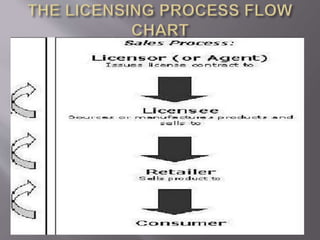
This document discusses license agreements between businesses. It defines a license agreement as a contractual arrangement where a licensor allows a licensee to use its technology, patents, trademarks, or intellectual property in exchange for a fee. License agreements benefit licensors by generating revenue without direct involvement and benefit licensees by allowing access to new markets or credibility. Key elements of a license agreement include financial terms, timeframe, quality control issues, intellectual property ownership, and dispute resolution procedures. Proper legal advice is important when drafting or entering into a license agreement.