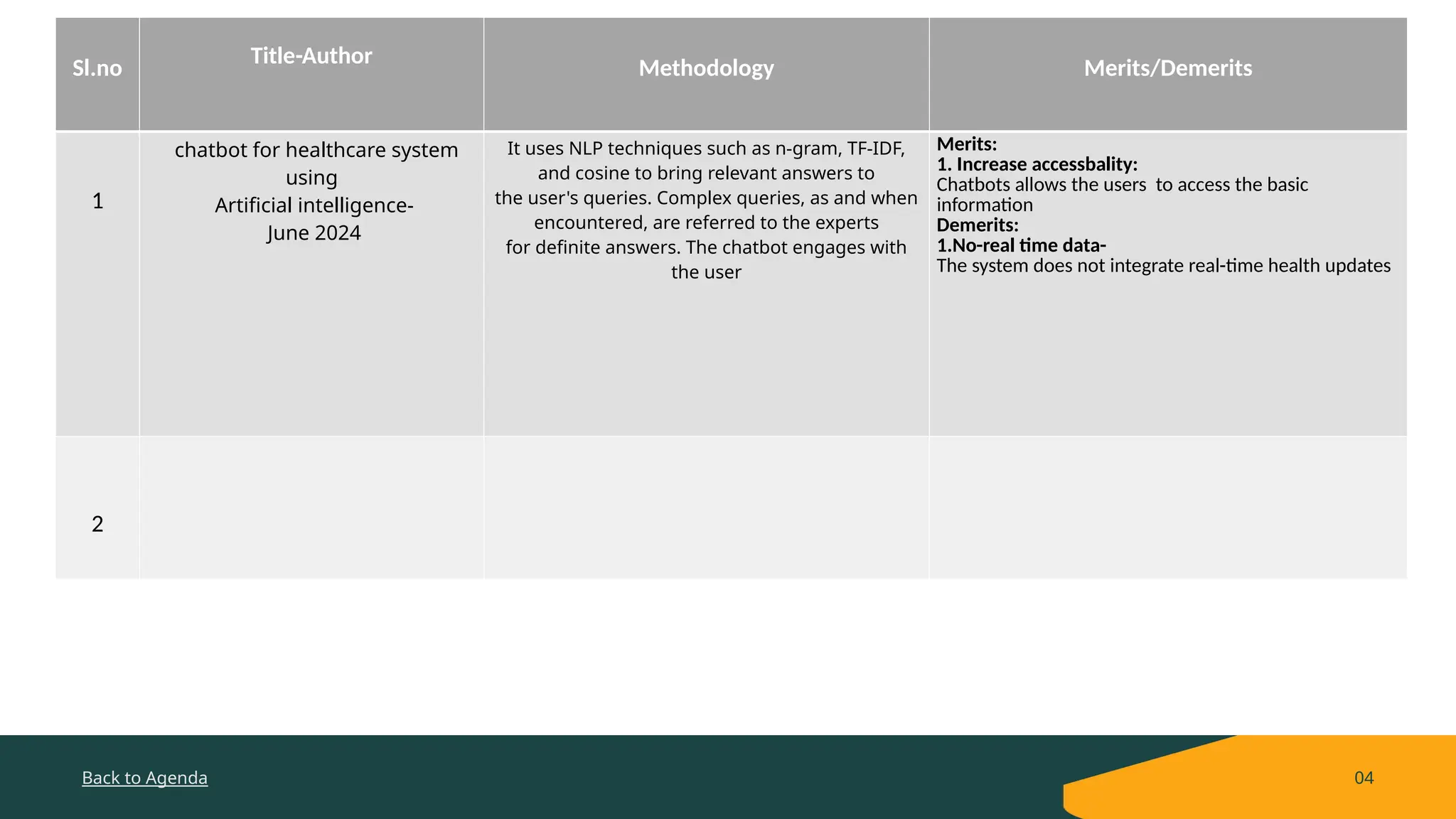
The document presents an AI healthcare chatbot that utilizes natural language processing to provide medical advice, symptom checking, and basic healthcare information to users, enhancing accessibility and reducing the workload on healthcare professionals. Its architecture involves understanding user queries, offering relevant information, and directing complex questions to experts. Key challenges include patient data privacy, accuracy of advice, and user trust, with proposed solutions focusing on data protection, rigorous testing, and transparent communication.