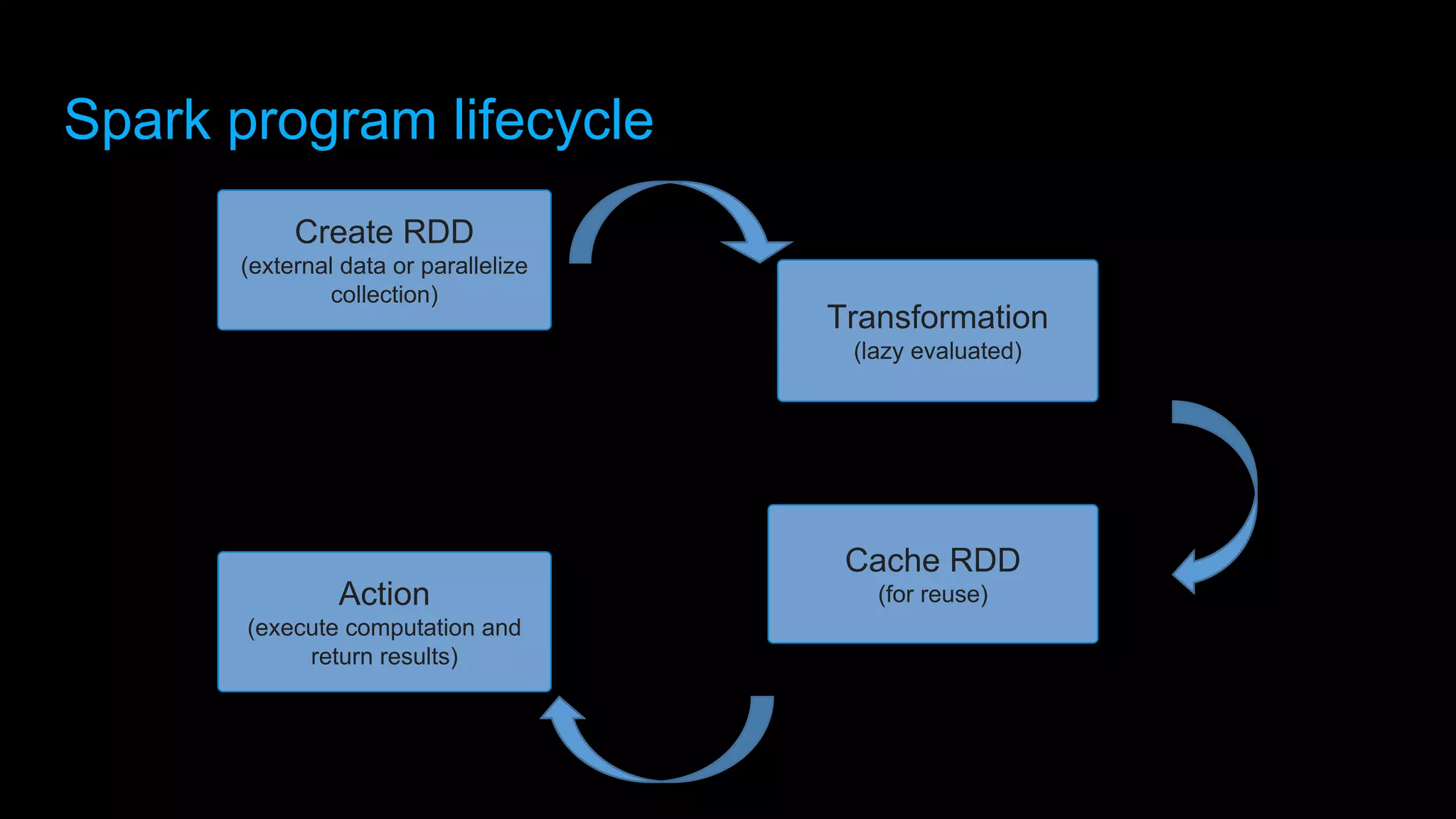
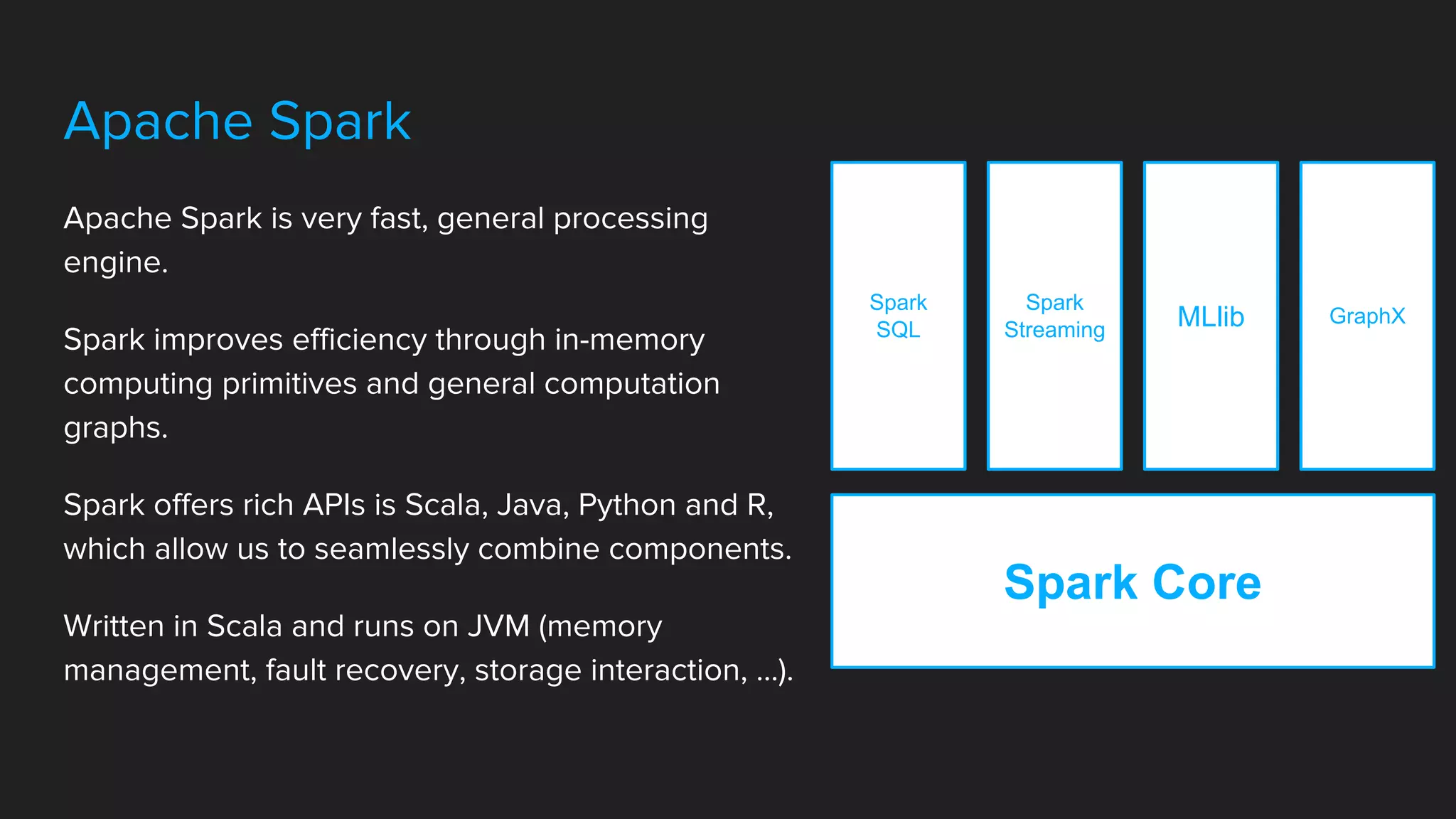
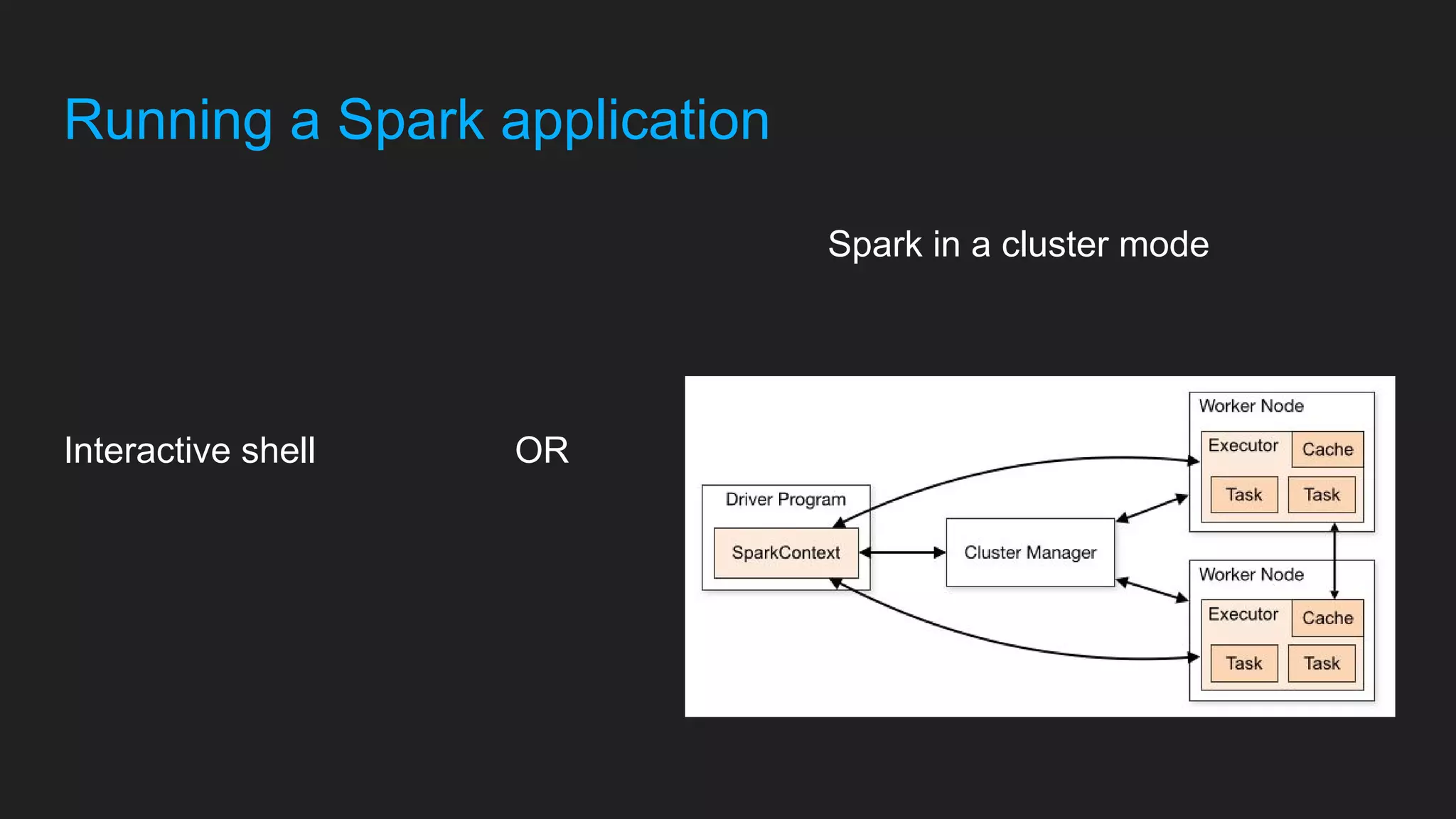
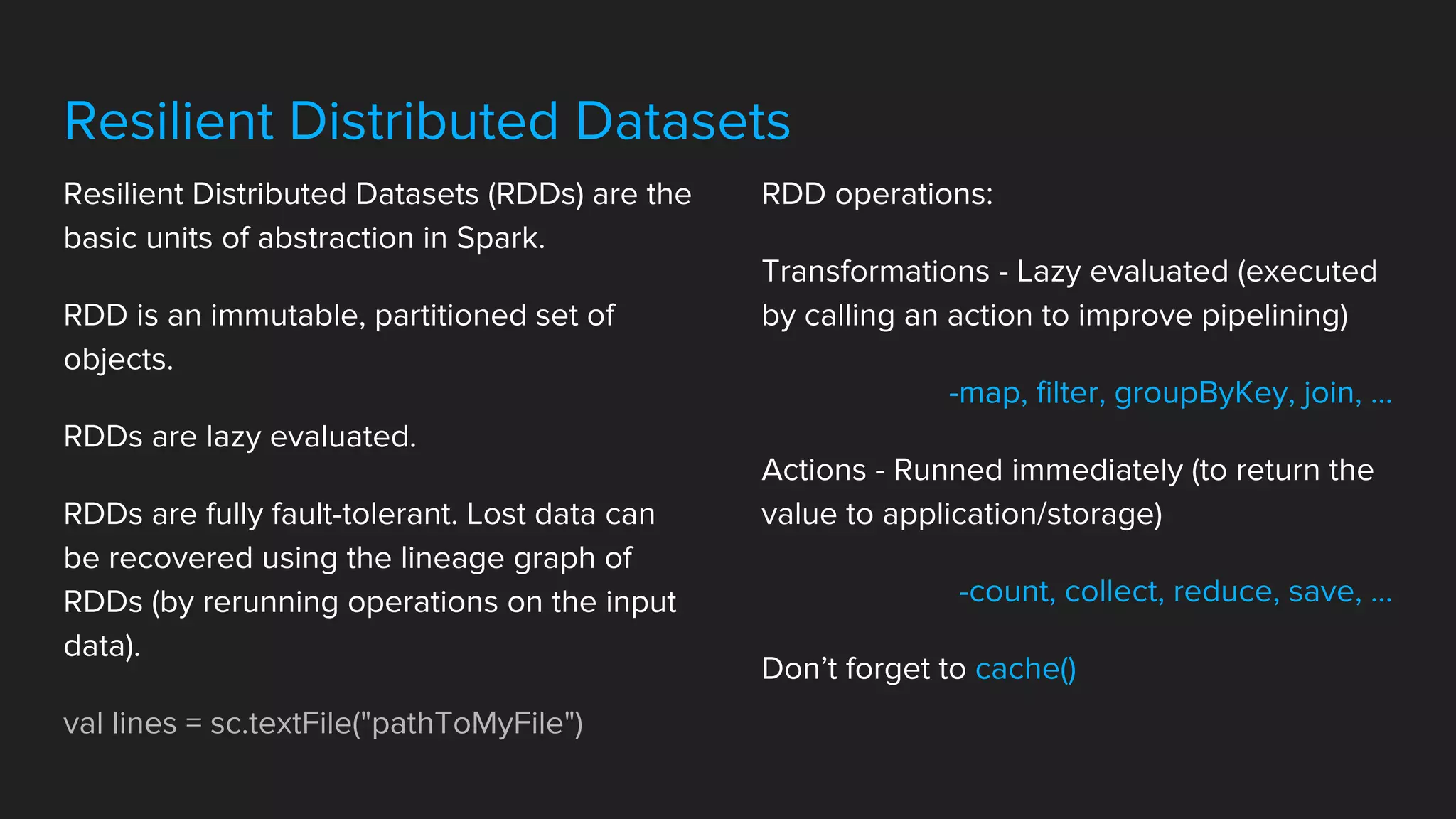
Spark is a fast, general processing engine that improves efficiency through in-memory computing and computation graphs. It offers APIs in Scala, Java, Python and R. Spark applications use Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) which are immutable, partitioned objects that support fault tolerance. Spark also supports Spark SQL for structured data querying and Spark MLlib for machine learning.


![Spark Datasets
Spark Dataset is a strongly-typed, immutable collection of objects that are mapped to a
relational schema. *
Encoder is responsible for converting between JVM objects and tabular representation.
API Preview in Spark 1.6
Main goal was to bring the object oriented programming style and type-safety, while
preserving performance.
Java and Scala APIs so far.
val lines = sqlContext.read.text("pathToMyFile").as[String]
*qoute: https://databricks.com/blog/2016/01/04/introducing-spark-datasets.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/letsstartwithspark-161031142154/75/Let-s-start-with-Spark-6-2048.jpg)