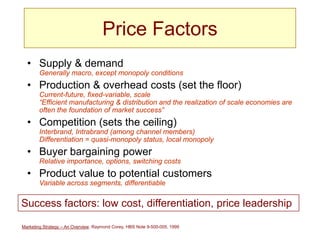
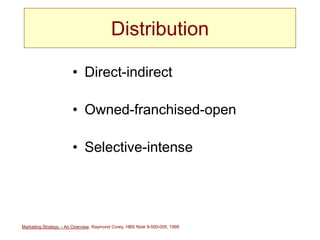
This document provides an overview of marketing strategy at multiple organizational levels and its key elements. It discusses that marketing strategy determines how products and services are delivered to markets through decisions around product/market selection, pricing, distribution channels, and communications. The marketing mix of these elements may vary depending on the product, stage of growth, and competitors. Product/market selection involves identifying target market segments and evaluating criteria like product value, growth potential, and company fit. Pricing considerations include costs, competition, customer bargaining power, and product value. Distribution decisions center on using direct or indirect, owned or third-party channels selectively or intensely. Communications objectives aim to create awareness, superiority, purchase information, and additional sales.