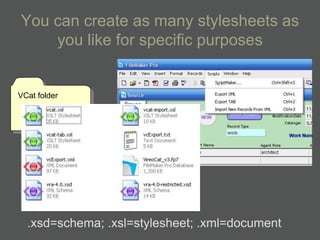
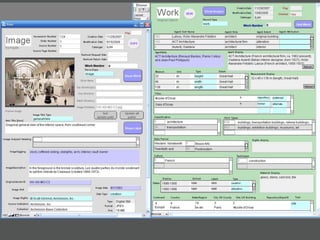
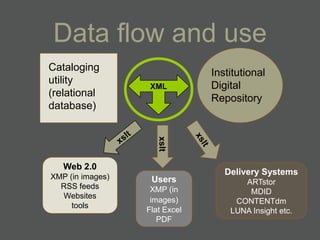
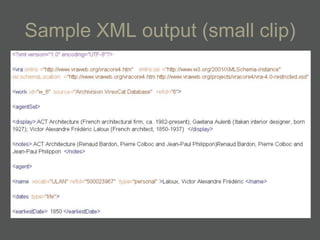
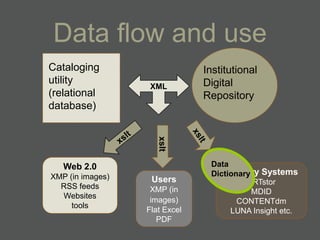
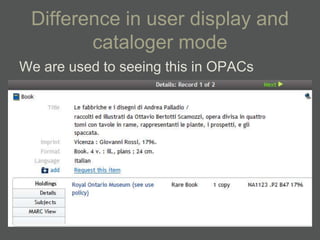
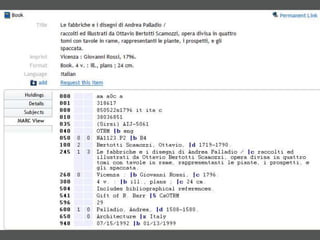
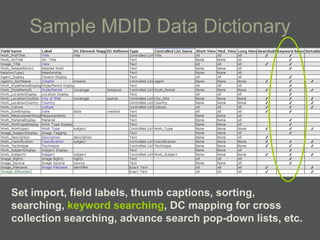
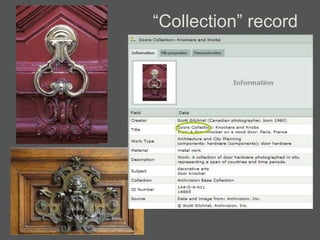
The document provides an overview of using relational databases and structured data to efficiently store and reuse cultural heritage metadata. Key points include:
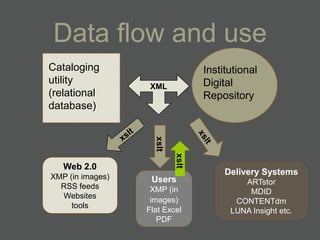
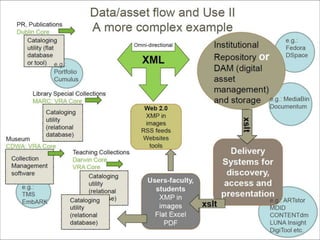
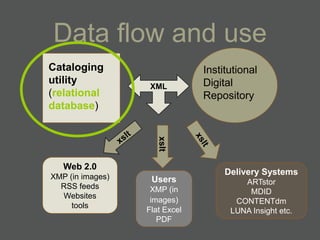
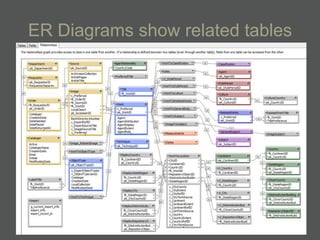
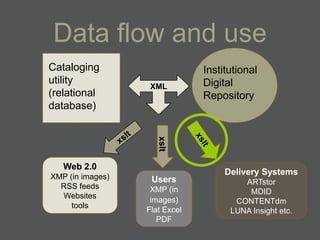
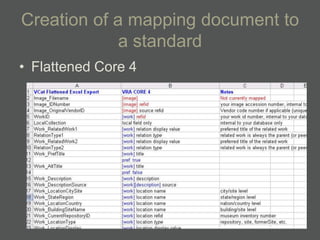
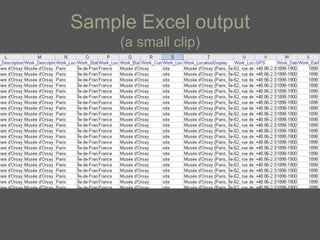
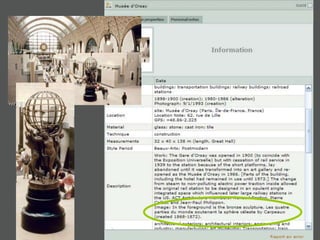
- Structured data stored in a relational database can be transformed and output in different formats like XML, Excel, or data dictionaries for various tools.
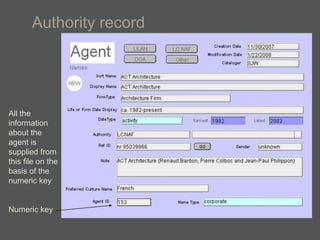
- Authority files are used to consistently represent entities and their information is linked to other records.
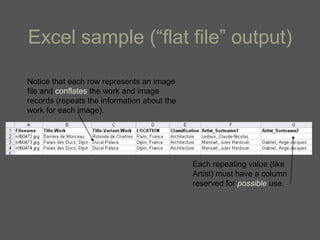
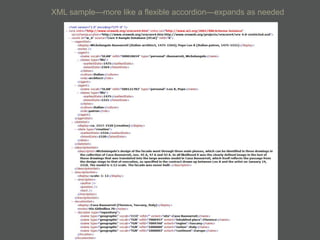
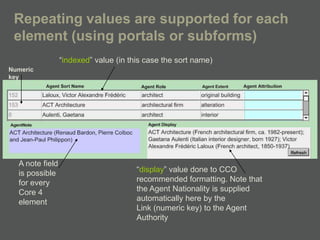
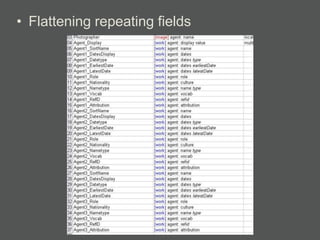
- XML is more flexible than flat files as it allows repeating fields and complex relationships between data.
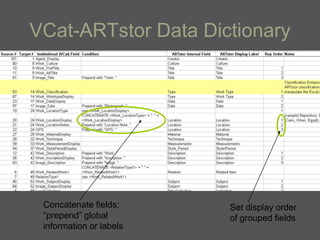
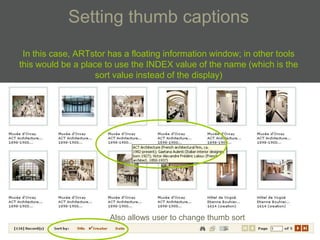
- Data dictionaries customize how metadata is displayed for different uses and users.