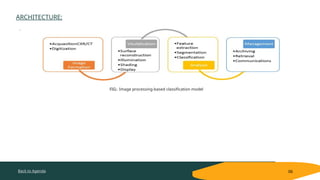
This document discusses a study on lung disease detection using deep learning techniques, specifically focus on pneumonia and COVID-19 identification through chest x-ray and CT scan analysis. It describes an automated system leveraging convolutional neural networks (CNN) and various pre-trained models to offer high accuracy in early detection, aimed at improving screening efficiency and accessibility in low-resource areas. The study culminates in the deployment of a web application for real-time diagnosis of lung diseases from medical imaging.