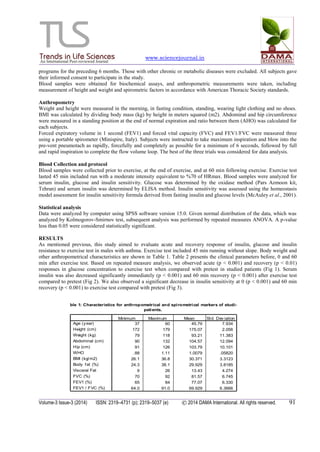
This document summarizes a study that examined the effect of a 45-minute running exercise on glucose, insulin, and insulin sensitivity in 14 inactive adult men with mild to moderate asthma. The study found that the exercise test was associated with acute and recovery responses in all variables. Specifically, serum insulin, glucose, and insulin sensitivity decreased immediately after and 60 minutes following the exercise test when compared to pre-test levels. This indicates that a single bout of aerobic exercise can positively impact diabetes markers in asthma patients.