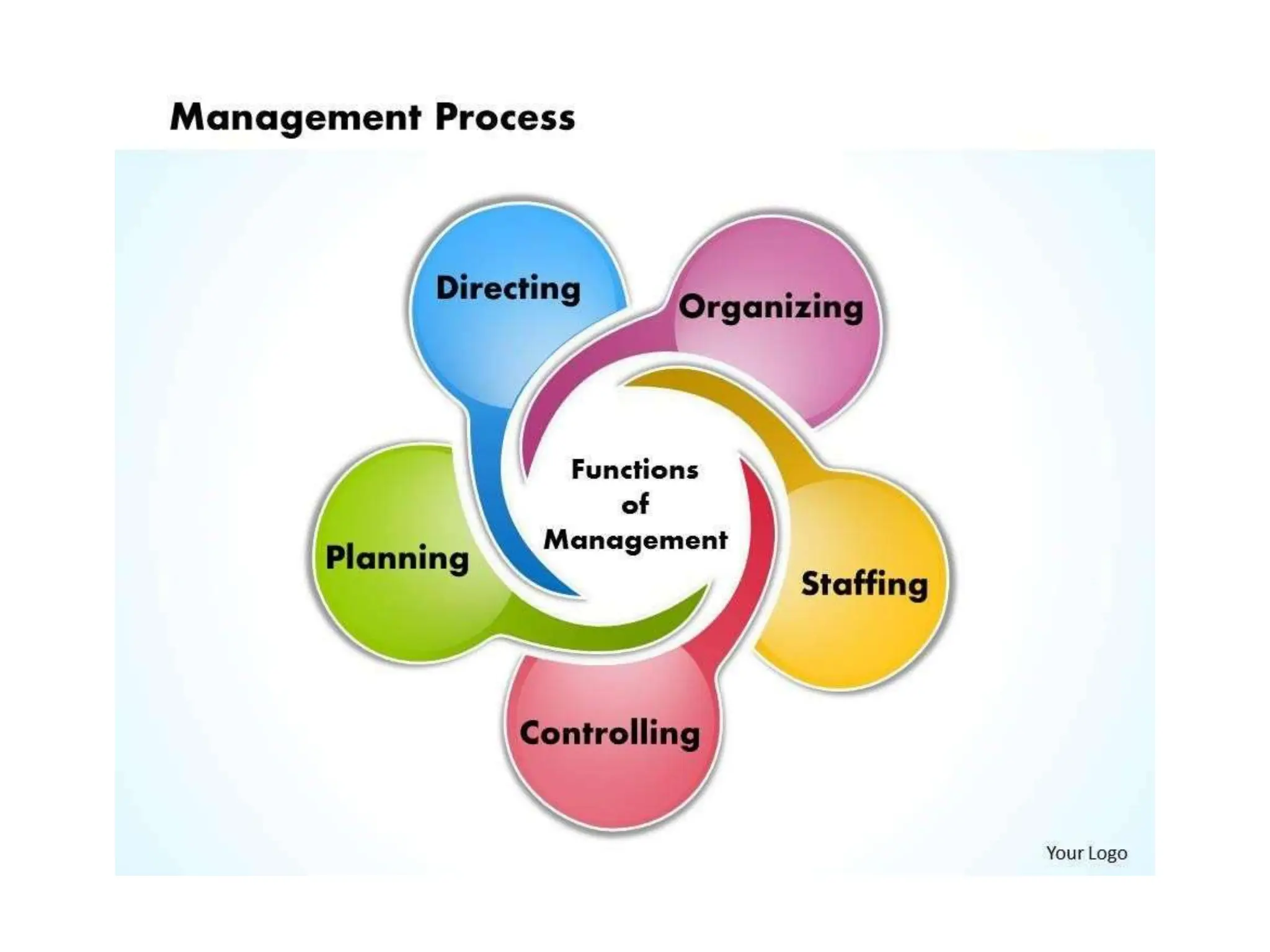
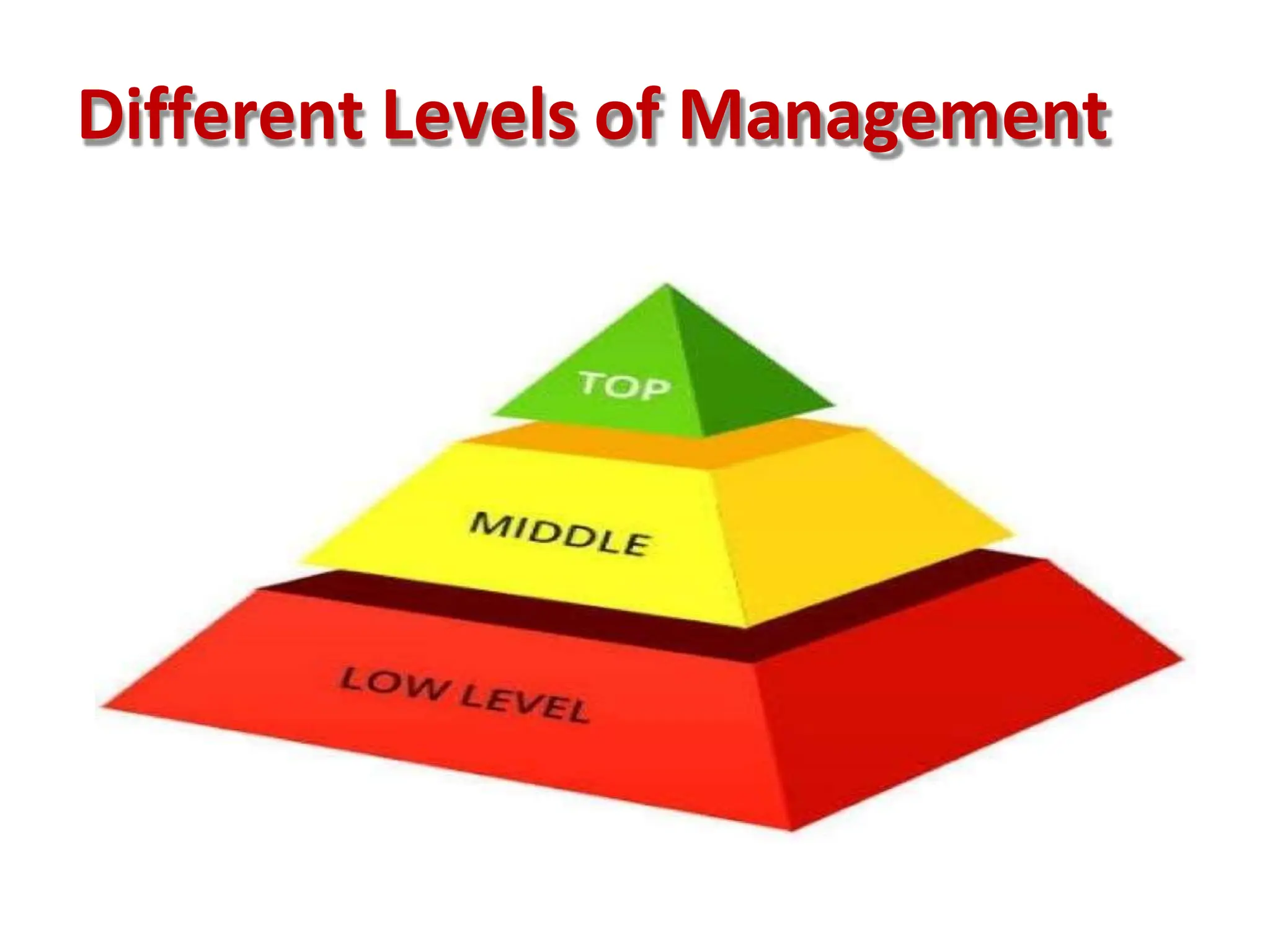
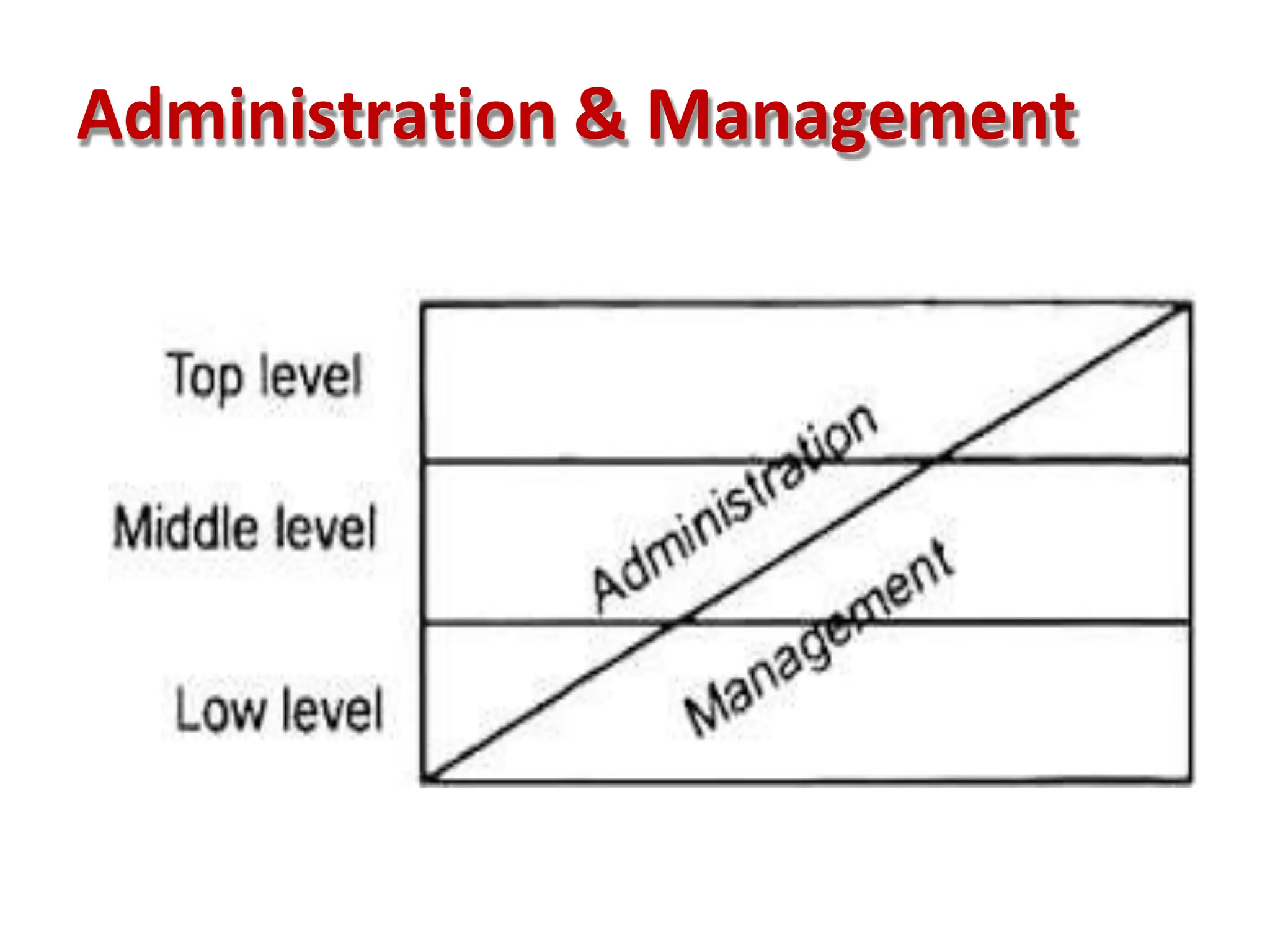
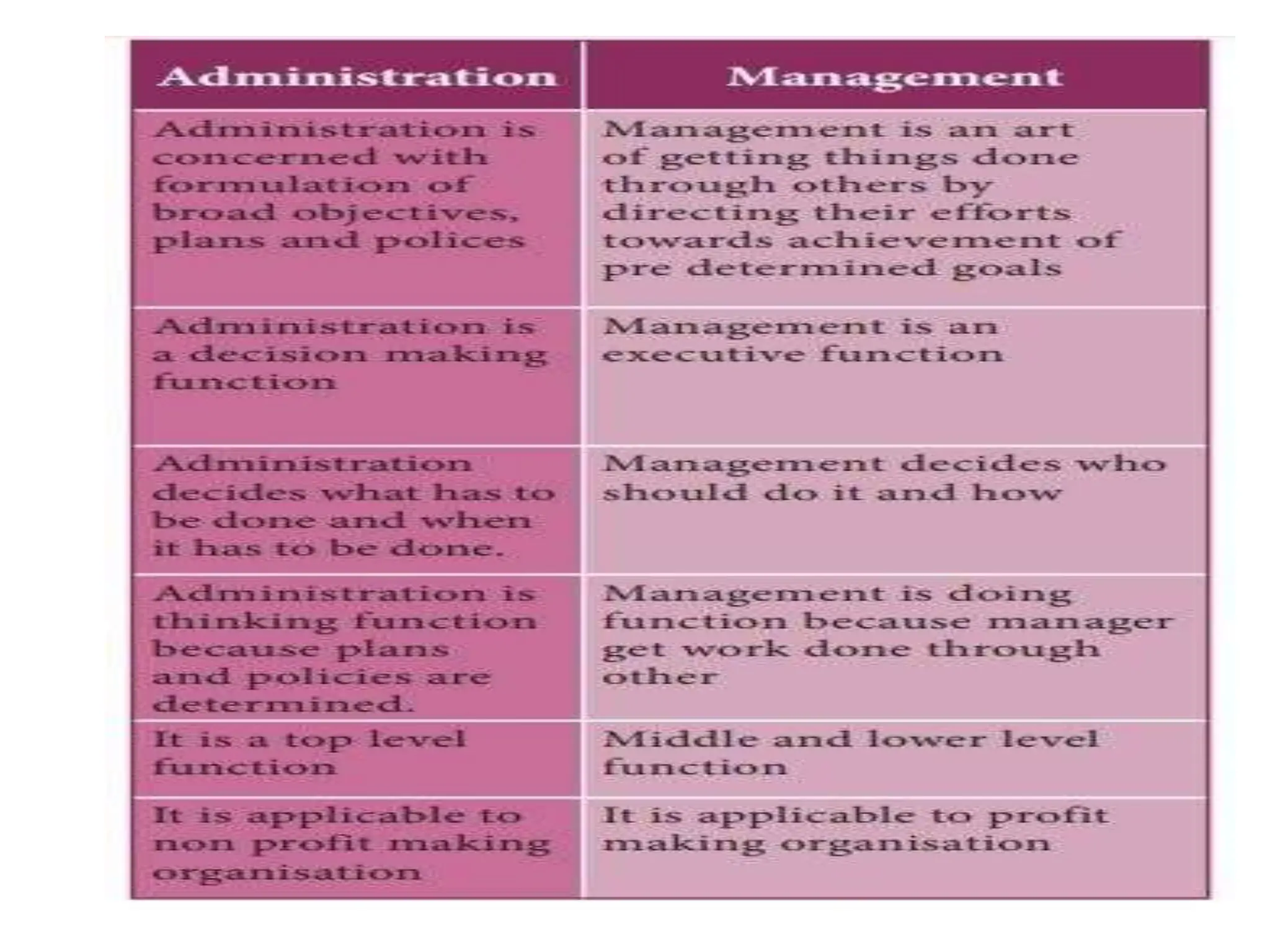
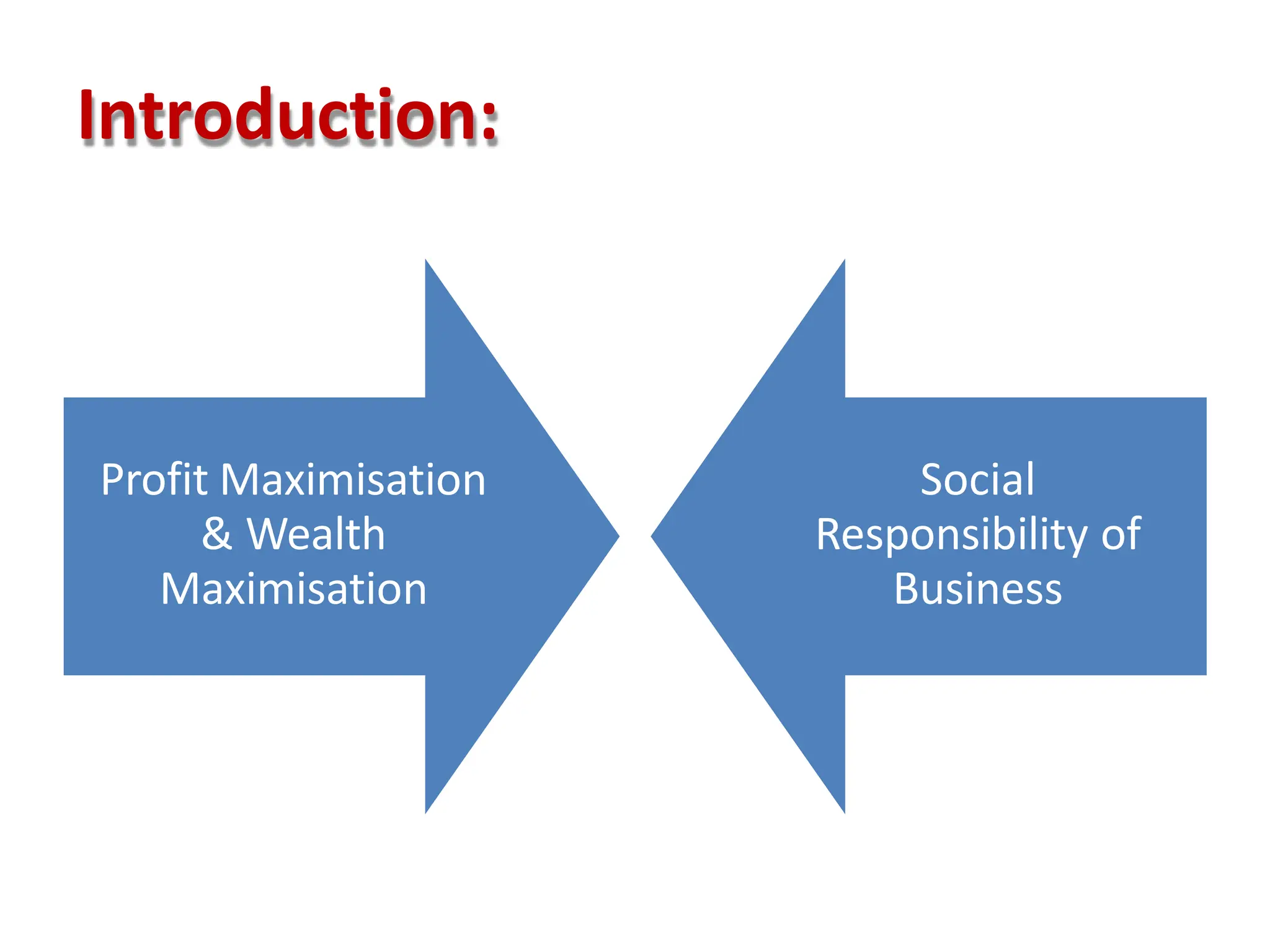
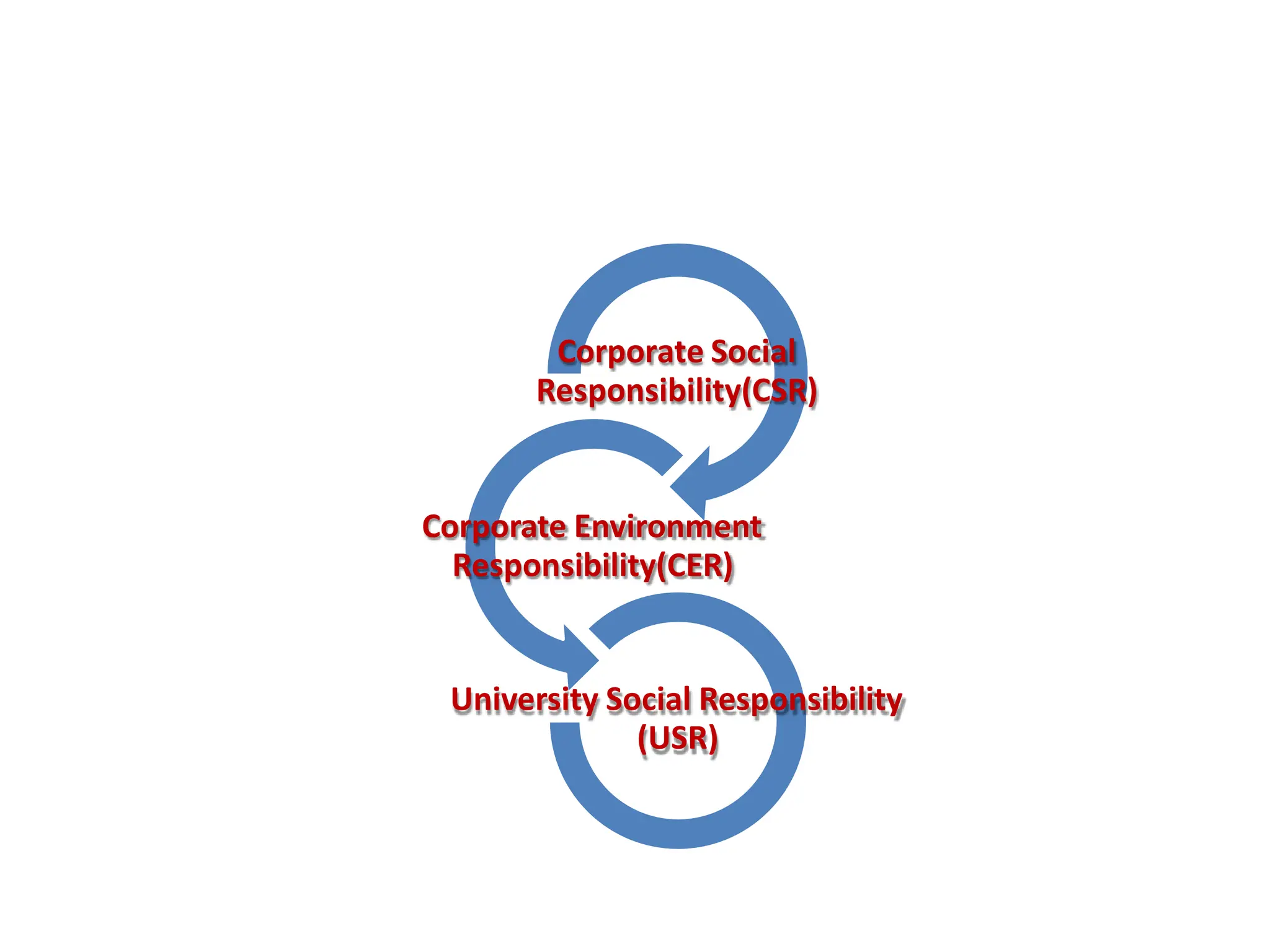
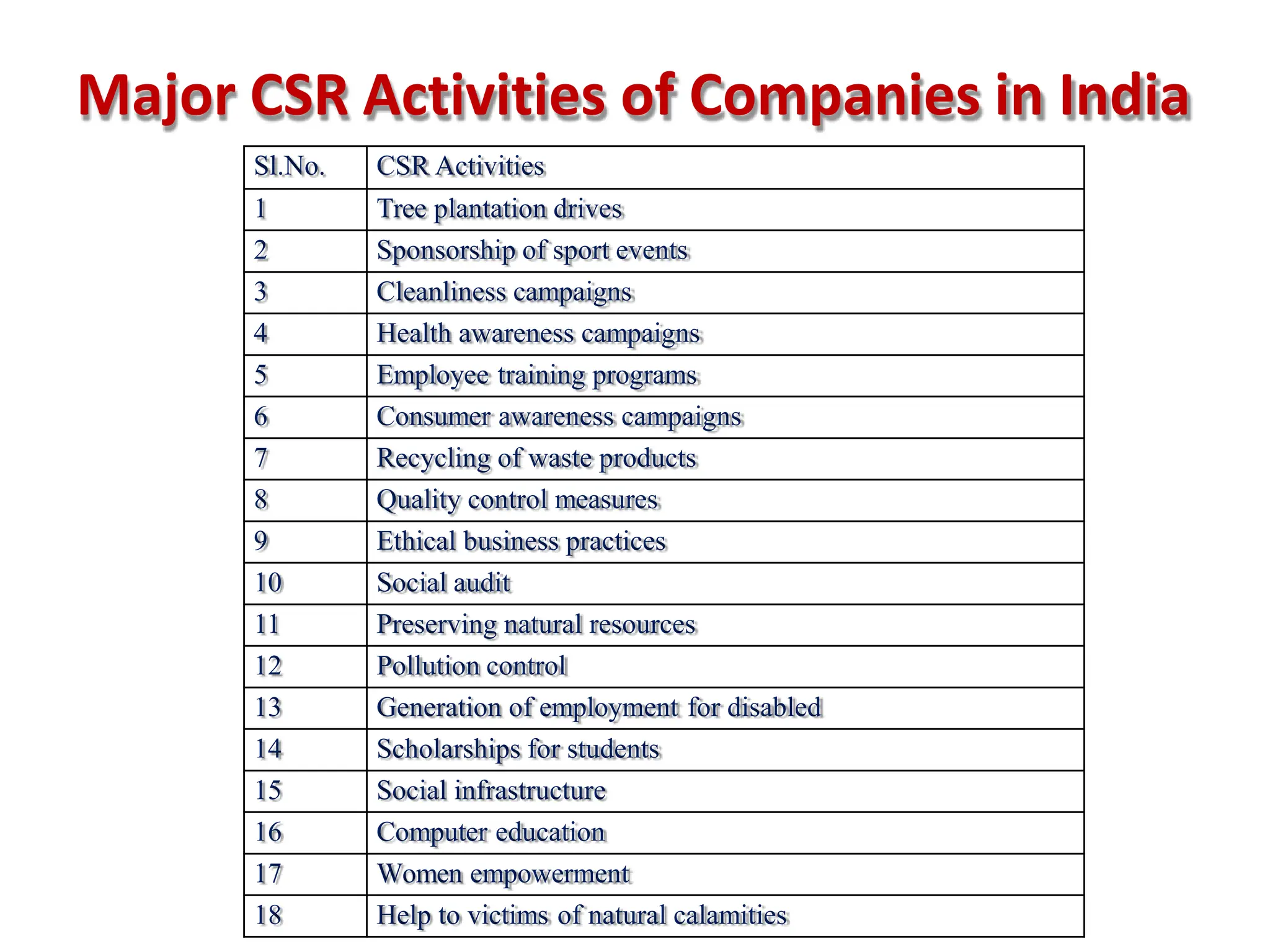
This document provides an overview of management concepts and organizational behavior as taught in an MBA program. It includes outlines of topics like the nature of management, levels of management, functions of management, and social responsibilities of business. Specifically, it discusses concepts like corporate social responsibility, business responsibilities toward shareholders, employees, customers, government, and community. It also addresses arguments that are sometimes made against requiring businesses to have social responsibilities.