This document provides an overview of management concepts including:
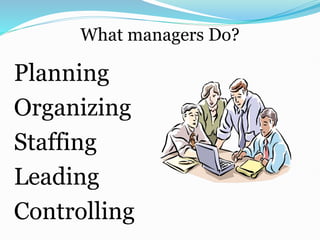
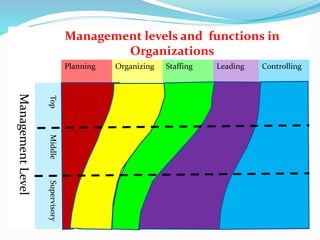
- Definitions of management as a process of planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling organizations.
- The importance of management for coordinating group activities and achieving goals.
- The development of management theories like classical, behavioral, and quantitative approaches.
- Key managerial functions such as planning, organizing, implementing, monitoring and evaluation.
- Managerial roles including interpersonal, informational, and decision-making roles.
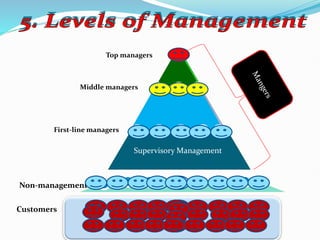
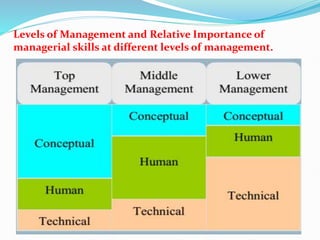
- Different levels and scopes of management from top to first-line managers.
- Resources and skills used by managers including technical, human relations, and conceptual skills.