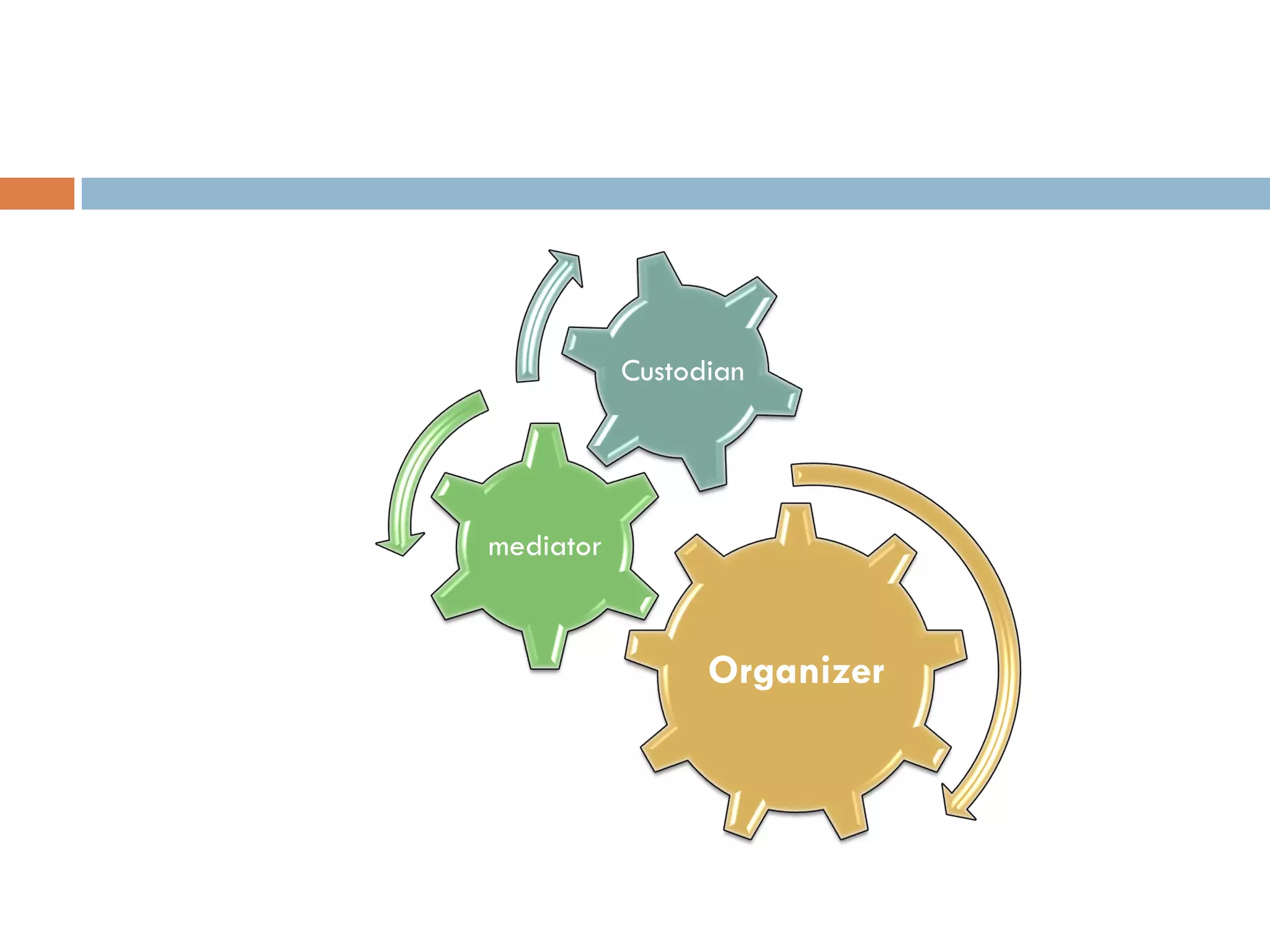
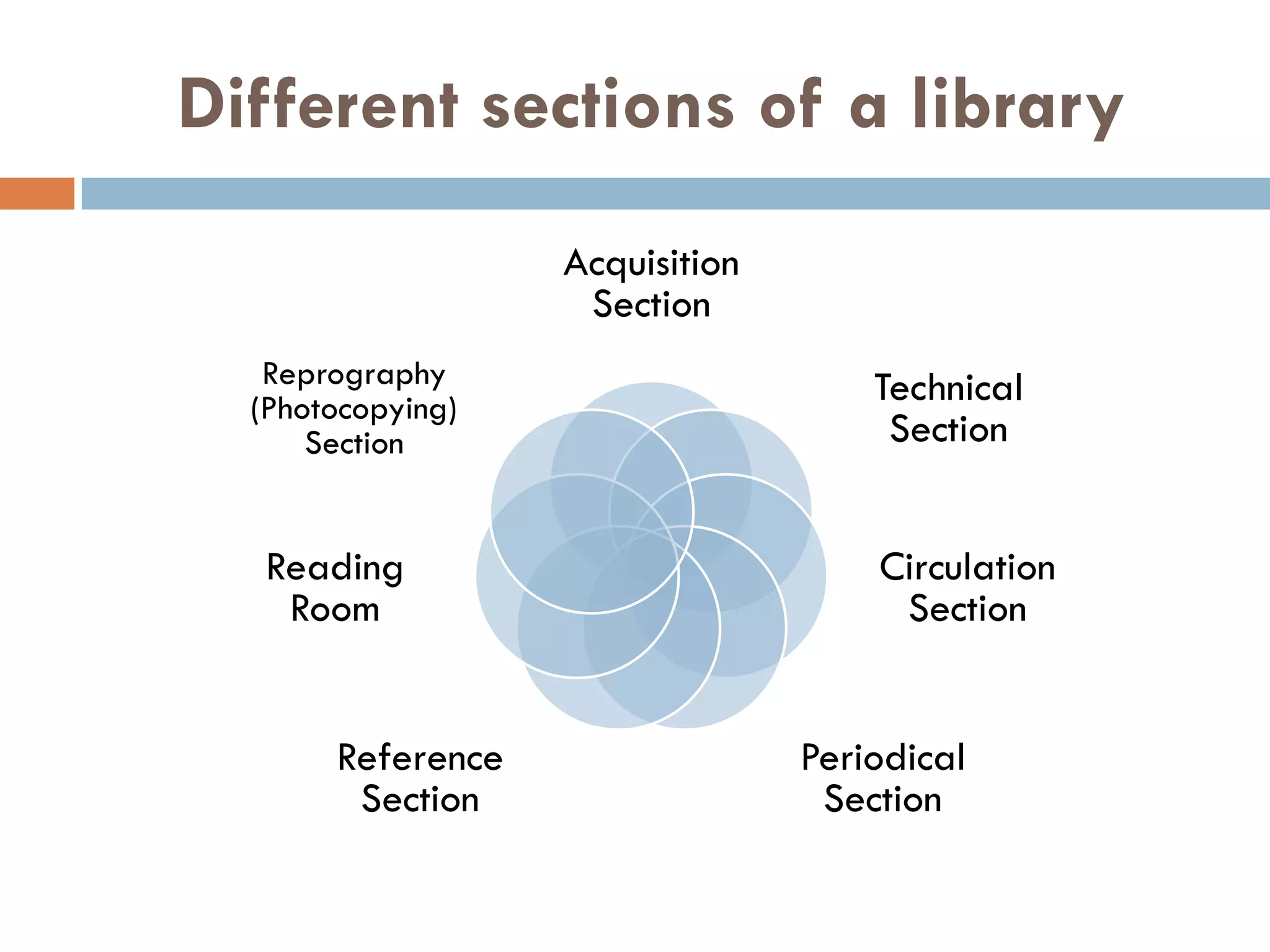
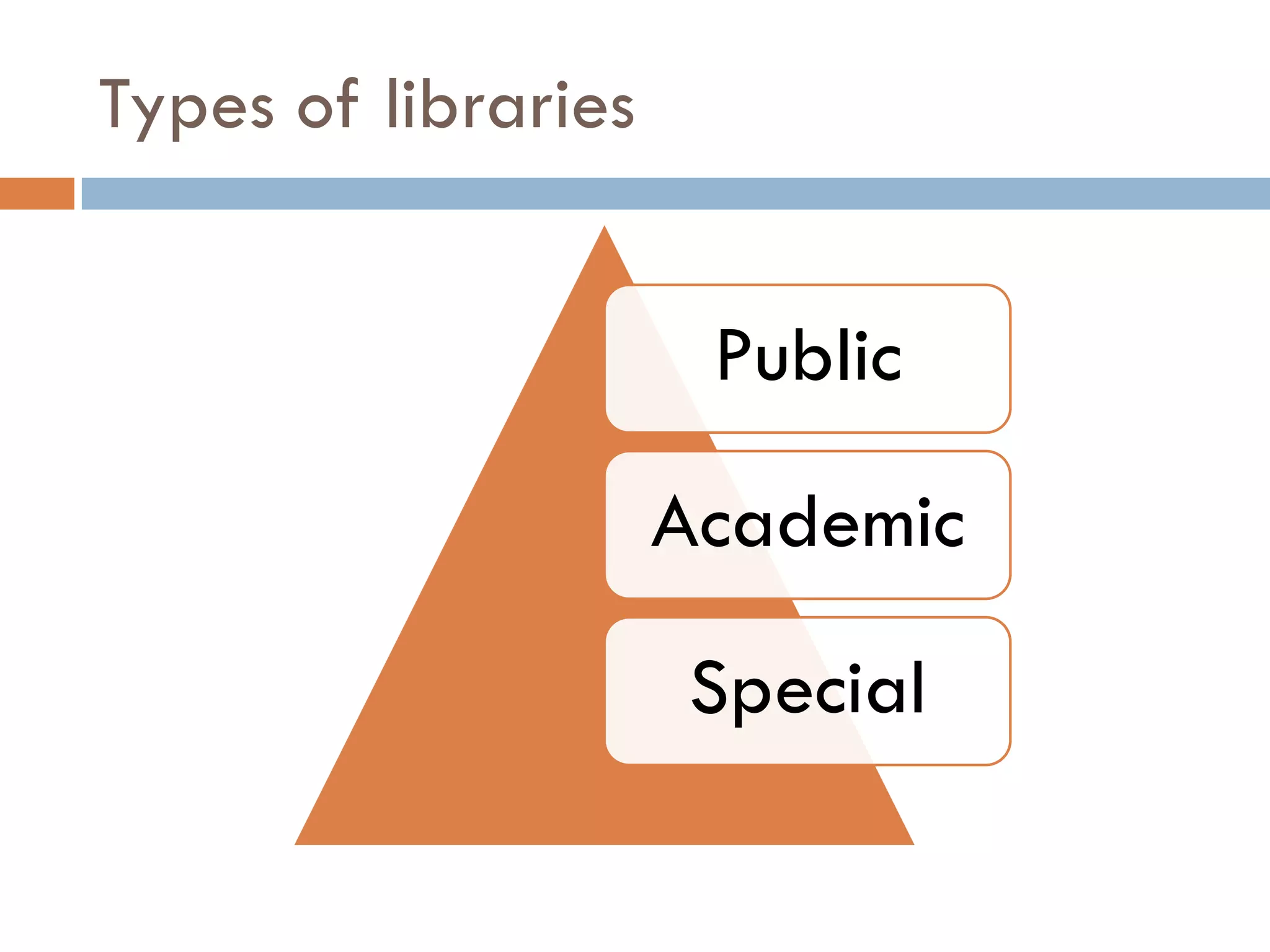
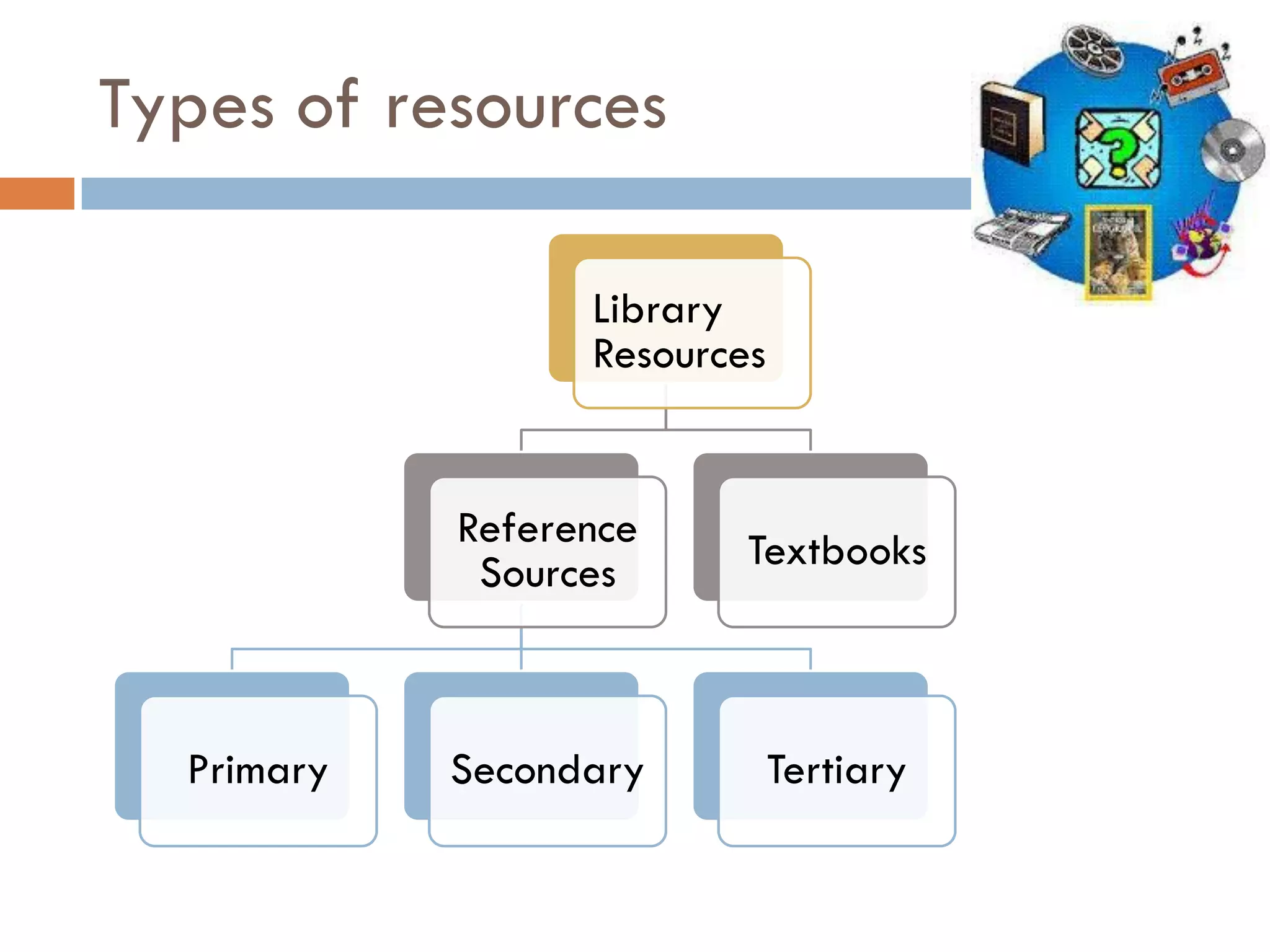
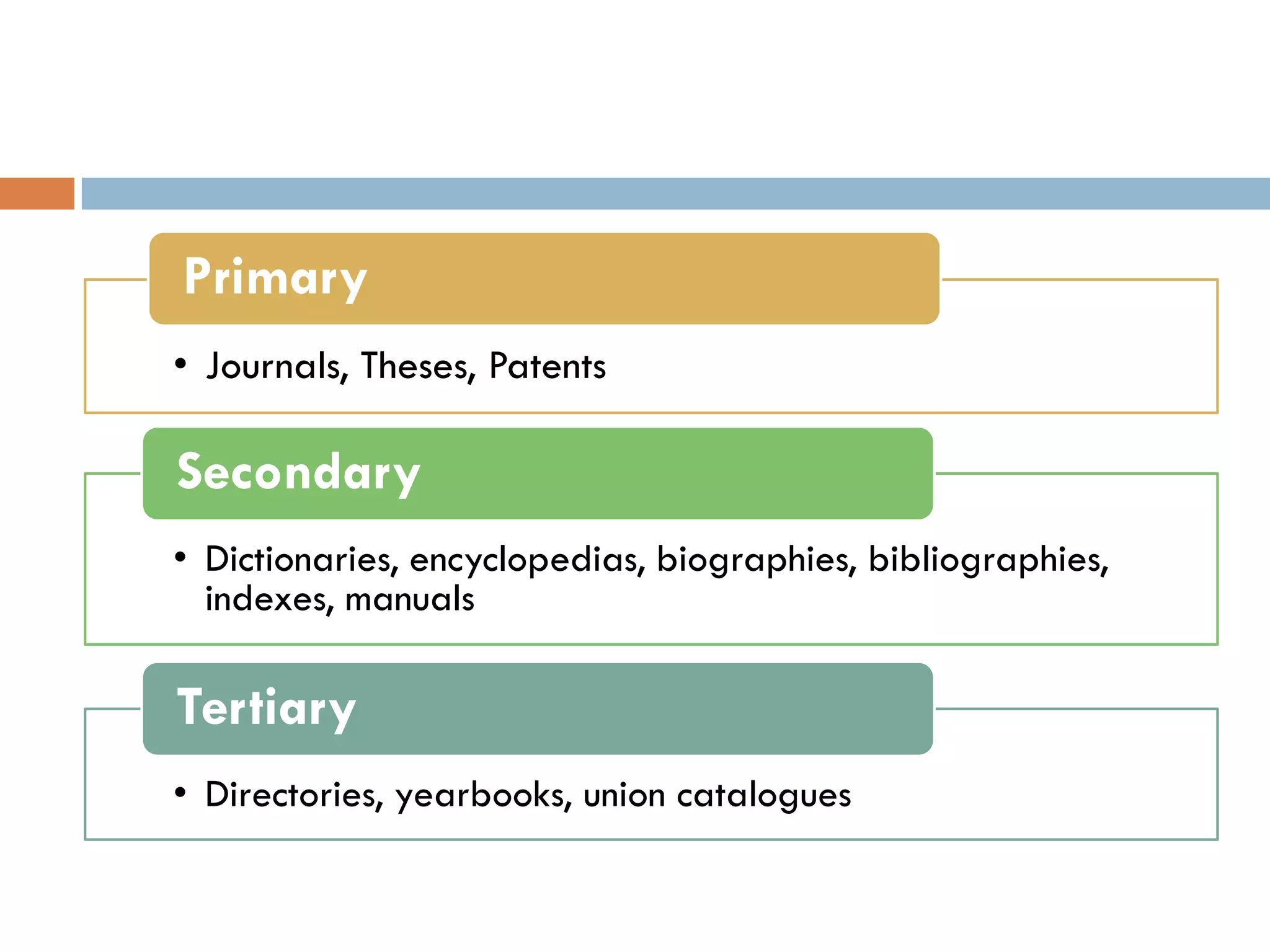
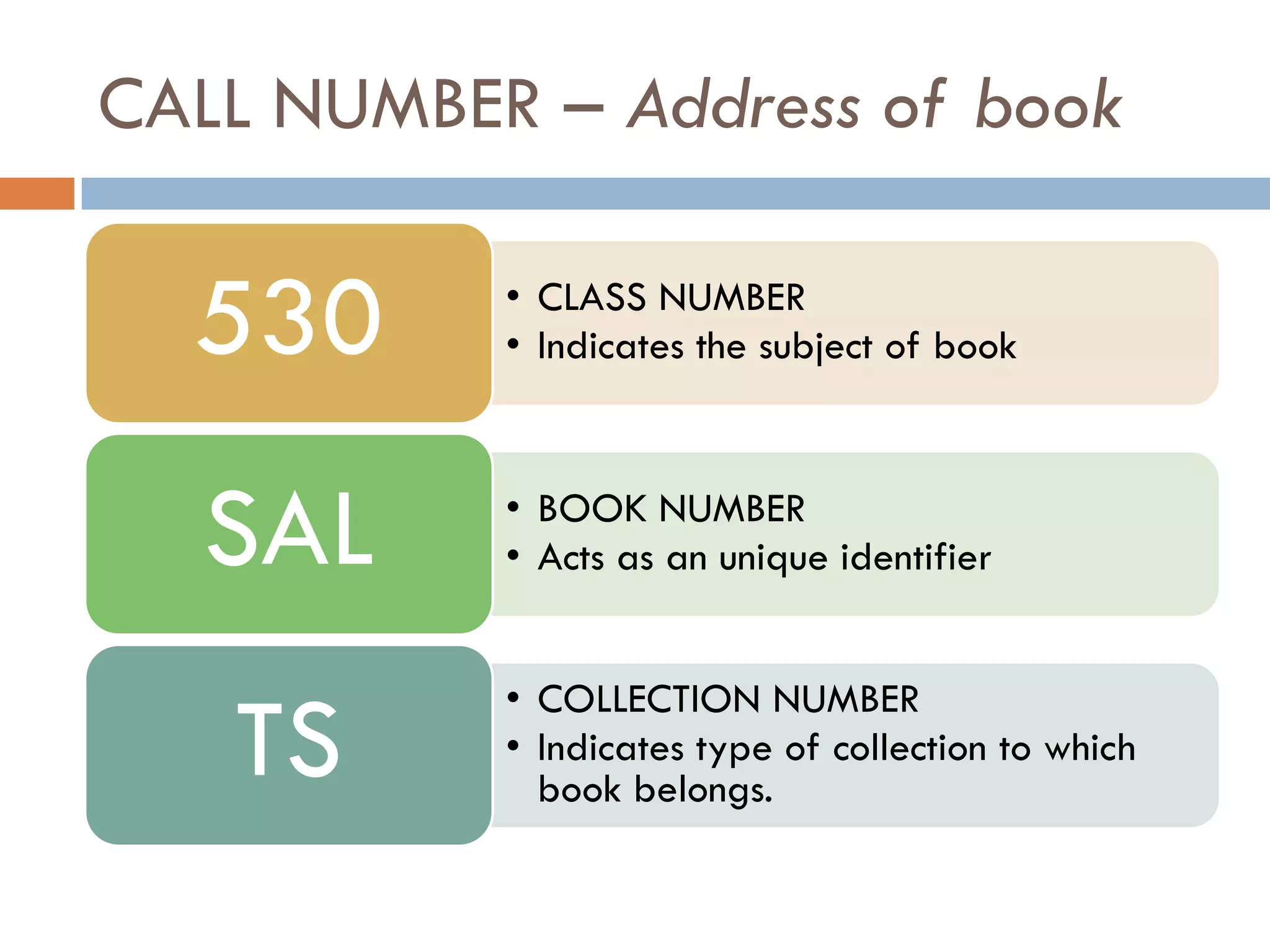
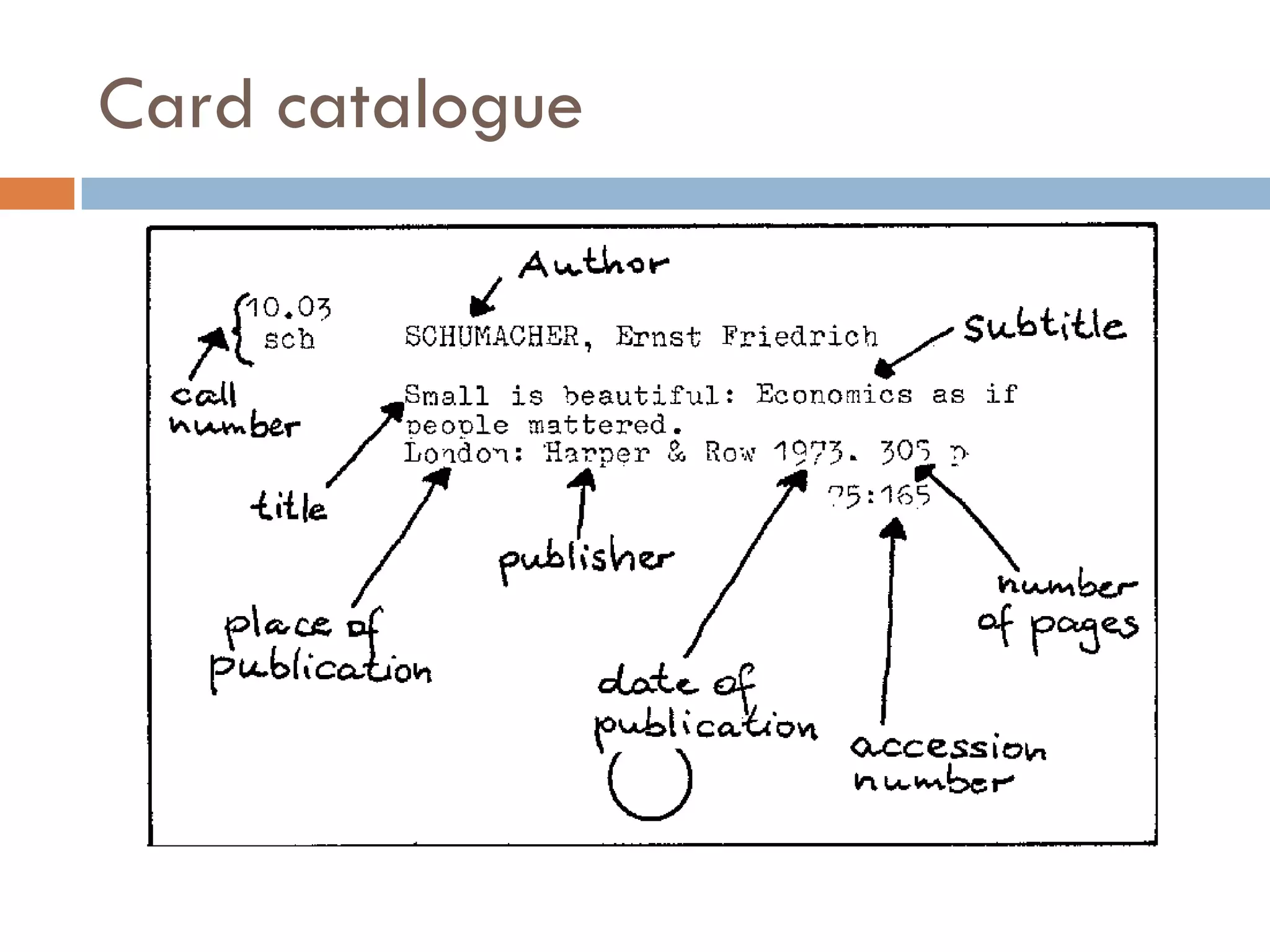
A library is an organized collection of documents from various formats that are preserved and made available for use by a community. Libraries serve various roles like supplementing education, providing resources for research and recreation, and acting as cultural and social hubs. They organize and provide access to their collections through classification systems, cataloguing, and online search tools in order to help users efficiently find the information they need.