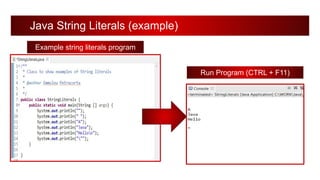
The document discusses Java literals and variables. It defines character literals as representing Unicode characters using single quotes. String literals are defined as sequences of characters placed within double quotes. Null literals are defined as using the null keyword to assign null values to object references. Variables in Java must specify a data type and name, and can be initialized with a value. The data type can be either a primitive type or reference type.







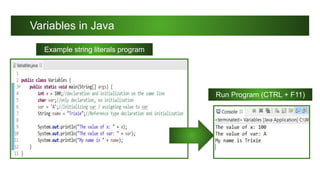
![Variables in Java
● A variable has a:
■ Data type - indicates the type of value, variable can hold. Ex. Integer numbers, floating
point numbers, String and so on.
■ Name type - the variable name must follow rules for identifiers.
● Declare a variable as follows:
<data type> <name> [=initial value];
● The Java programming language is statically-typed, which means that the
<data type> must first be declared before variables can be used and it can’t
be changed later.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/literalsandvariables1-230417135746-473913e9/85/LITERALS-AND-VARIABLES-1-pdf-9-320.jpg)