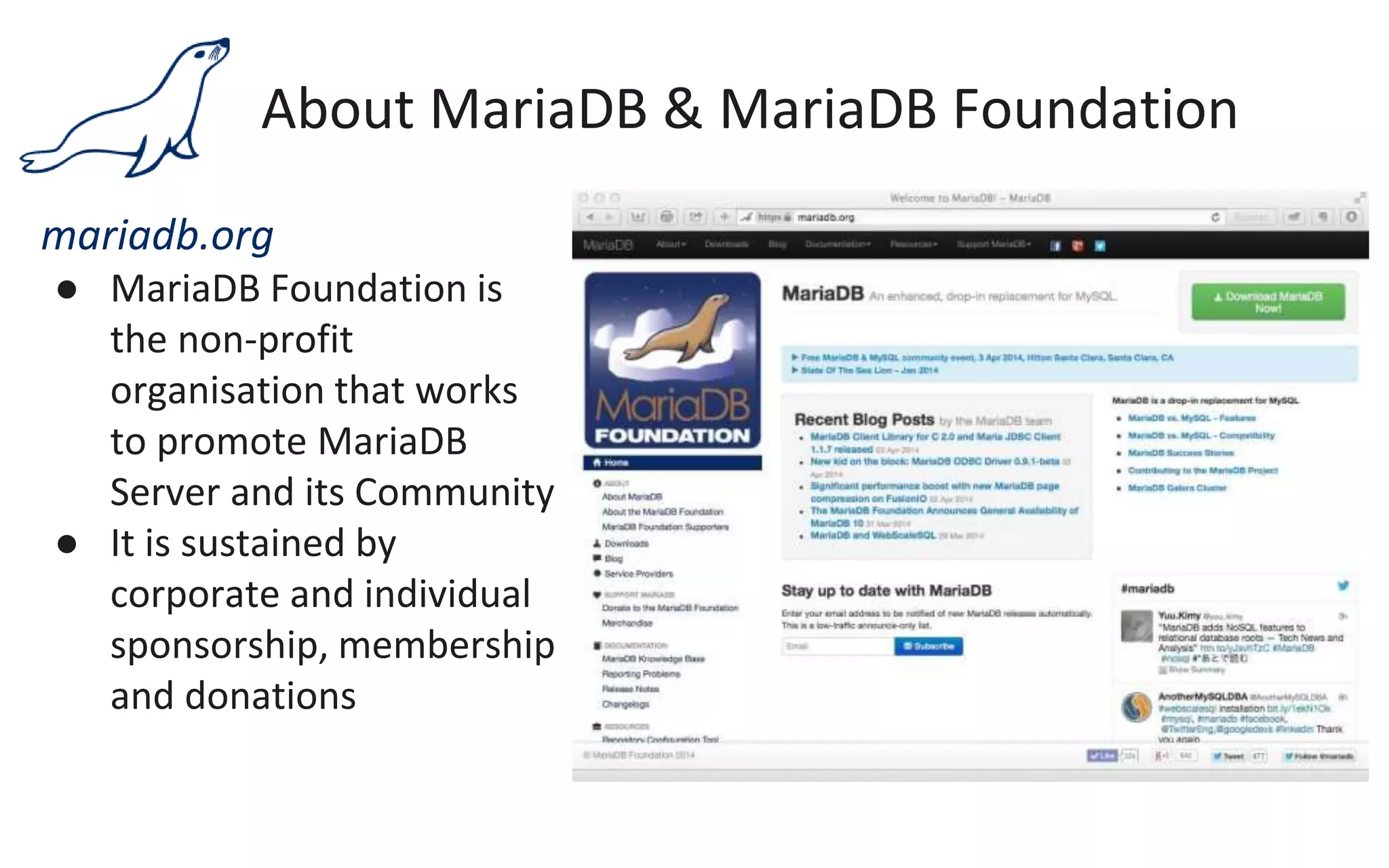
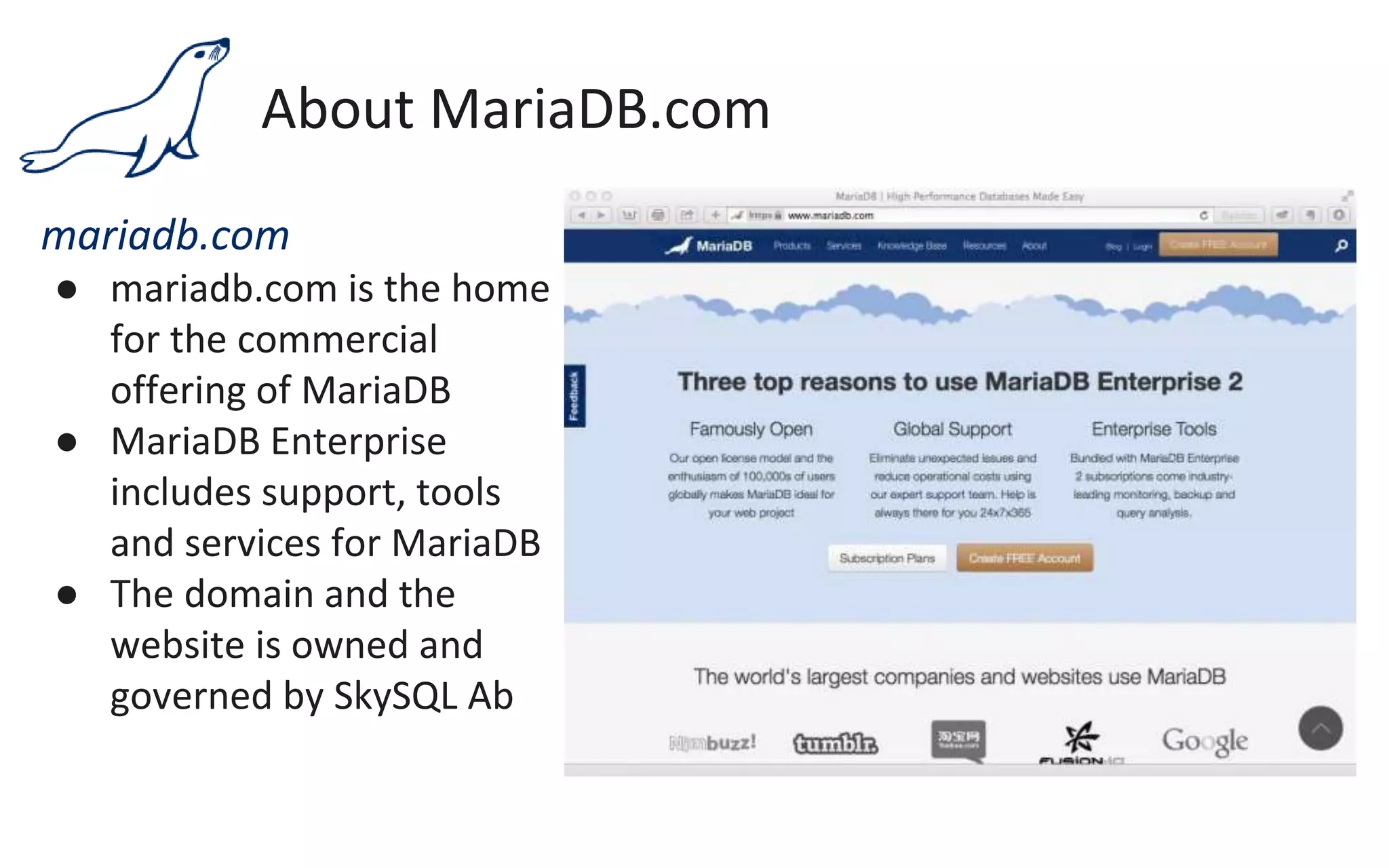
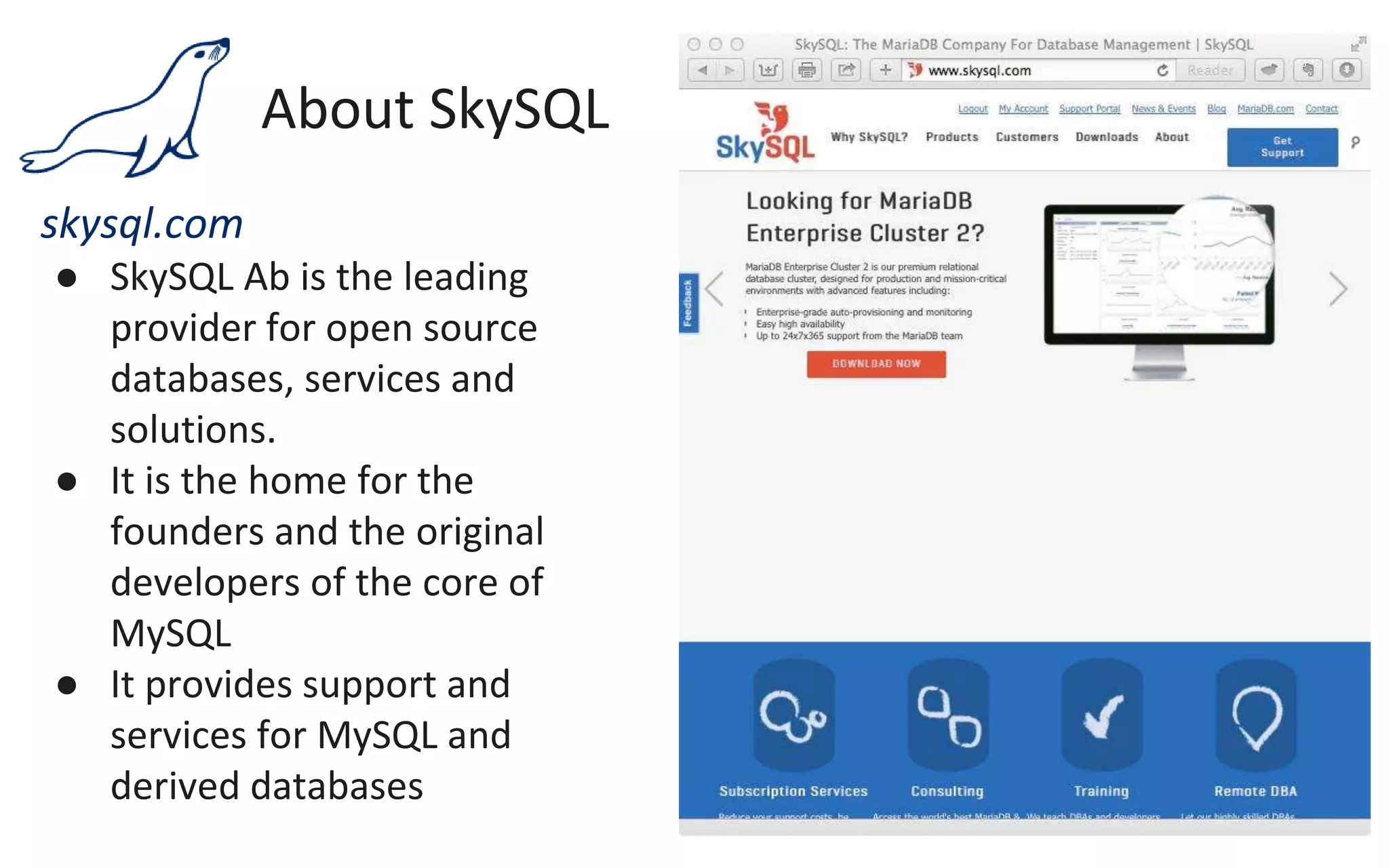
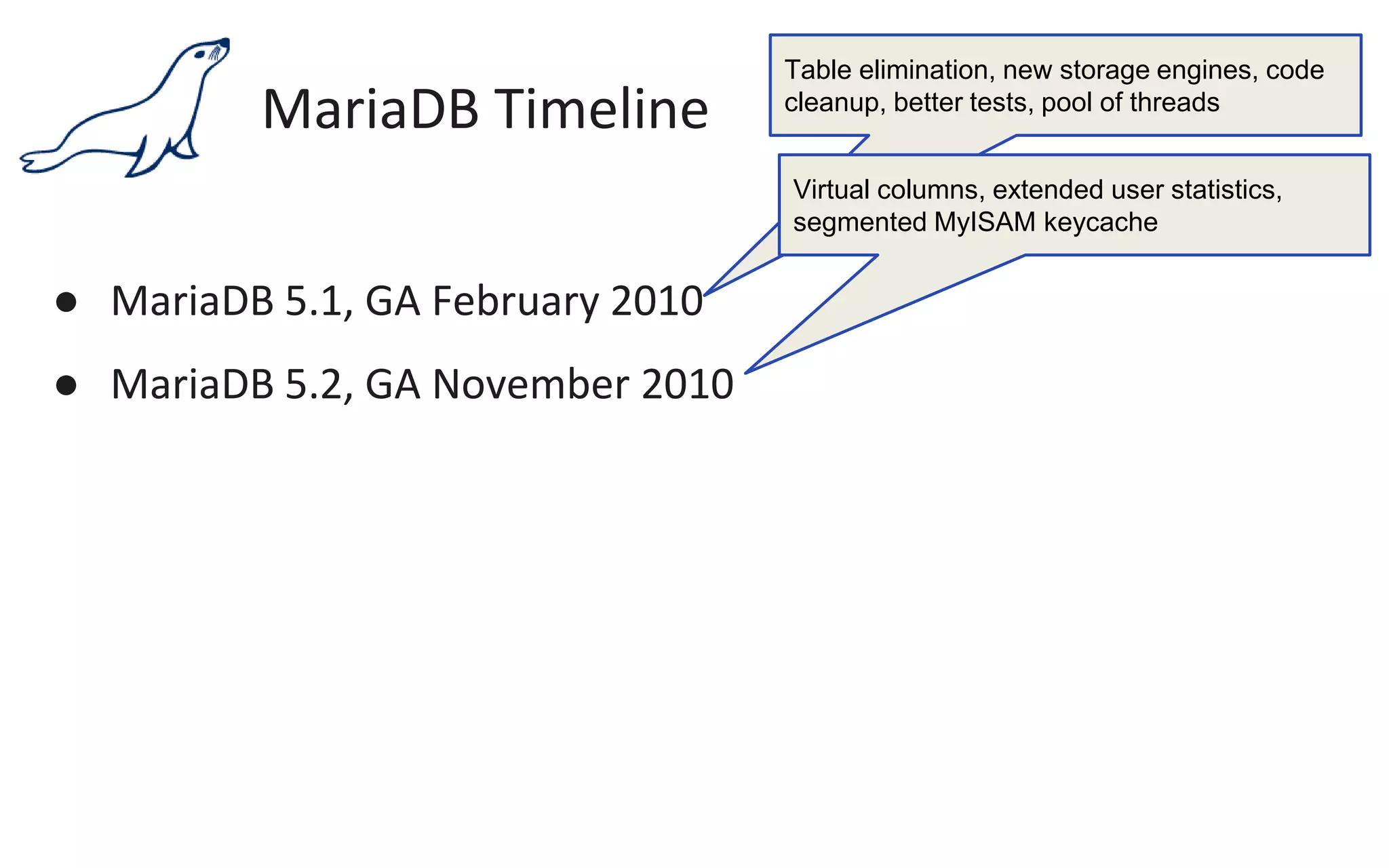
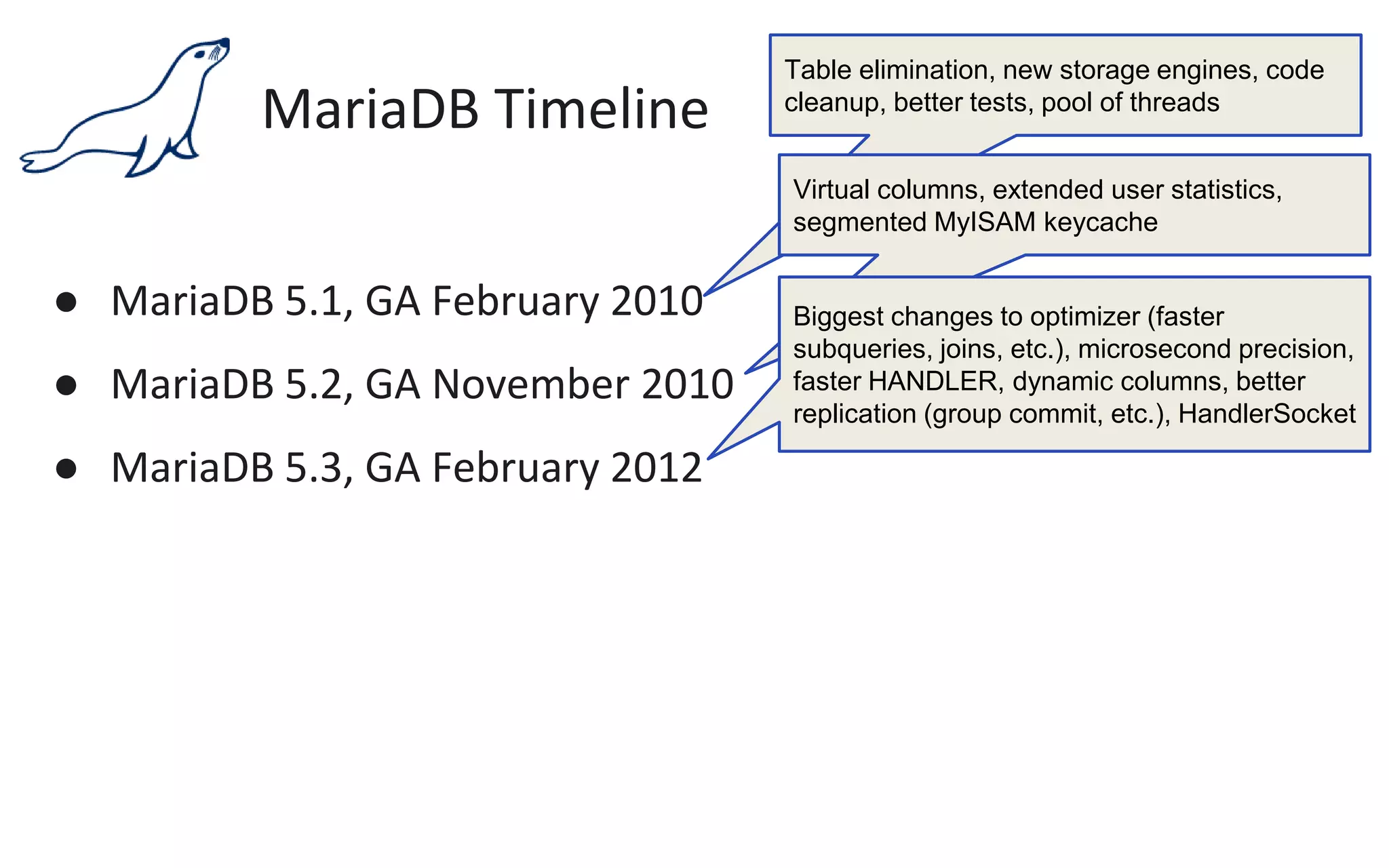
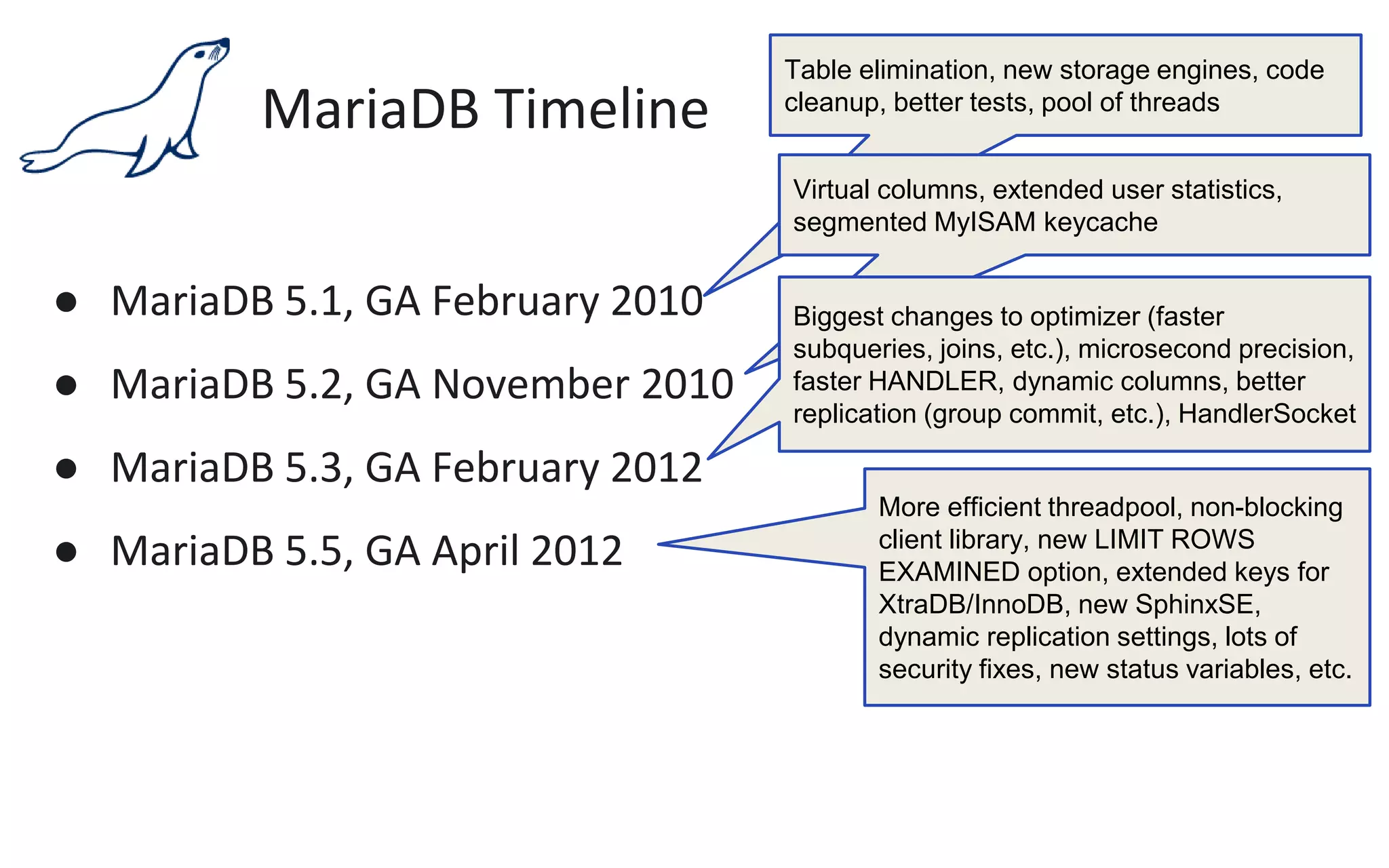
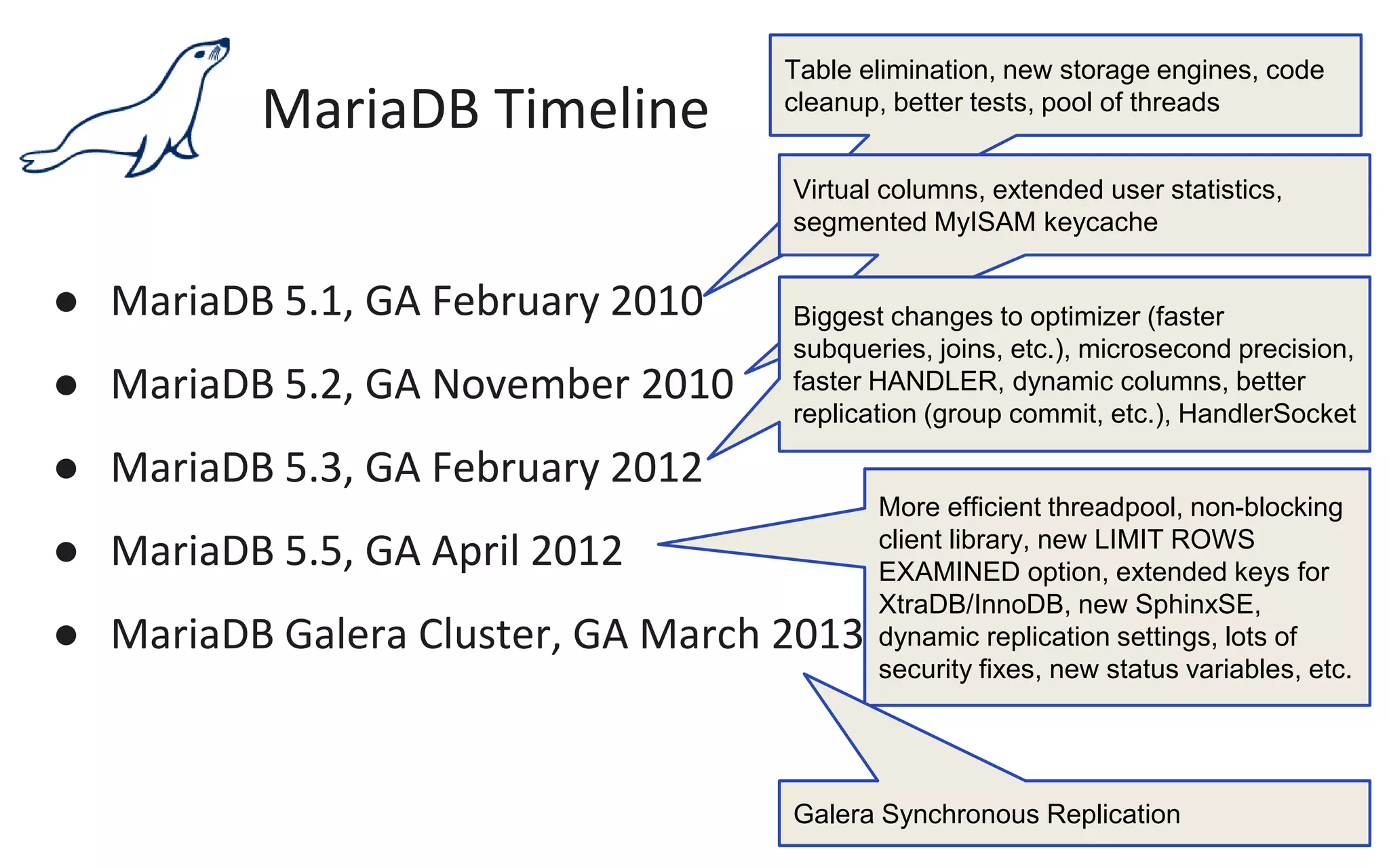
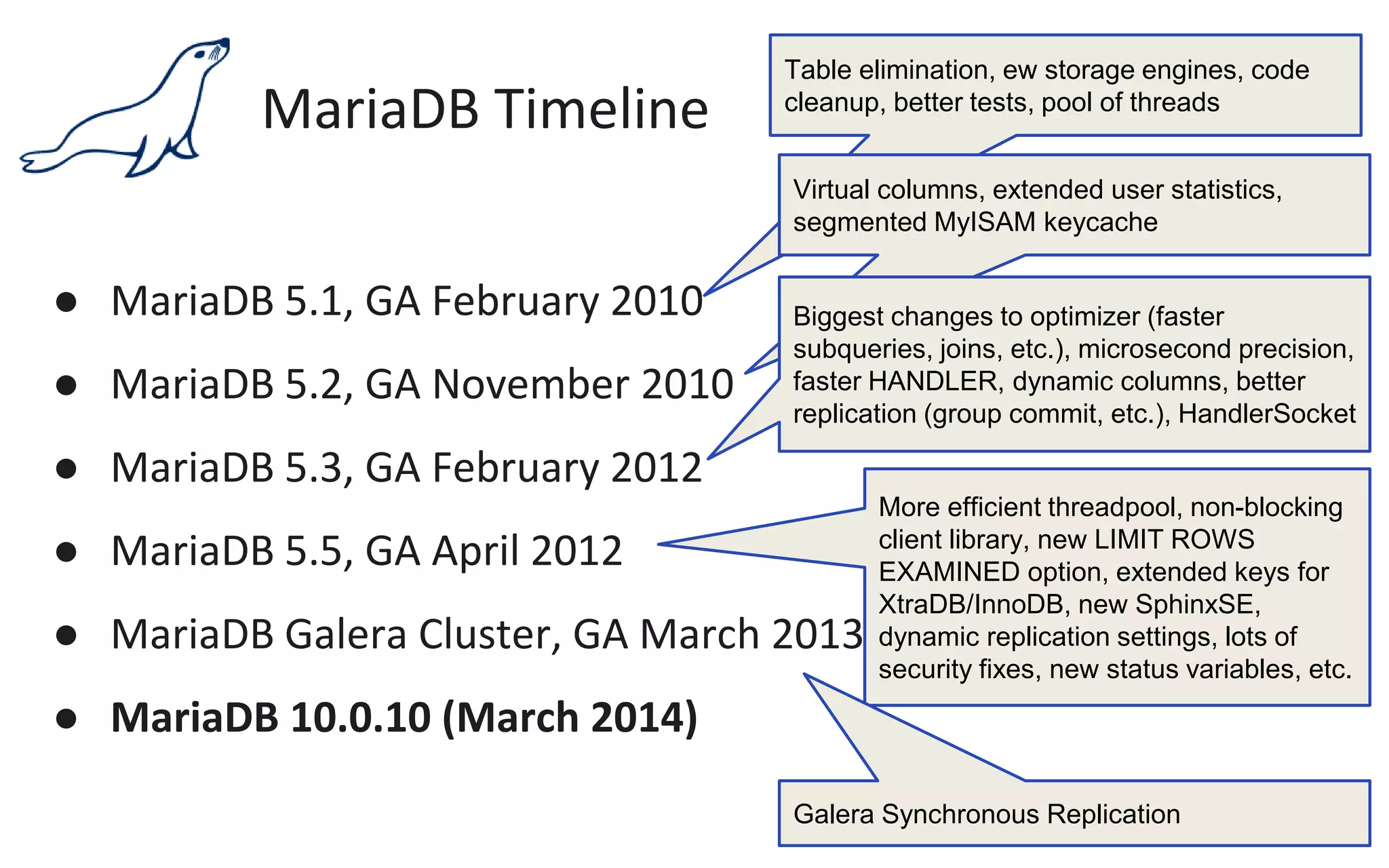
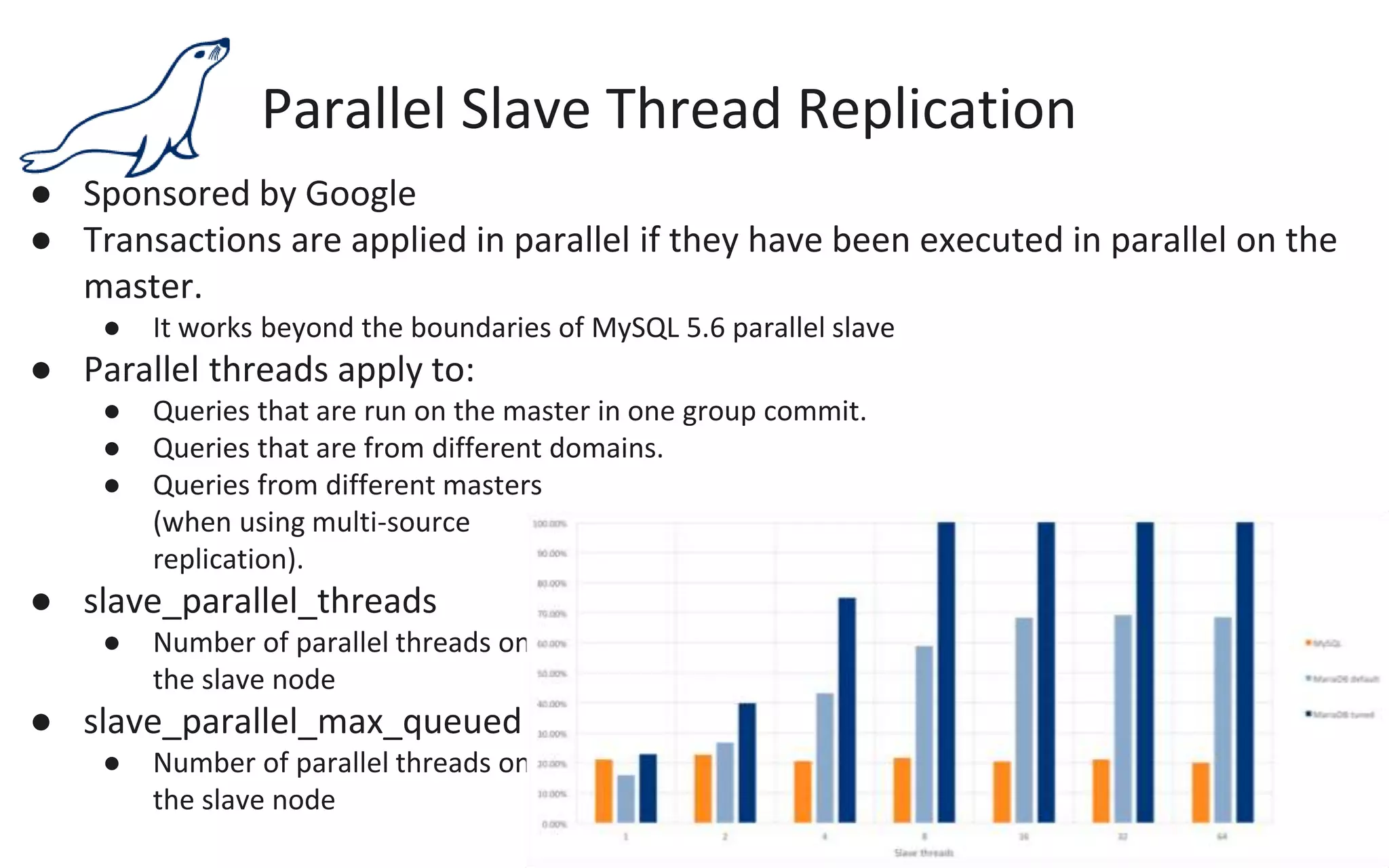
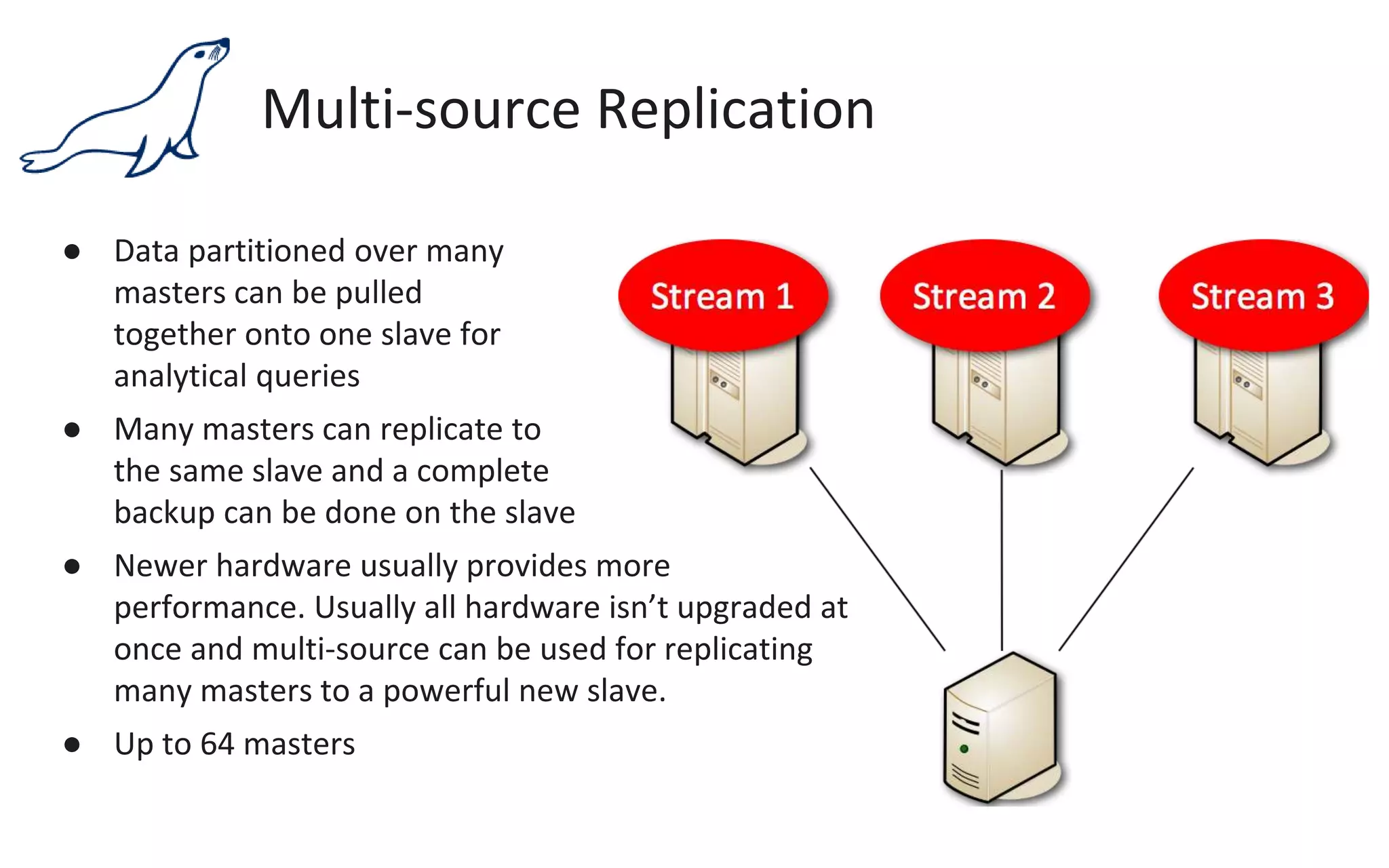
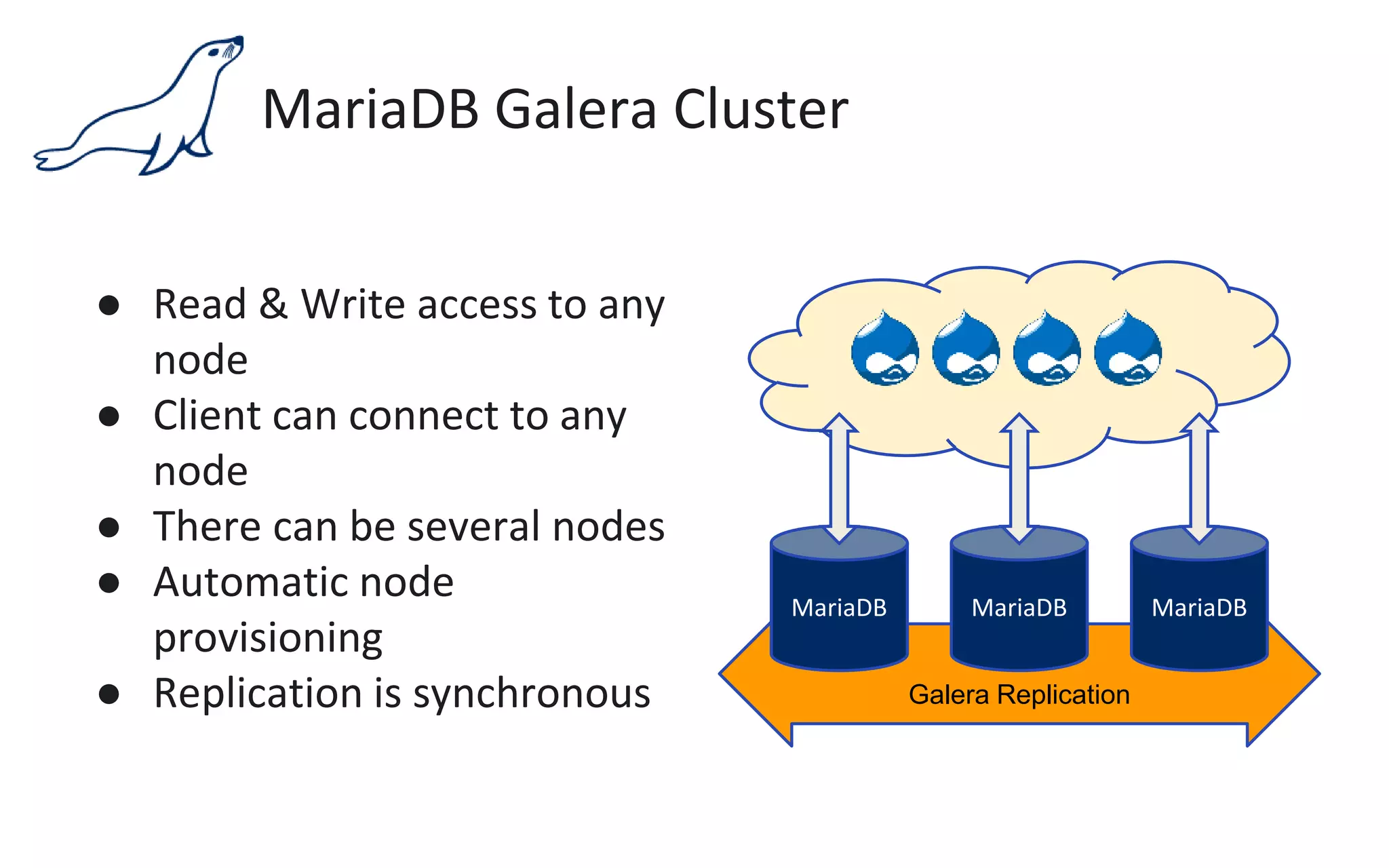
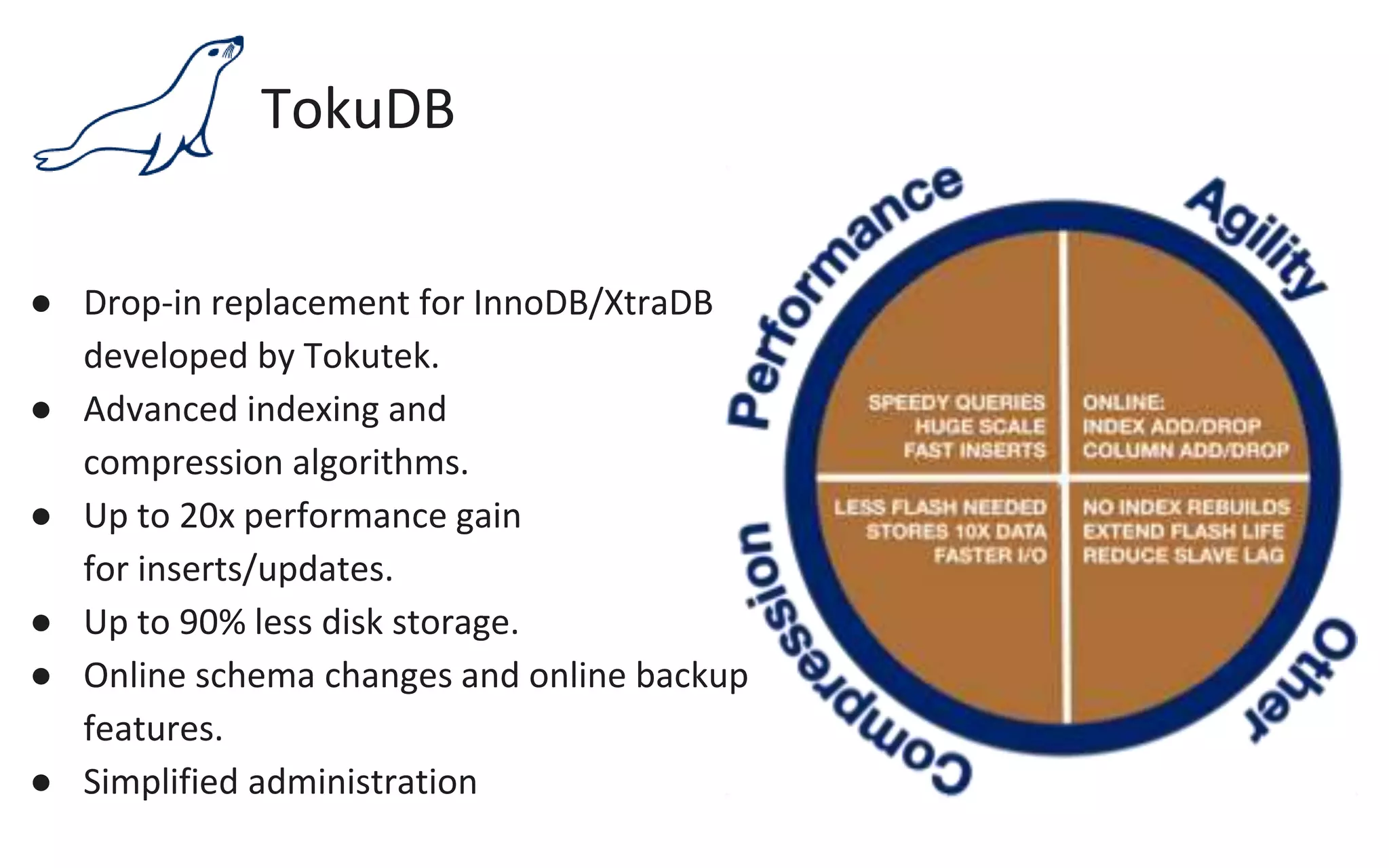
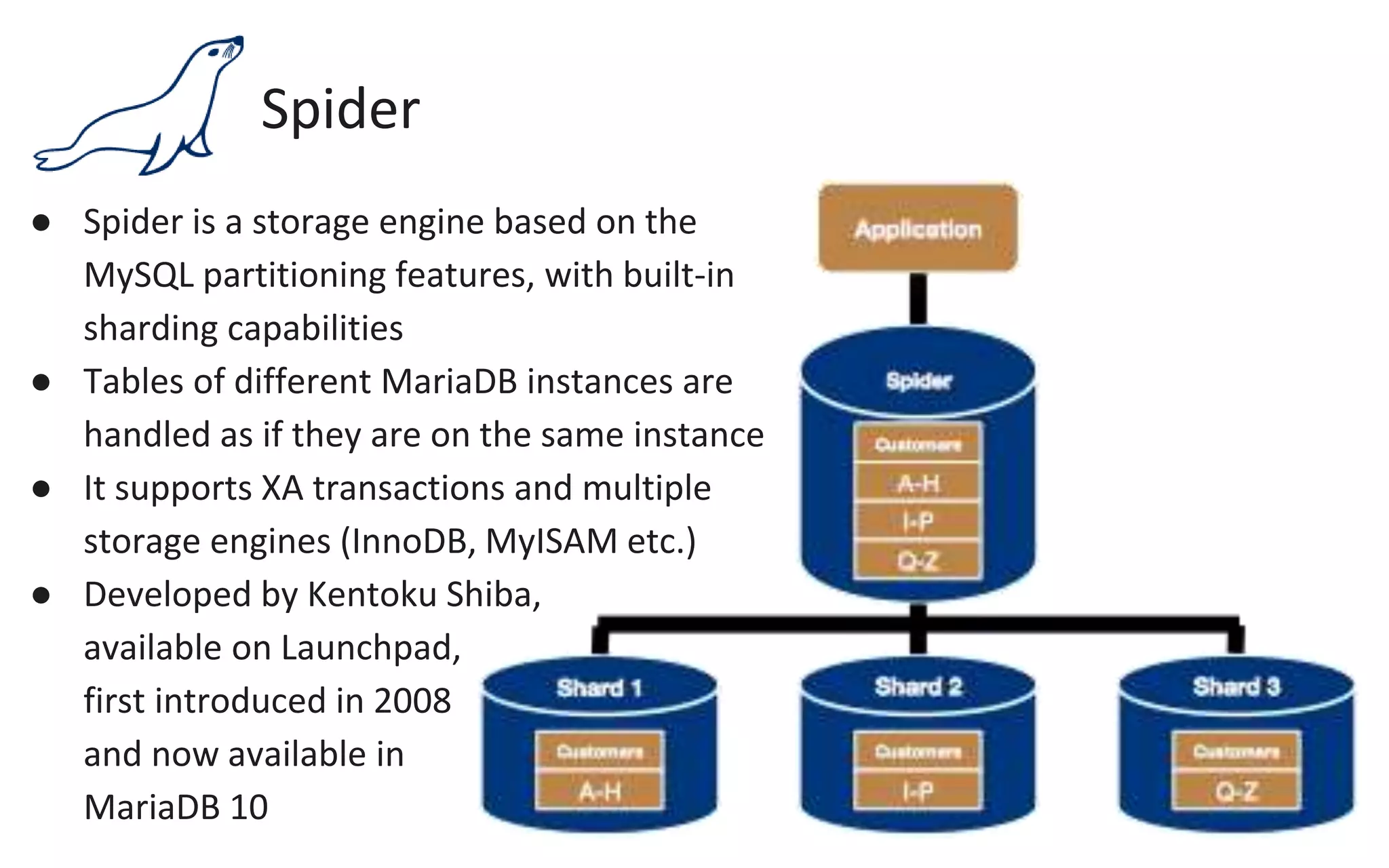
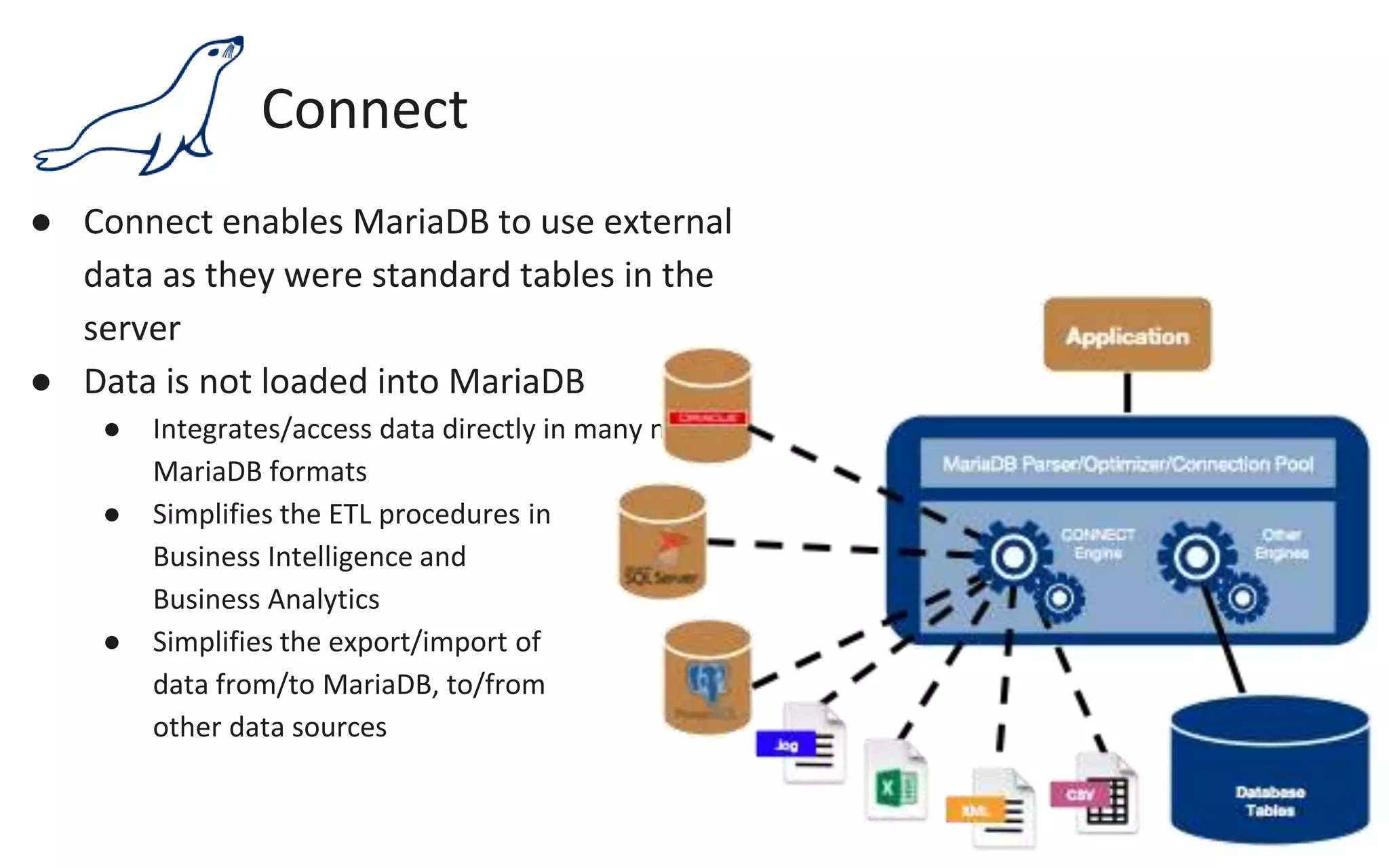
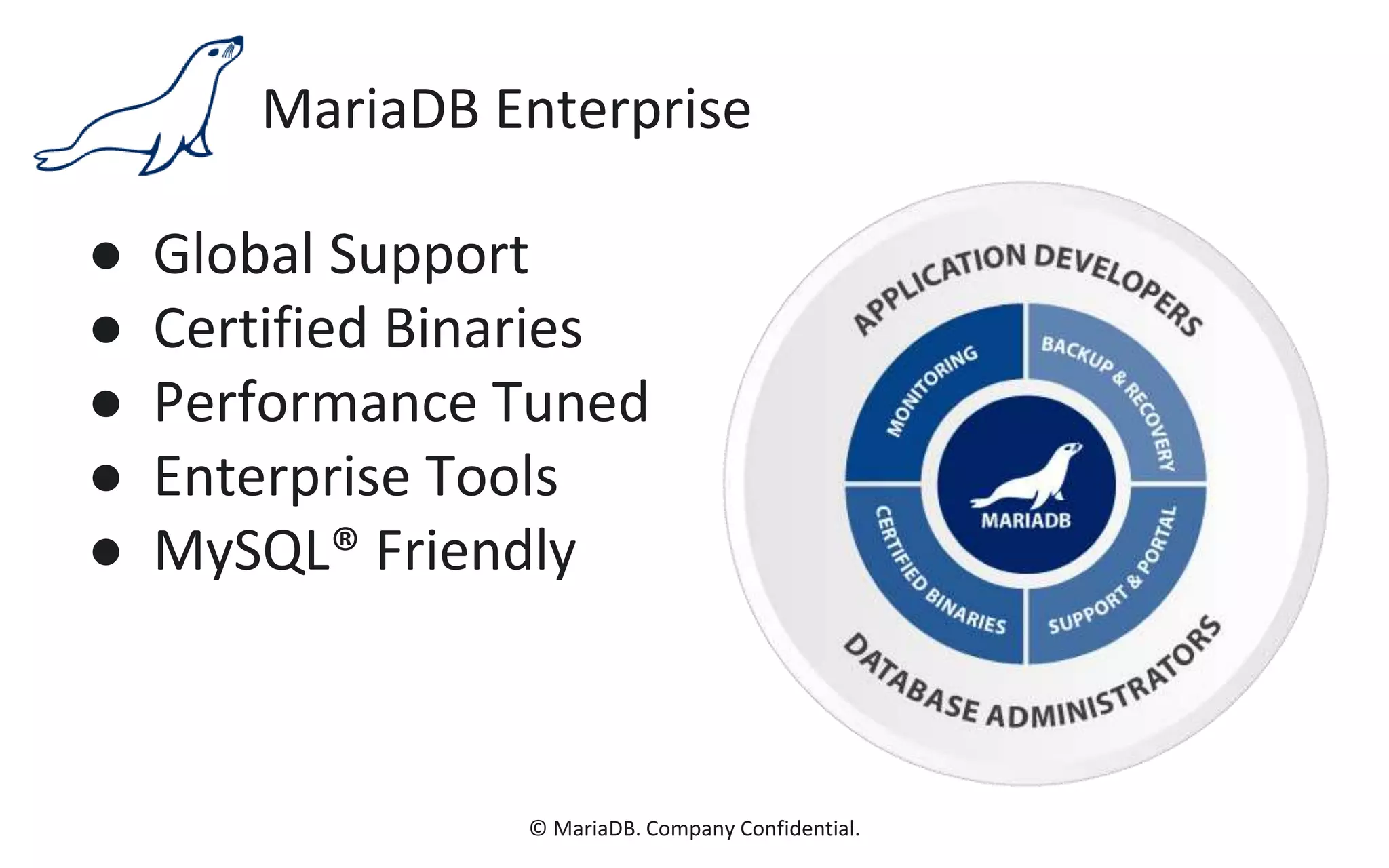
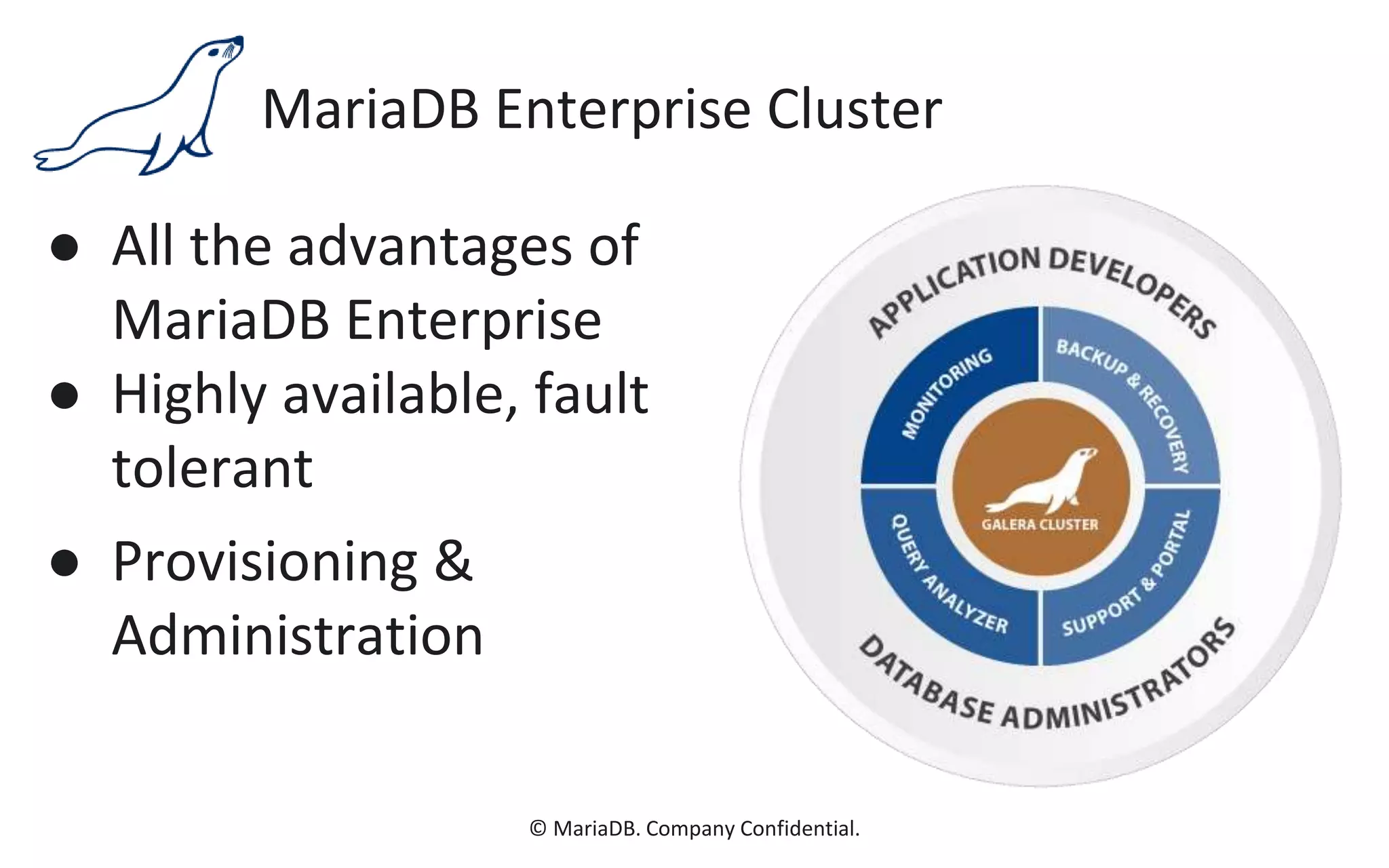
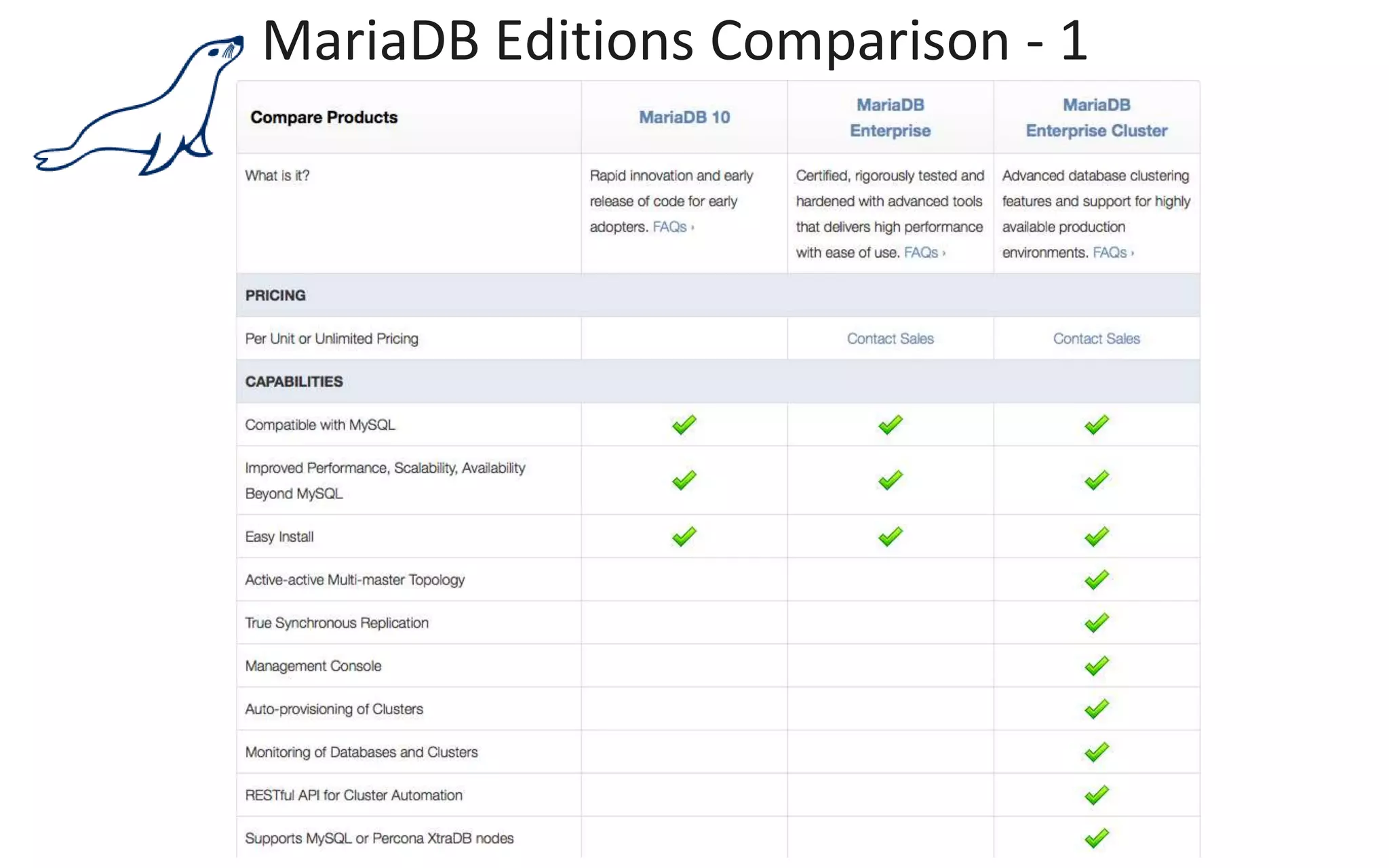
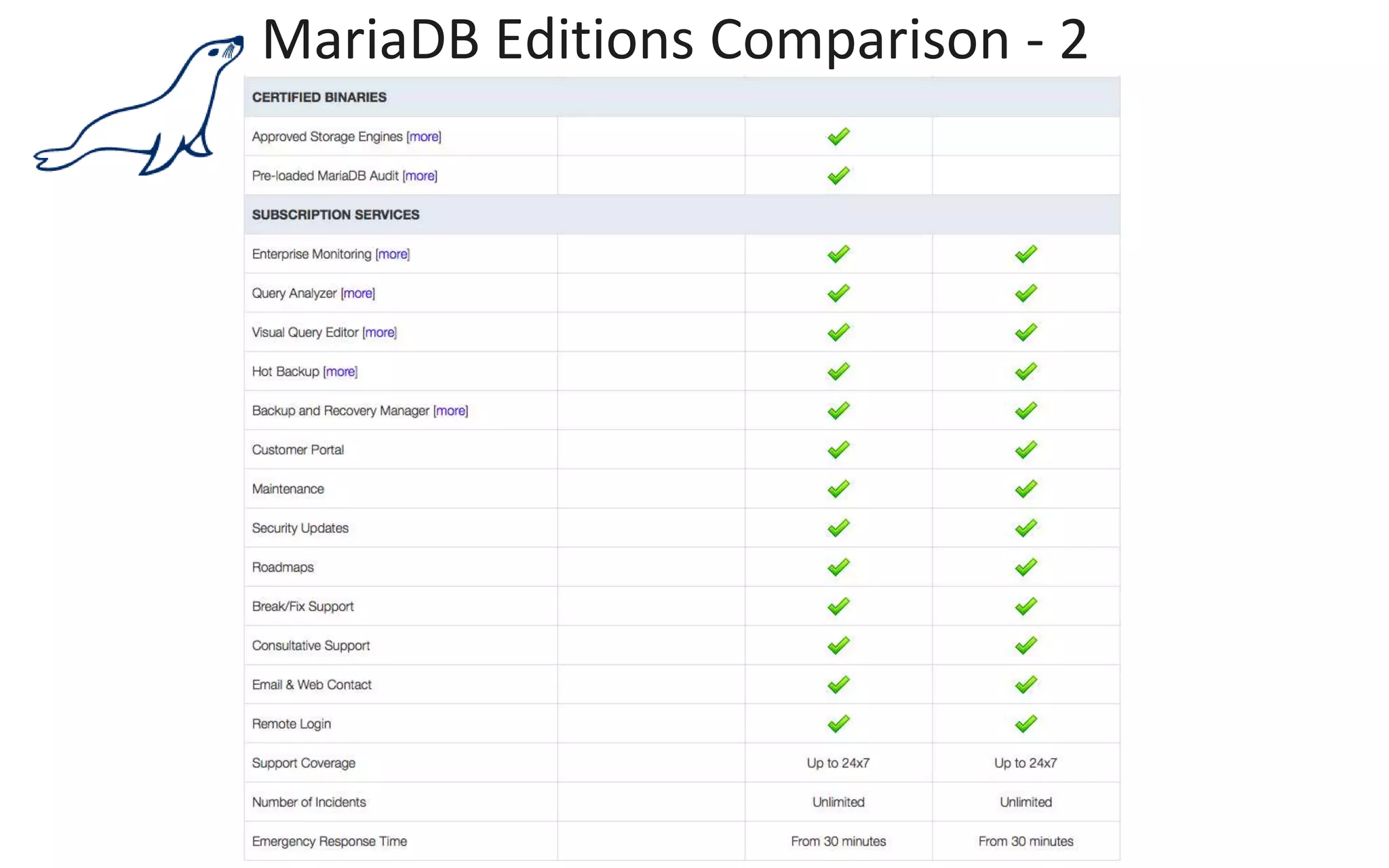
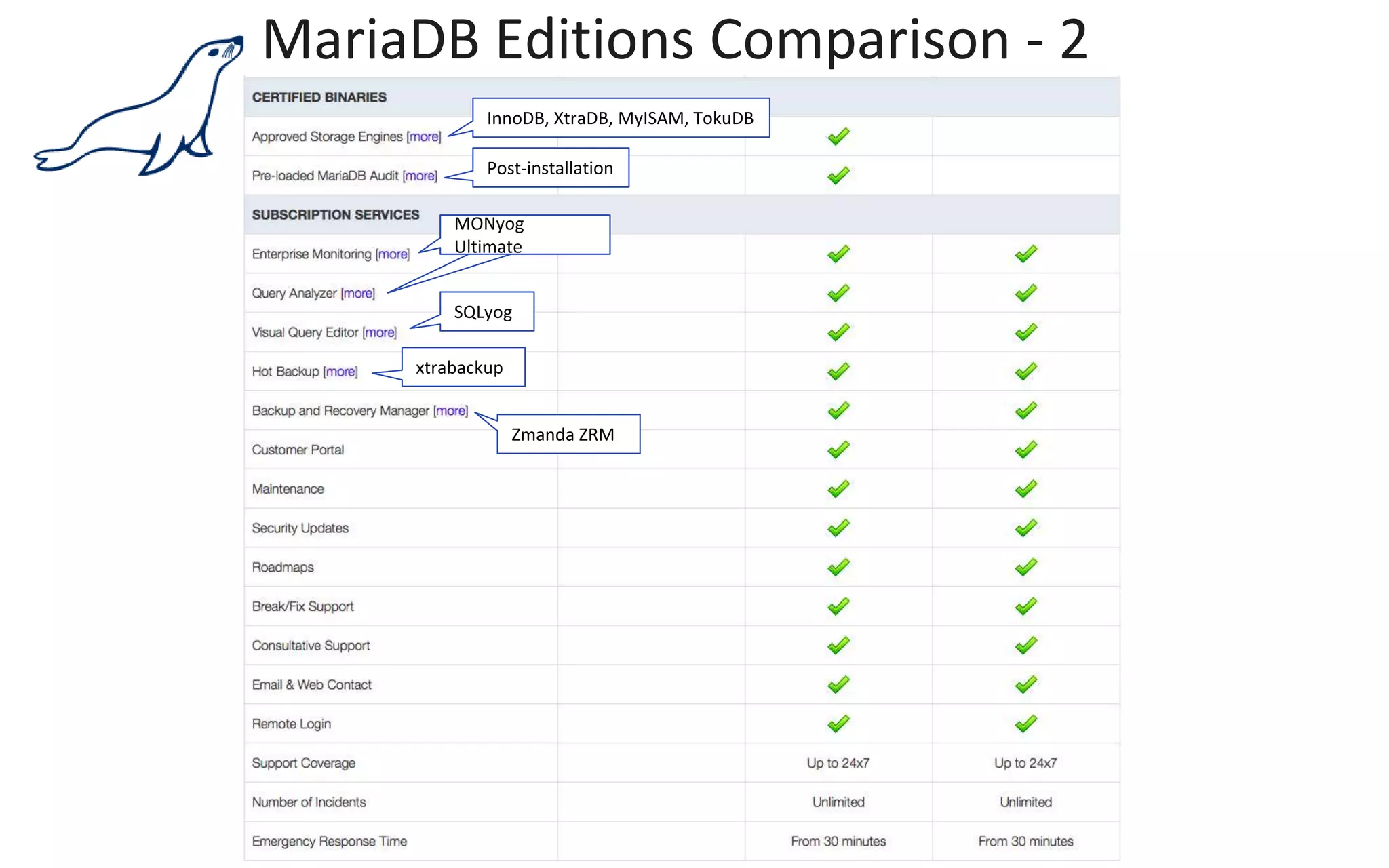
The document presents an overview of MariaDB, a community-developed database management system that is a fork of MySQL, highlighting its history, features, and various editions including MariaDB Enterprise and MariaDB Enterprise Cluster. It discusses significant enhancements across different versions, with a focus on performance improvements, replication techniques, and various storage engines like Tokudb and Spider. The webinar also outlines support options and resources available through MariaDB and its associated organizations.