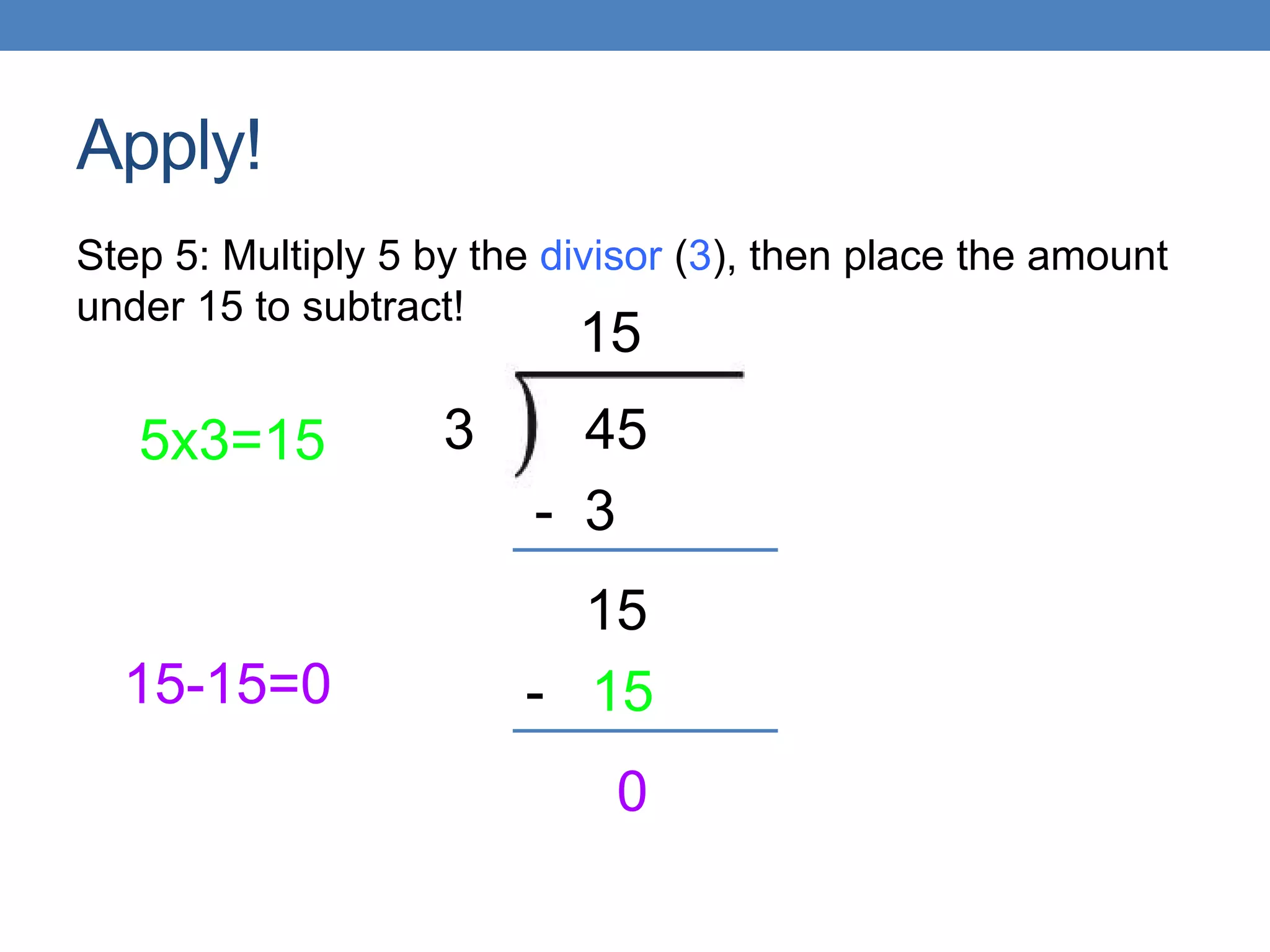
Long division is explained in 5 steps: 1) Determine how many times the divisor goes into the first digit of the dividend and place that number above the digit. 2) Multiply the divisor by that number and place it under the digit. 3) Subtract and bring down the next digit. 4) Repeat steps 1-3 until there are no more digits to bring down. 5) The final number is the quotient of the long division problem. As an example, the document walks through 45/3 in detail using these steps, with the solution being 45/3=15.