reliably](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/masterclassfasfobdraft1-130508110828-phpapp02/75/Masterclass-fasfo-bdraft-1-13-2048.jpg)