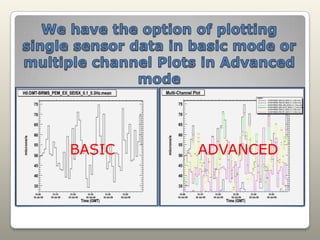
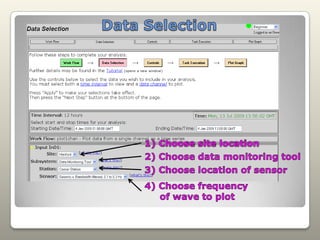
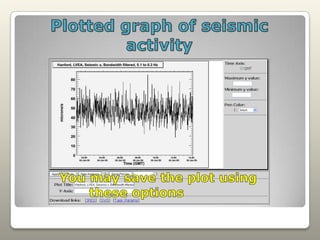
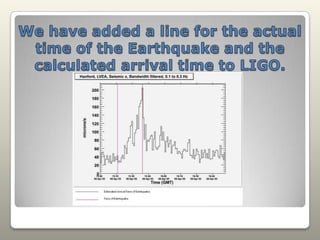
Seismometers, tiltmeters, magnetometers, and anemometers are sensors used at LIGO facilities to measure seismic waves, ground tilt, magnetic fields, and wind velocity. Seismometers detect seismic waves using a suspended magnetic mass within coils that induces a current as the coils move. Tiltmeters similarly measure tilt. Magnetometers monitor magnetic fields including from solar storms. Anemometers measure wind speed and direction. Sensors are located at various LIGO sites. Data from individual or multiple sensors can be plotted and analyzed to study earthquakes and seismic wave propagation.