Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX







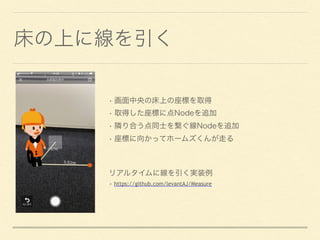
![///
///
/// - Parameter screenPosition: CGPoint
/// - Returns: SCNVector3
func realWorldVector(screenPosition: CGPoint) -> SCNVector3? {
let results = self.hitTest(screenPosition, types: [.existingPlane])
//
guard let result = results.first else {
return nil
}
// SCNVector3
return SCNVector3.positionFromTransform(result.worldTransform)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/armatarai-180314053320/85/LIFULL-HOME-S-App-Night-AR-8-320.jpg)


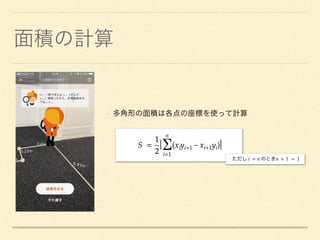




![// Node
let constraint = SCNLookAtConstraint(target: SCNNode)
constraint.isGimbalLockEnabled = true
textNode.constraints = [constraint]
☺](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/armatarai-180314053320/85/LIFULL-HOME-S-App-Night-AR-17-320.jpg)



The document outlines a function in ARKit for converting screen positions to real-world 3D vectors using SCNVector3. It describes the implementation of a hit test to find existing planes and includes a link to a GitHub repository for additional resources. Additionally, the document touches on node constraints in SceneKit, emphasizing the use of look-at constraints.







![///
///
/// - Parameter screenPosition: CGPoint
/// - Returns: SCNVector3
func realWorldVector(screenPosition: CGPoint) -> SCNVector3? {
let results = self.hitTest(screenPosition, types: [.existingPlane])
//
guard let result = results.first else {
return nil
}
// SCNVector3
return SCNVector3.positionFromTransform(result.worldTransform)
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/armatarai-180314053320/85/LIFULL-HOME-S-App-Night-AR-8-320.jpg)








![// Node
let constraint = SCNLookAtConstraint(target: SCNNode)
constraint.isGimbalLockEnabled = true
textNode.constraints = [constraint]
☺](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/armatarai-180314053320/85/LIFULL-HOME-S-App-Night-AR-17-320.jpg)

