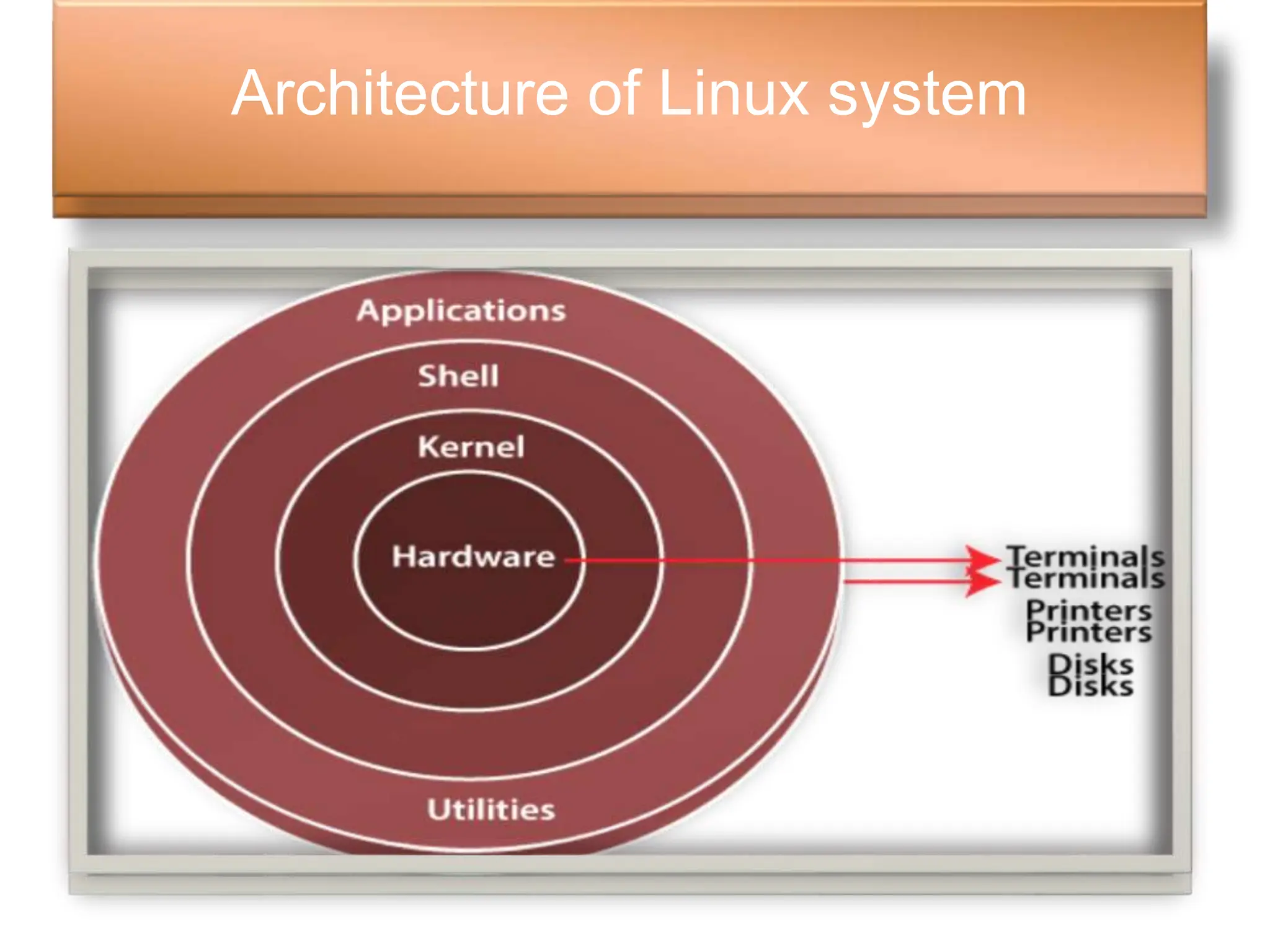
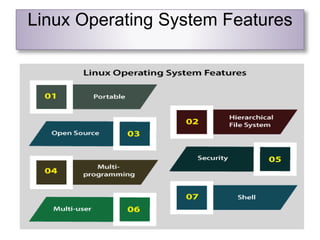
The document outlines the architecture of the Linux operating system, detailing its components such as the kernel, system libraries, hardware layer, and shell interfaces. It highlights features like portability, open-source nature, multiprogramming, multi-user capabilities, hierarchical file systems, and security measures. Additionally, it notes the widespread use of Linux in various electronic devices and its cost-effectiveness for organizations.