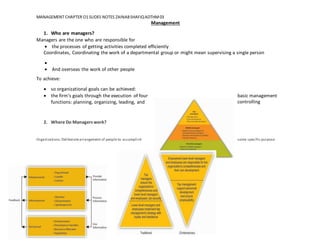
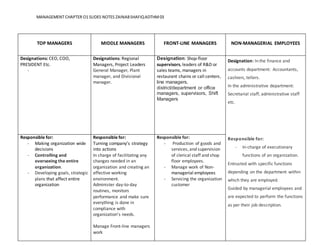
This document discusses the evolving role of managers. It argues that managers must move from directive to instructive approaches as artificial intelligence takes over more routine tasks. They should also shift from restrictive to expansive approaches that encourage independent thinking among employees. Additionally, managers need to become more inclusive by incorporating diverse perspectives rather than making exclusive decisions. The role also requires moving from repetitive routines to innovative practices that challenge the status quo. Overall, the document advocates for managers to transition from solely focusing on problem-solving to taking a broader role as a challenger who encourages new ways of growing the business.