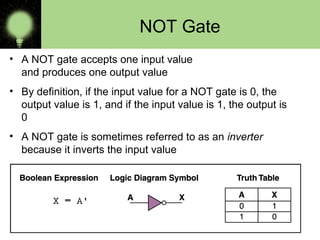
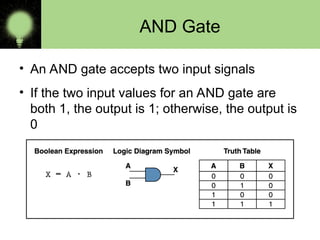
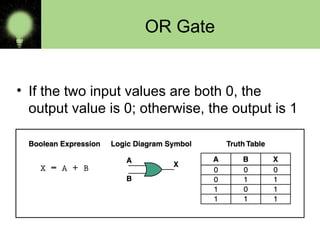
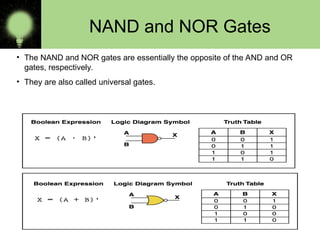
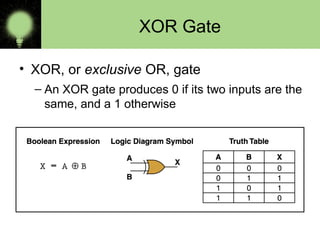
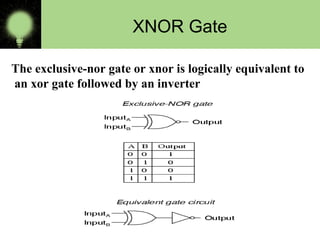
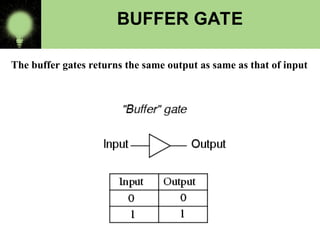
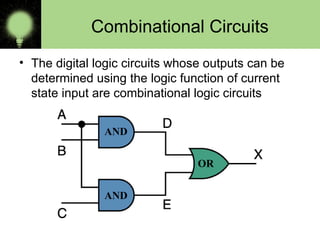
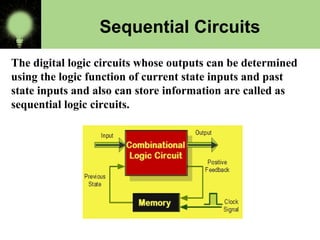
The document explains the basics of logic gates and their functions within digital circuits, covering types such as NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR gates. It distinguishes between combinational circuits, which have no memory and rely solely on current inputs, and sequential circuits that utilize past inputs and memory elements. Examples of combinational circuits include adders and multiplexers, while sequential circuits are exemplified by flip-flops and counters.