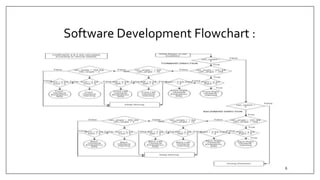
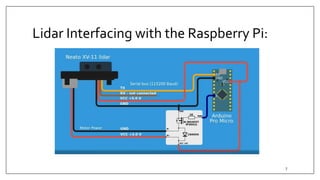
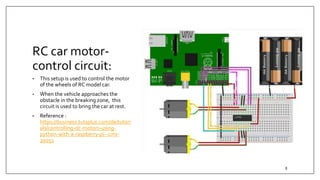
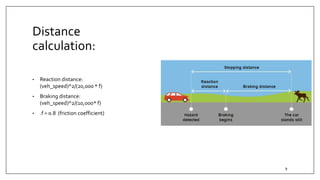
This document summarizes an embedded research project involving Lidar-based obstacle detection for a vehicle from March to June 2019. The project used a XV11 Lidar sensor with a Raspberry Pi on a ROS platform to detect obstacles based on vehicle speed and provide warning and emergency braking zones. Challenges included interfacing the Lidar, processing data, and developing dynamic zones and motor control for an RC model car. Software was created to detect obstacles based on direction and steering angle and provide warning and braking signals to slow or stop the vehicle. The system was tested and validated on the RC car.