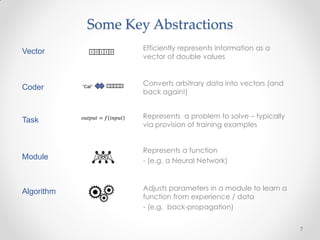
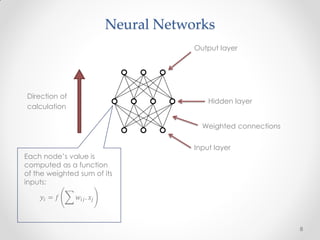
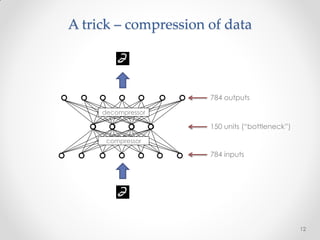
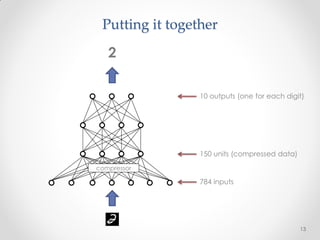
This document summarizes a presentation about machine learning. It begins with a definition of machine learning as giving computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed. It then provides examples of tasks that machine learning can perform, such as spam filtering and stock market prediction. The document notes that machine learning works to some degree but not perfectly. It introduces a company called Nuroko that is building a machine learning toolkit with certain desirable properties such as being general purpose, powerful, scalable, real-time, and pragmatic. The document explains why the company chose Clojure as its programming language and provides an overview of some key machine learning concepts and abstractions like vectors, coders, tasks, modules, and algorithms. It concludes