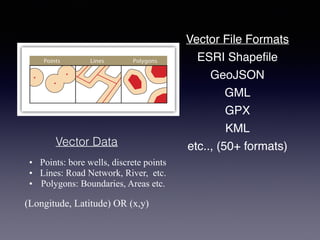
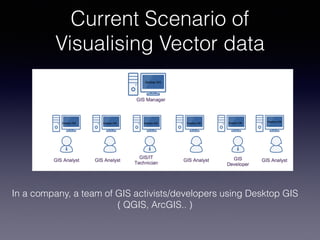
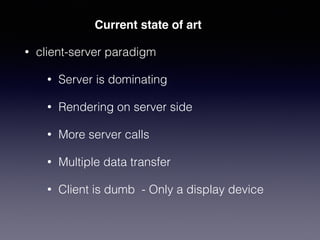
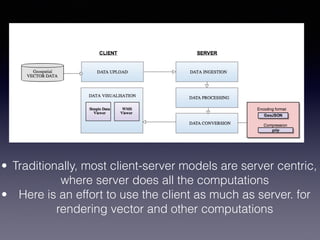
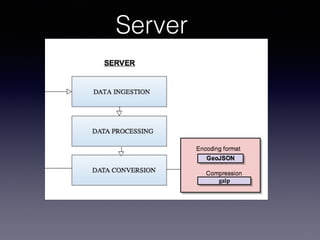
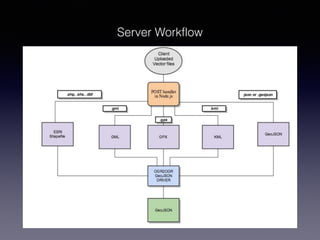
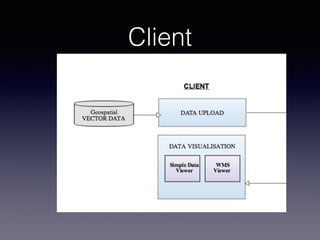
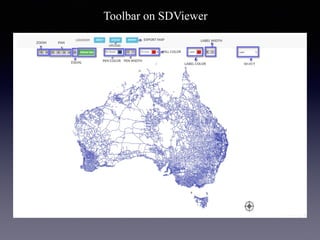
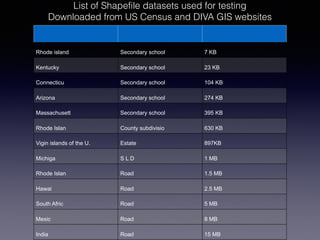
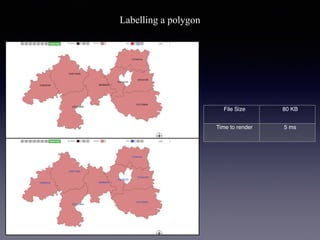
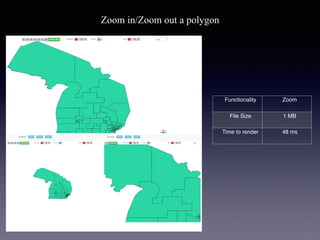
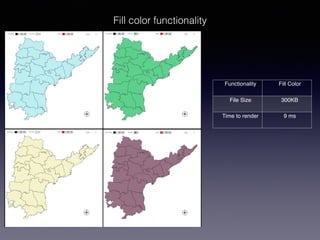
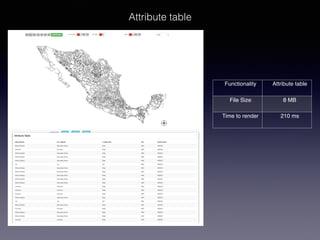
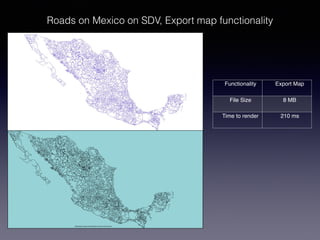
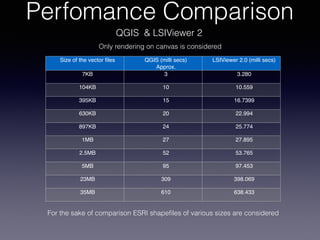
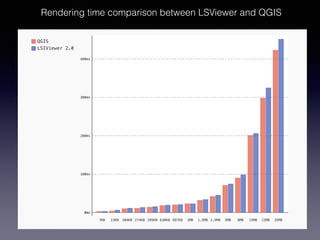
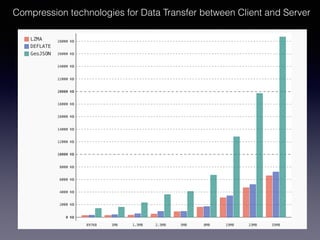
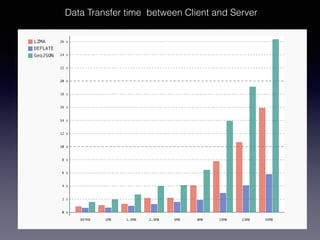
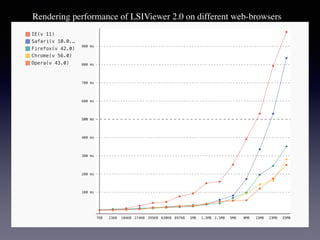
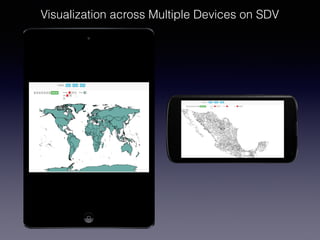
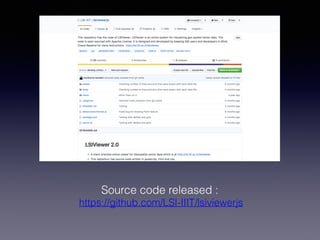
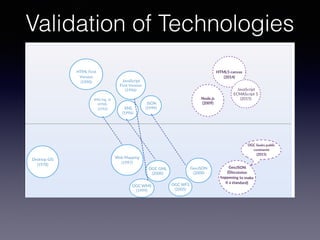
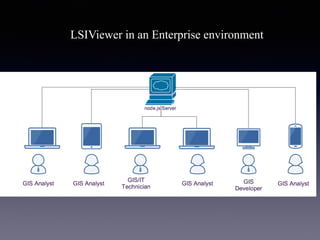
LSIViewer 2.0 is an online geospatial vector visualization tool designed to operate independently on multiple devices without the need for installation. It introduces a client-oriented approach, shifting computations from the server to the client, and supports various vector file formats with functionalities like zoom, pan, and map export. The tool aims to provide a collaborative framework similar to Google Docs while promising improved performance and rendering capabilities compared to traditional desktop GIS applications.