More Related Content
More from themassmaker (20)
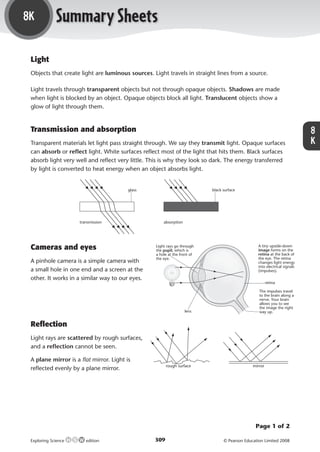
Light
- 1. 8K Summary Sheets
Light
Objects that create light are luminous sources. Light travels in straight lines from a source.
Light travels through transparent objects but not through opaque objects. Shadows are made
when light is blocked by an object. Opaque objects block all light. Translucent objects show a
glow of light through them.
Transmission and absorption 8
Transparent materials let light pass straight through. We say they transmit light. Opaque surfaces K
can absorb or reflect light. White surfaces reflect most of the light that hits them. Black surfaces
absorb light very well and reflect very little. This is why they look so dark. The energy transferred
by light is converted to heat energy when an object absorbs light.
glass black surface
transmission absorption
Cameras and eyes Light rays go through
the pupil, which is
A tiny upside-down
image forms on the
a hole at the front of retina at the back of
the eye. the eye. The retina
A pinhole camera is a simple camera with changes light energy
into electrical signals
a small hole in one end and a screen at the (impulses).
other. It works in a similar way to our eyes.
retina
The impulses travel
to the brain along a
nerve. Your brain
allows you to see
the image the right
lens way up.
Reflection
Light rays are scattered by rough surfaces,
and a reflection cannot be seen.
A plane mirror is a flat mirror. Light is
rough surface mirror
reflected evenly by a plane mirror.
Page 1 of 2
Exploring Science edition 309 © Pearson Education Limited 2008
M011_ES_AB_Y8_5415_U8K.indd 309 28/8/08 13:36:05
- 2. 8K Summary Sheets (continued)
When light shines onto an object viewed in a inci angle of
den
t ray incidence
mirror, the rays are reflected into the eye. The rays
seem to come from a position behind the mirror. plane
normal
The image is the same size as the object and (at right angles to
(flat) mirror
the same distance from the mirror. In the image the mirror)
ray
cted angle of
left is right and right becomes left. The angle of refle reflection
incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
8 Refraction
K
When light hits something transparent it changes speed and direction. This is called refraction.
Refraction takes place at the interface between two substances. When light is transmitted through
glass it slows down and changes direction towards the normal. When it travels back out it speeds
up again and changes direction away from the normal.
ray box incident ray normal (at right angles
to the interface)
incident ray
angle of
incidence interface
air
glass
paper glass
block
angle of
refraction refracted ray
emergent ray
Lenses are curved pieces of glass or transparent plastic that are designed to refract light in
particular ways. Some lenses make rays of light come together, and some lenses make the light
spread out. Lenses are used in cameras, microscopes and telescopes.
Colour
white screen
White light is a mixture of colours. White
light can be split up using a prism to give ligh
t
sun red
a spectrum of seven colours (red, orange, orange
prism yellow
yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet).
green
The splitting of colour into a spectrum is blue
indigo
called dispersion. spectrum violet
We are able to see colours because objects
do not reflect all the colours in light. White
objects reflect all the colours, but a red object only reflects red and all other colours are absorbed.
This idea applies to all colours except black – black objects absorb all colours.
Page 2 of 2
Exploring Science edition 310 © Pearson Education Limited 2008
M011_ES_AB_Y8_5415_U8K.indd 310 28/8/08 13:36:05