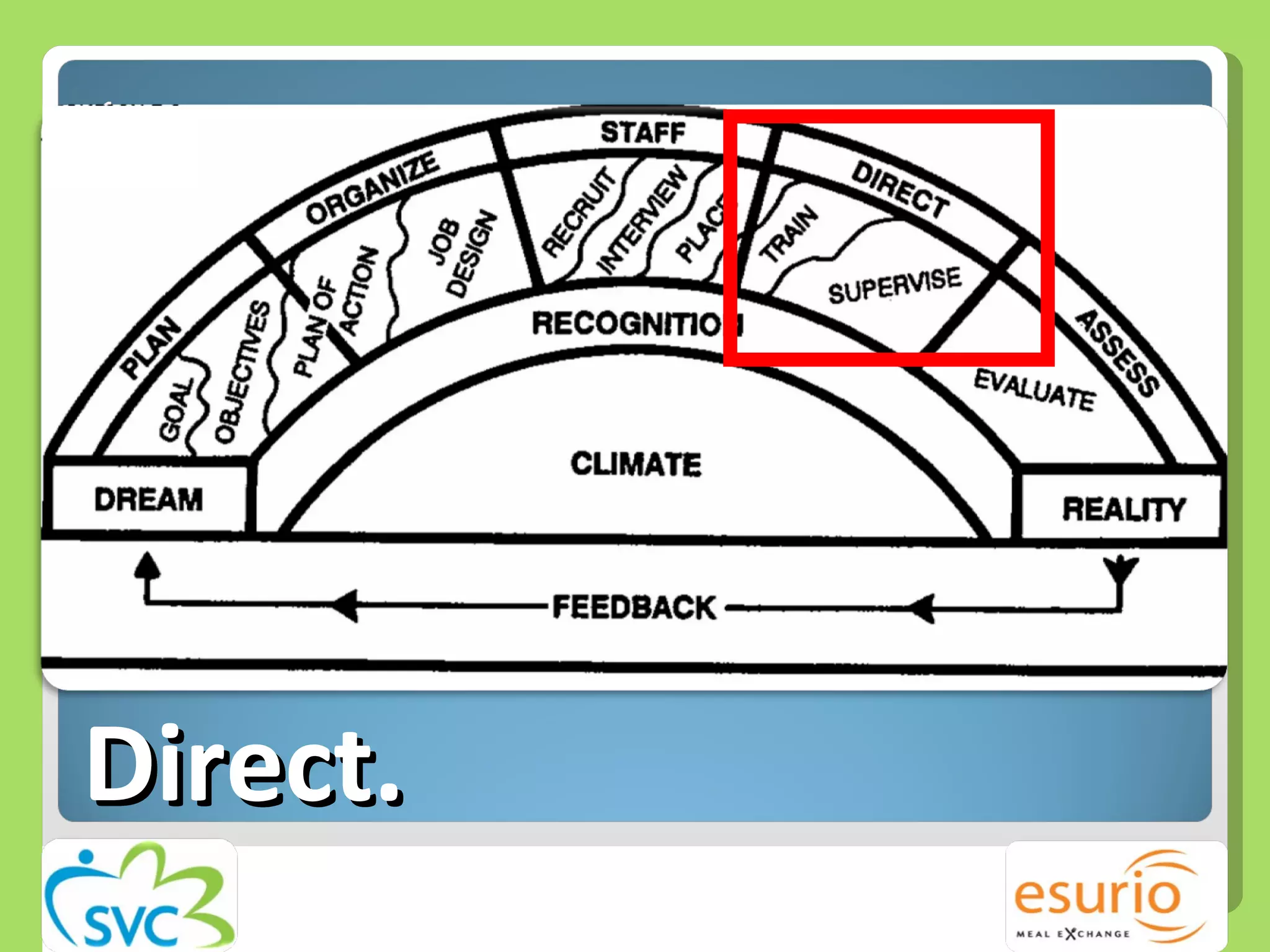
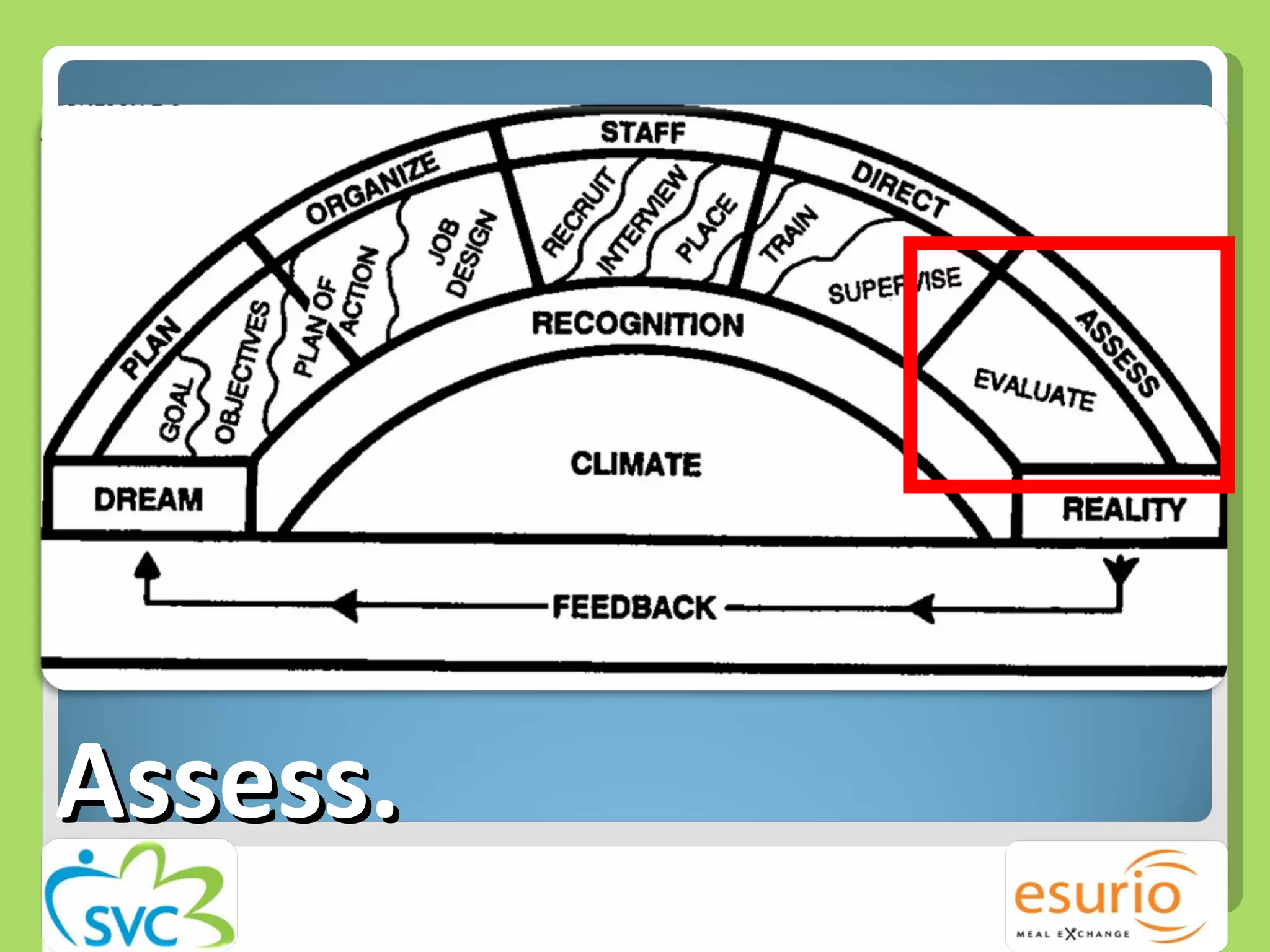
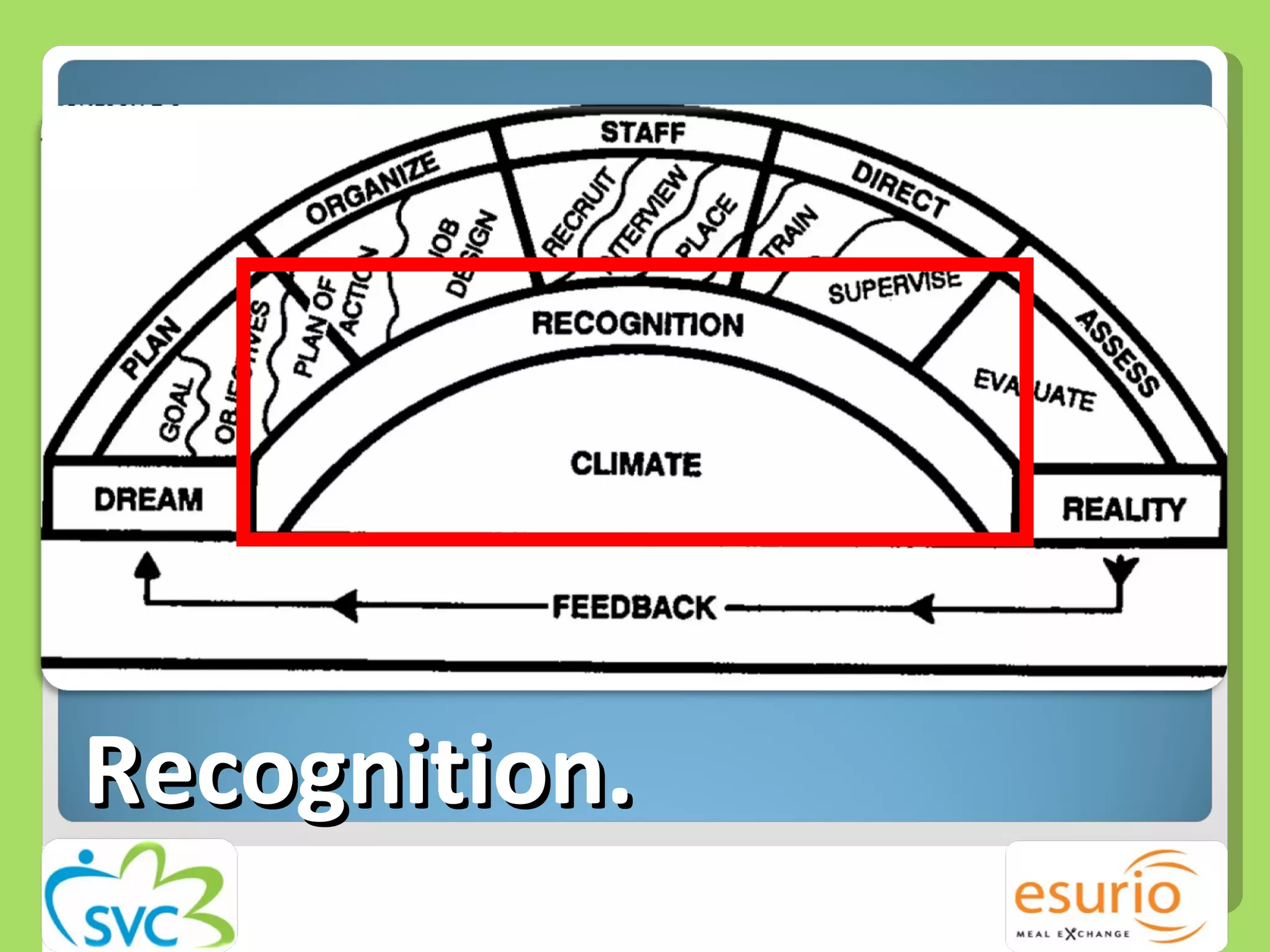
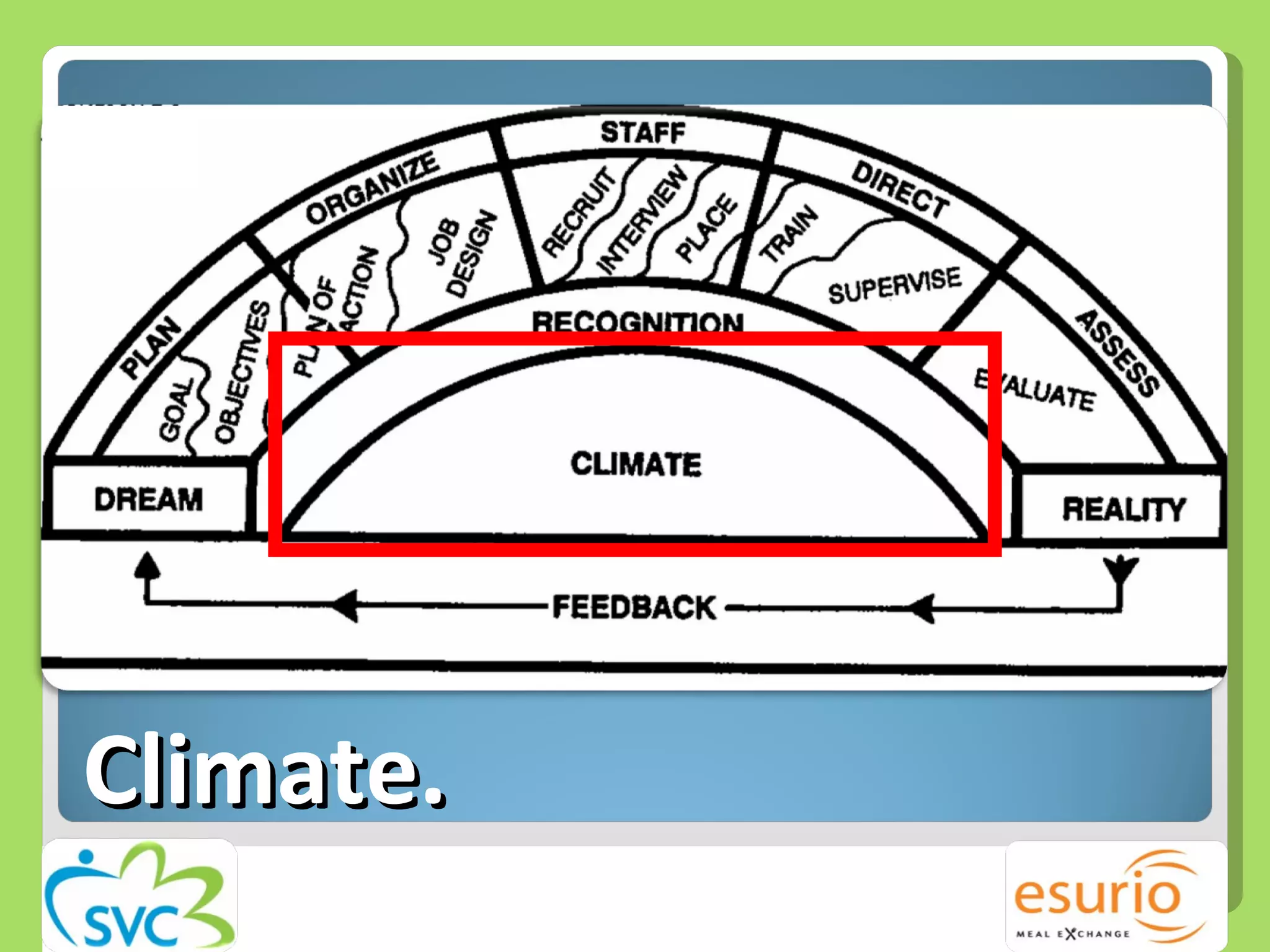
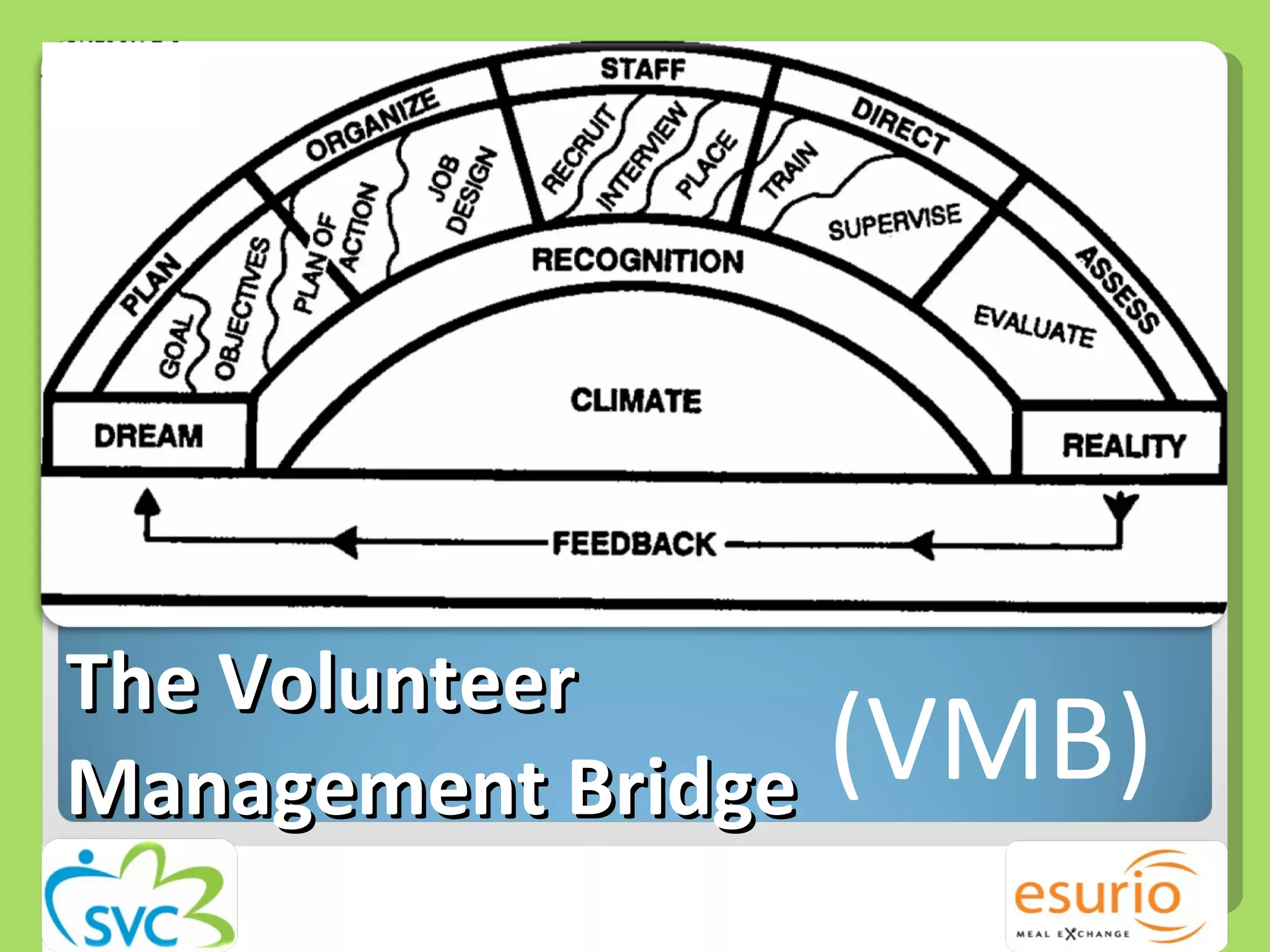
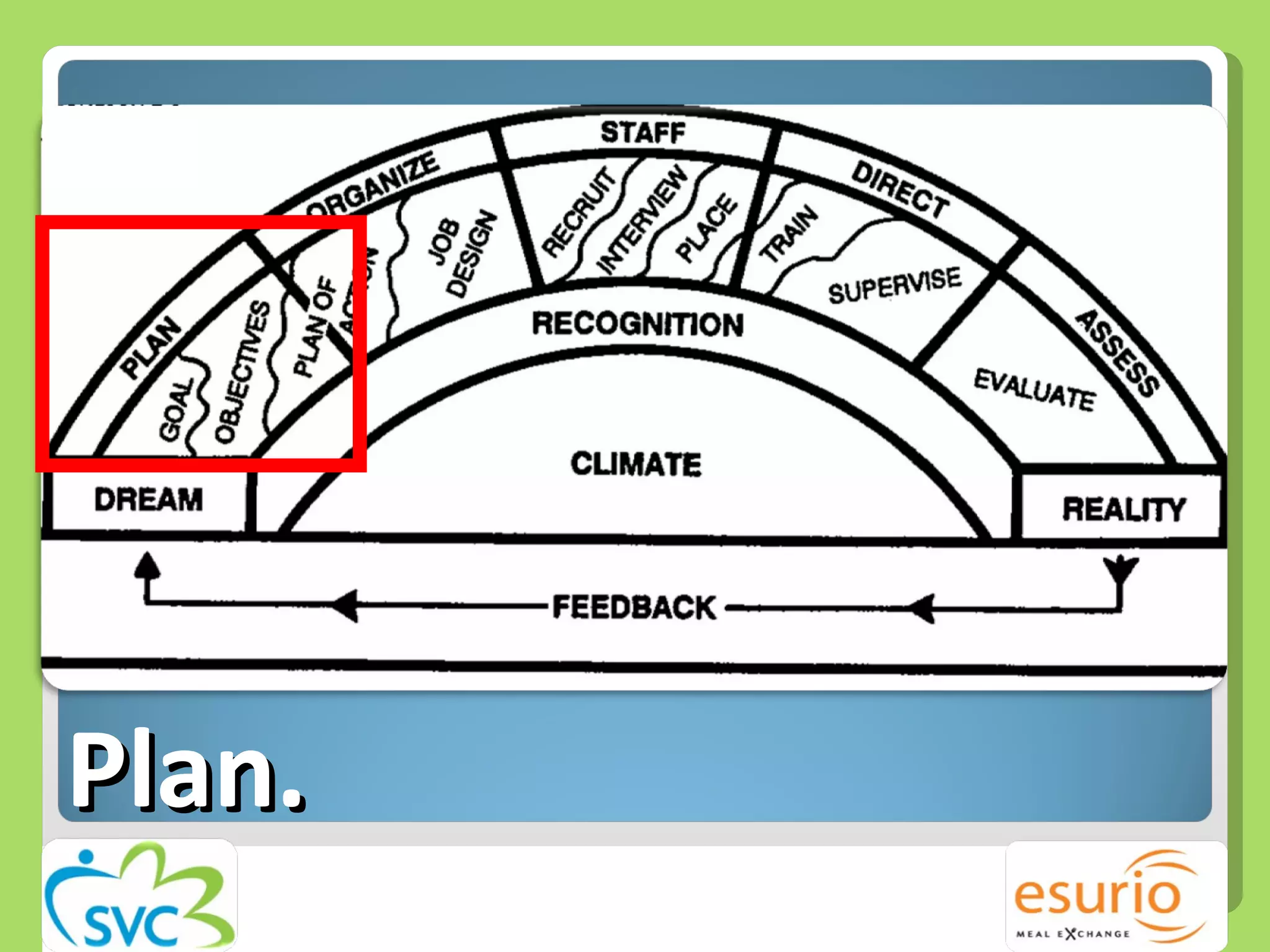
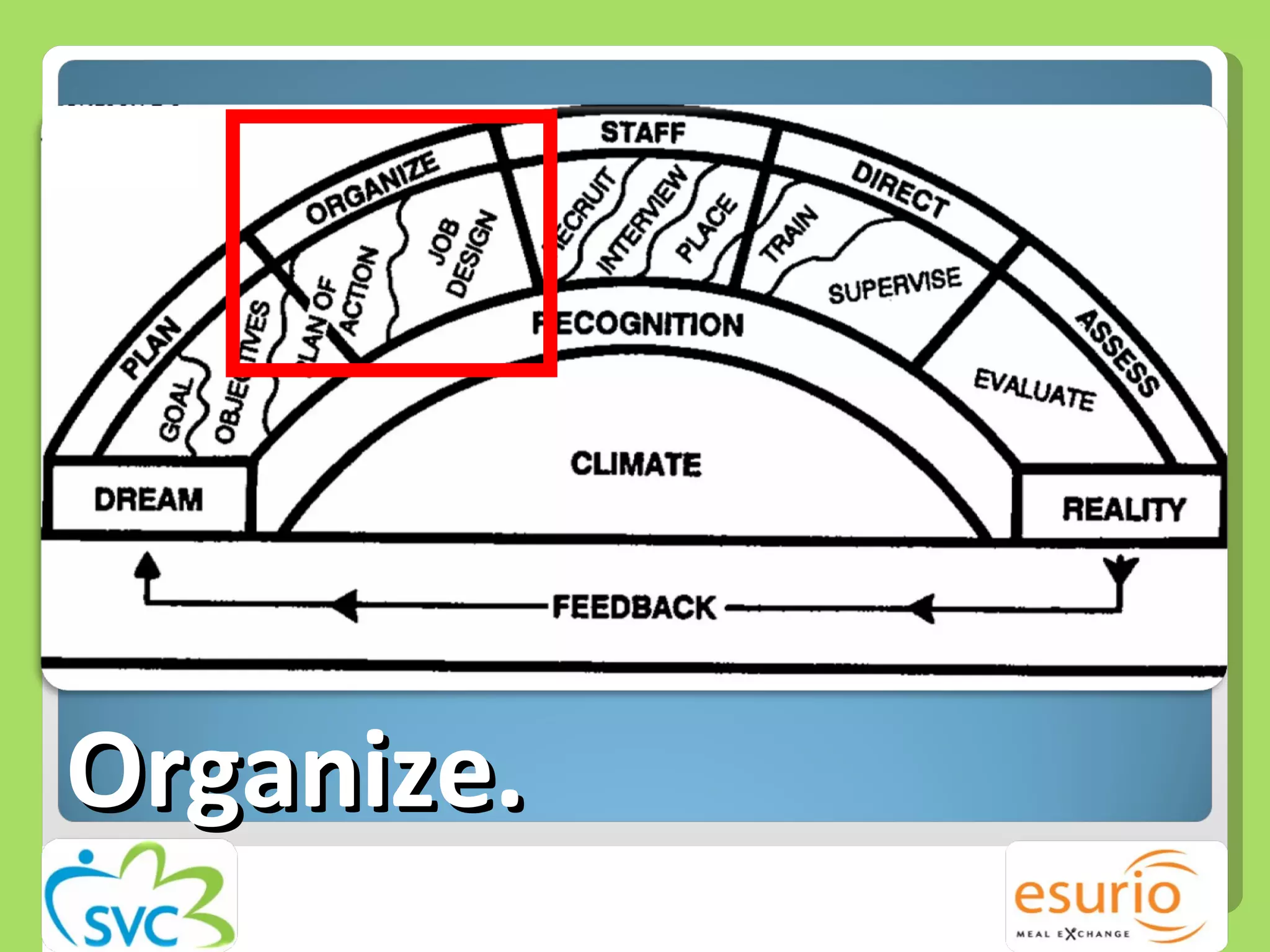
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to managing volunteers, emphasizing the importance of defining roles, effective recruitment, and ongoing training and support. It highlights the need for recognizing volunteer contributions to maintain motivation and engagement. Resources for improving volunteer management practices are also provided, along with strategies to create a positive organizational climate.








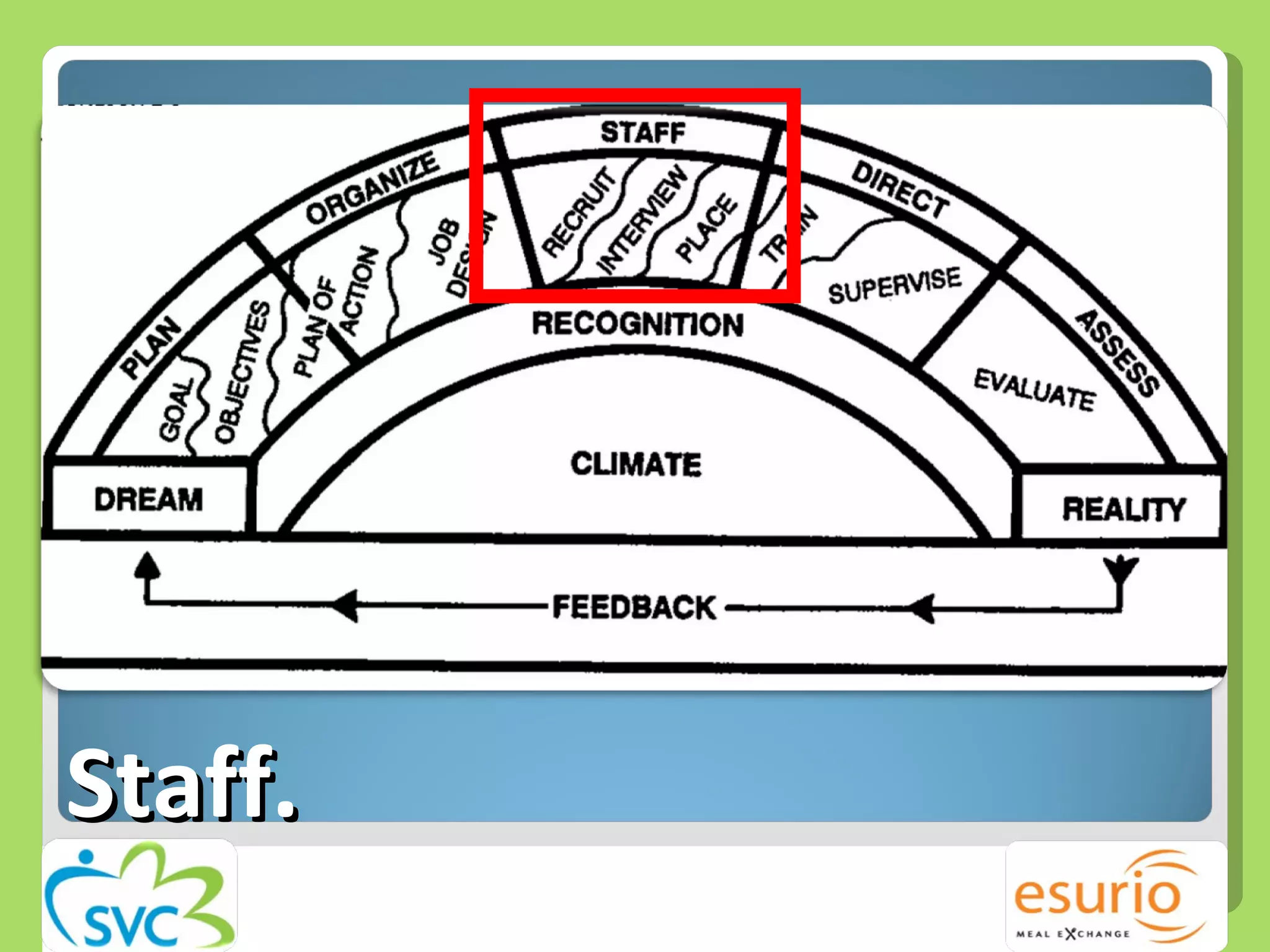
![Staff | Recruitment 1. How 2.When 3.Where 4. Who 5. Why [if you did the planning, This is common sense.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/managingvolunteerssuccessfully-100906162036-phpapp01/75/Managing-volunteers-successfully-13-2048.jpg)