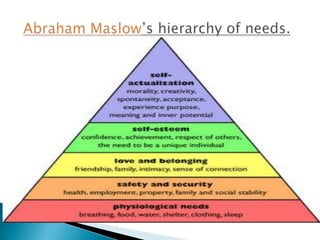
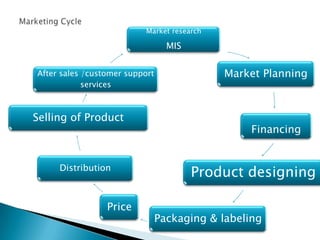
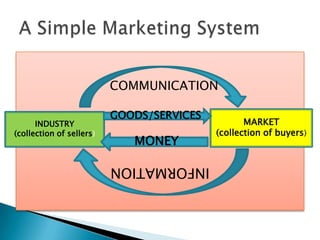
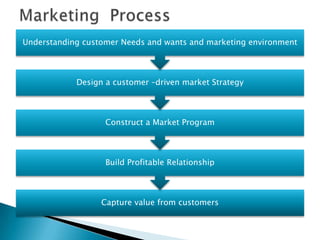
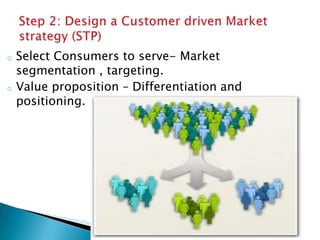
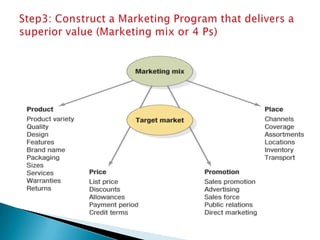
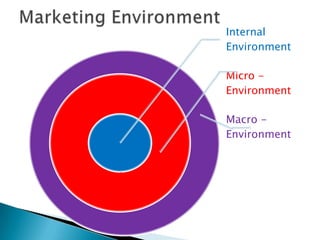
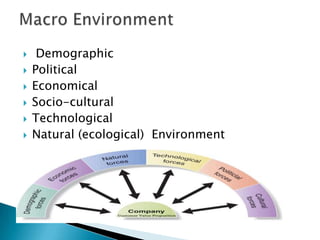
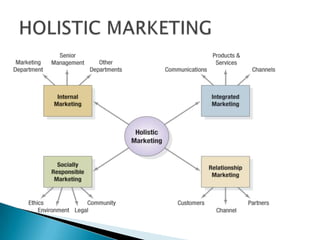
The document discusses key concepts in marketing. It defines marketing as a process of identifying and meeting consumer needs profitably through creating, stimulating, and fulfilling demands. Marketing involves understanding customers and the environment, developing strategies, implementing marketing programs, building relationships, and capturing value. The marketing mix of product, price, place, and promotion are used to create and deliver customer value. Marketing also requires understanding internal operations and external factors like competitors, suppliers, and the broader social, economic, technological environment.