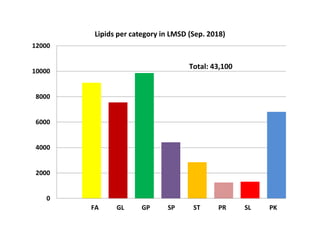
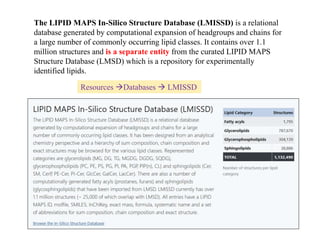
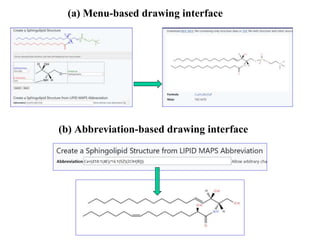
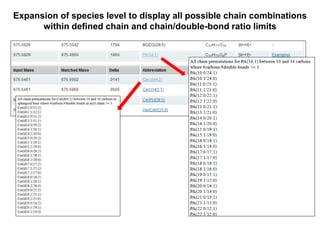
The document summarizes a Lipidomics Gateway workshop presented by Eoin Fahy at the University of California San Diego. It discusses the LIPID MAPS Lipidomics Gateway, which provides lipid classification resources and databases. Key points include that LIPID MAPS is now hosted in the UK, it defines lipids and outlines eight categories, and describes databases like LMSD that contain over 43,000 classified lipid structures.