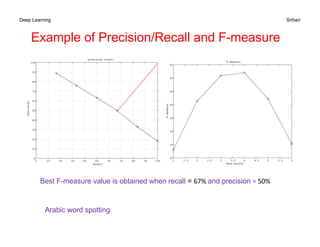
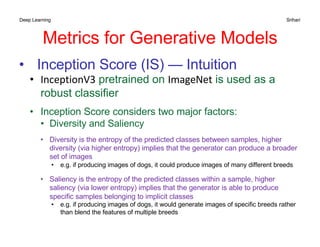
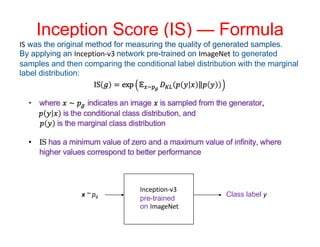
The document discusses performance metrics for machine learning tasks, including regression, classification, density estimation, and image analysis. Key metrics such as accuracy, error rates, precision, recall, and specific metrics for generative models like inception score and Fréchet inception distance are explained. It highlights the importance of selecting appropriate metrics based on the task and validating model performance through these metrics.






![Deep Learning Srihari
F =
2
1
P
+
1
R
=
2PR
P + R
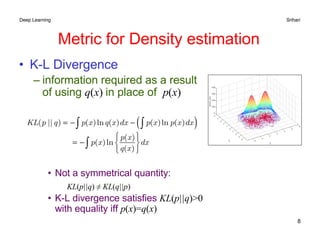
Harmonic mean of precision and recall
High value when both P and R are high
uR
P
u
PR
R
u
P
u
E
+
-
-
=
-
+
-
=
)
1
(
1
1
1
1 u = measure of relative importance of P and R
Combined Precision-Recall
The coefficient u has range [0,1] and can be equivalently written as
)
1
/(
1 2
+
= v
u
R
P
v
PR
v
E
+
+
-
= 2
2
)
1
(
1
R
P
PR
R
P
v
PR
v
E
F
+
=
+
+
=
-
=
2
)
1
(
1 2
2
E-measure reduces to F-measure when precision and recall are
equally weighted, i.e. v=1 or u=0.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/11-240724012350-976808d5/85/Machine-learning-Performance-Metrics-pdf-12-320.jpg)