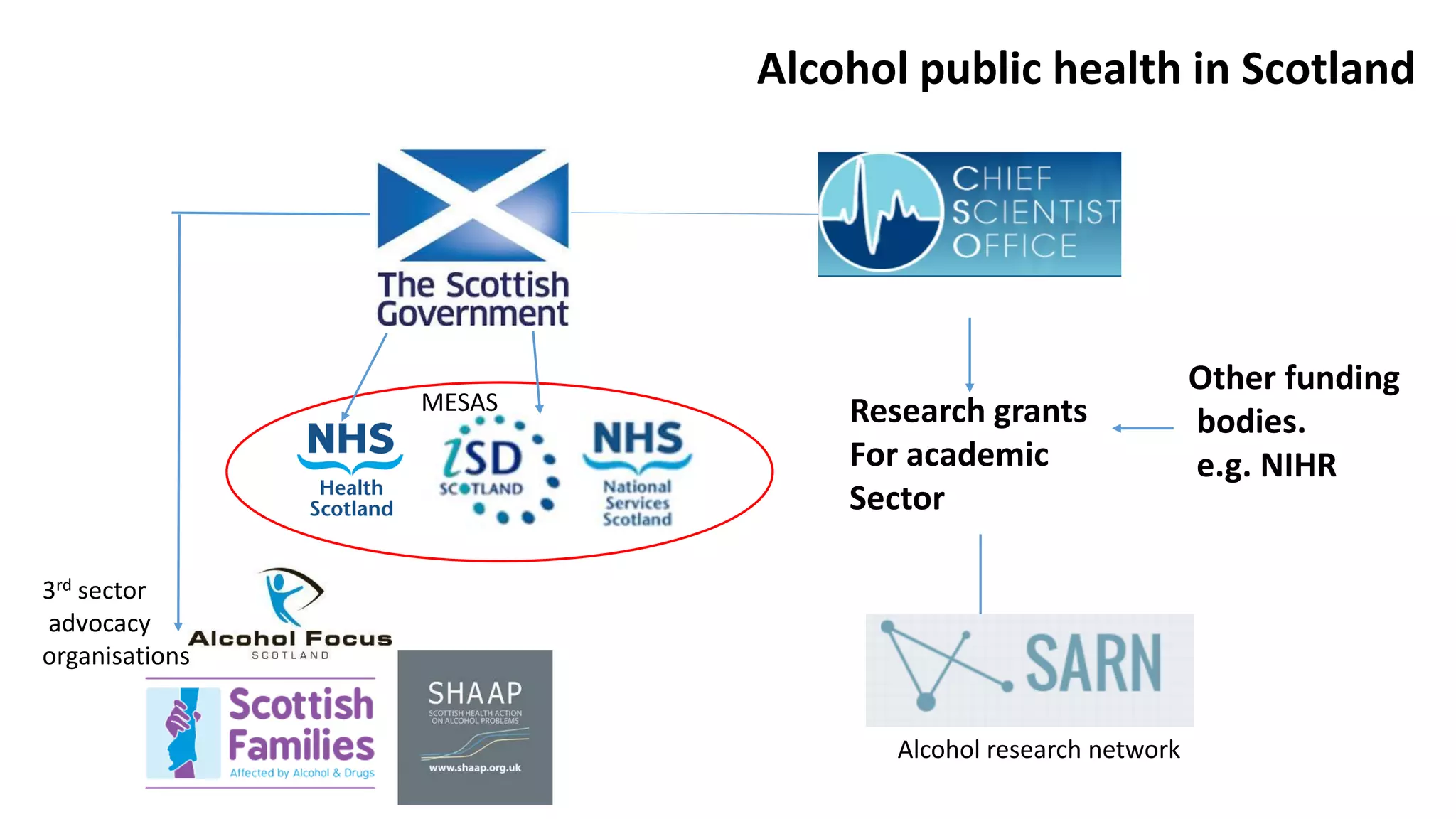
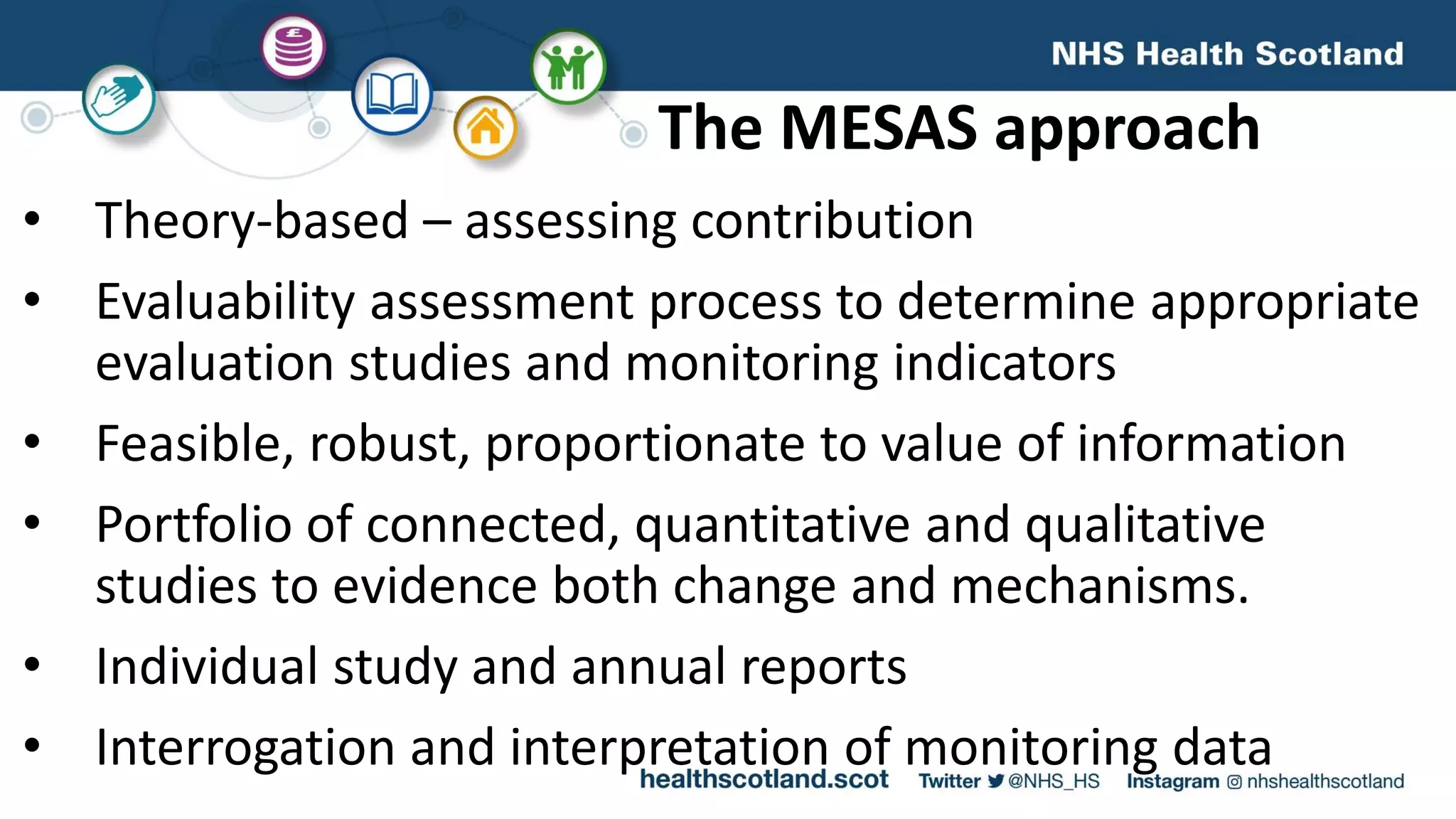
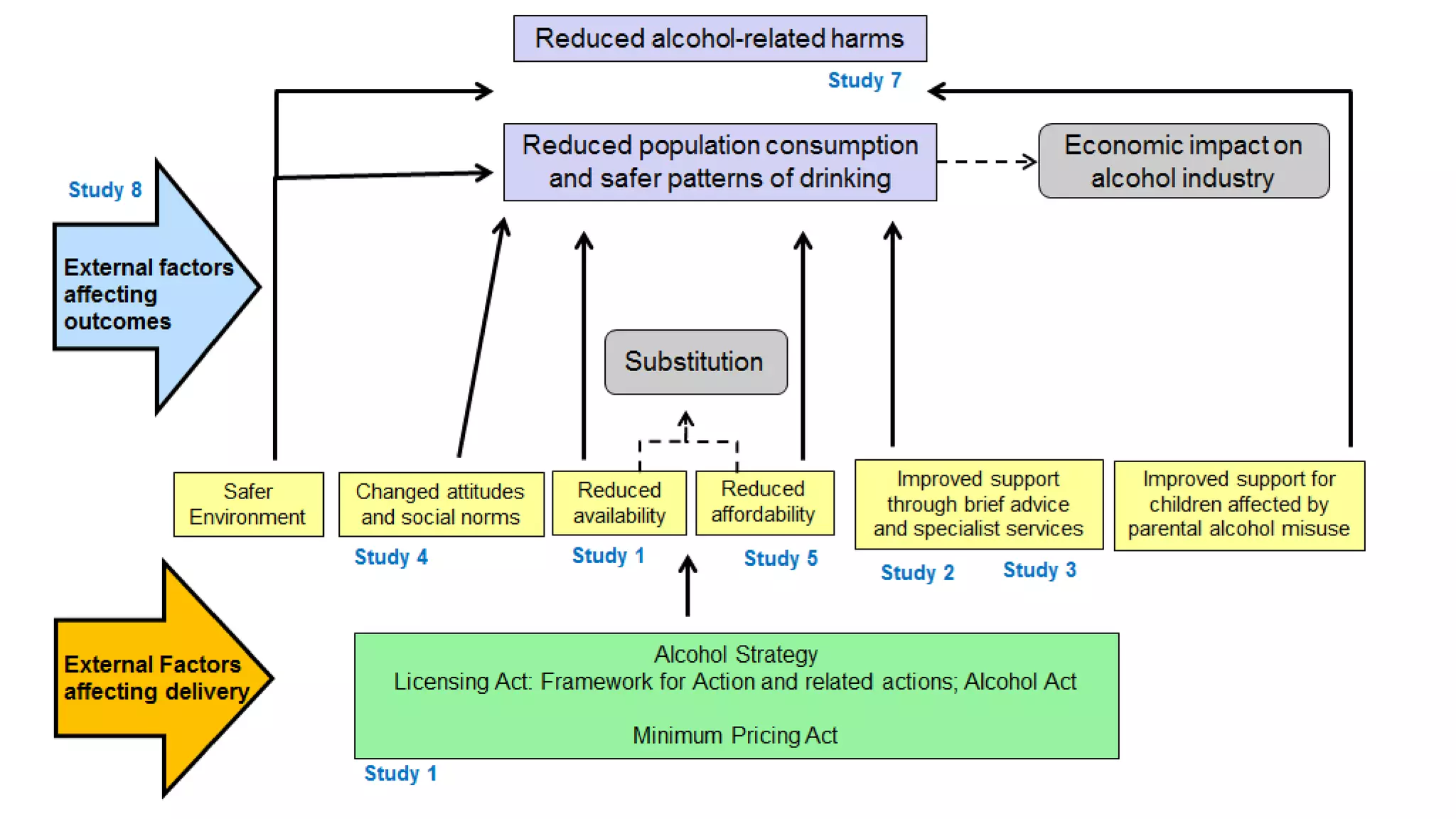
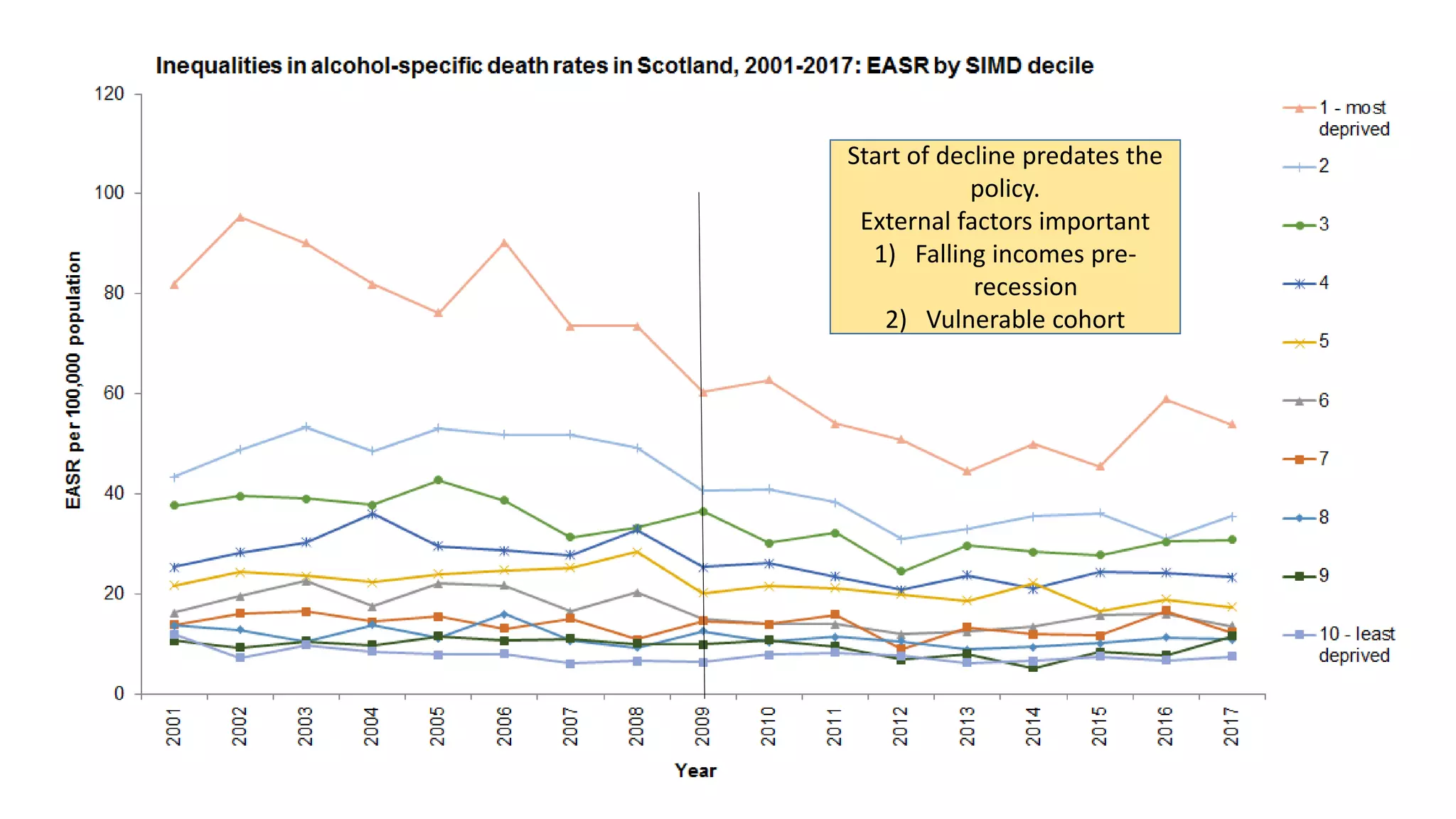
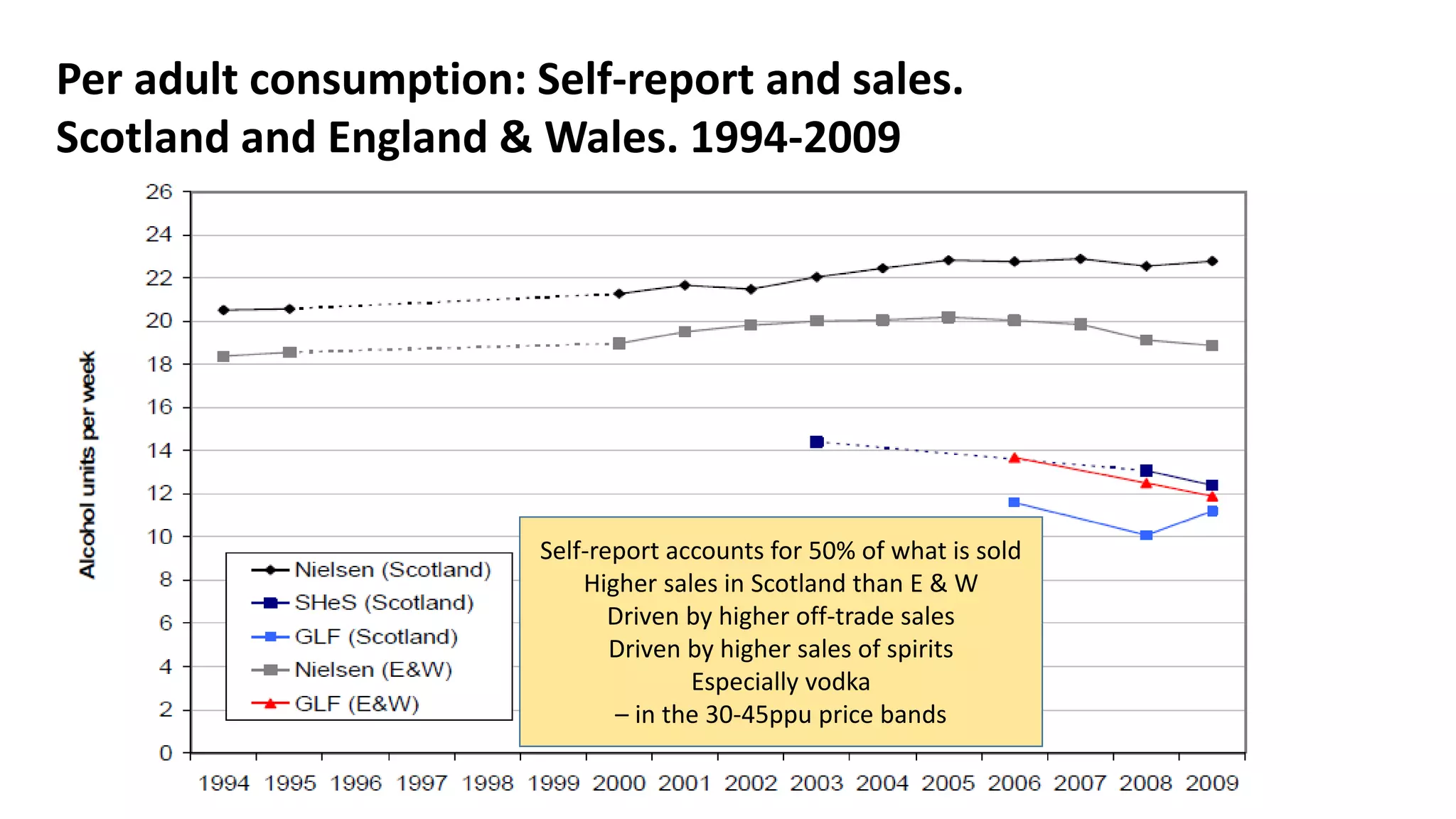
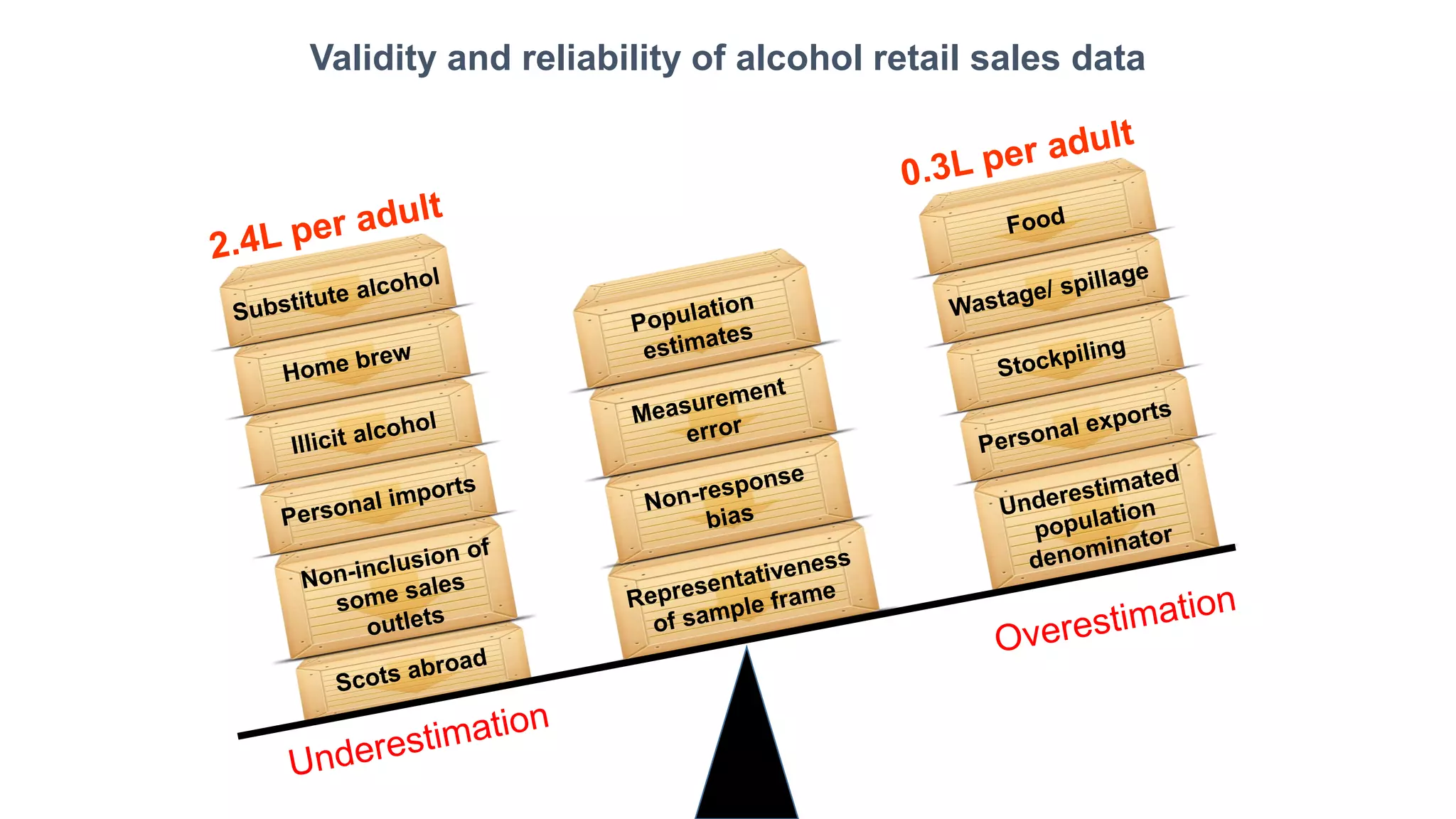
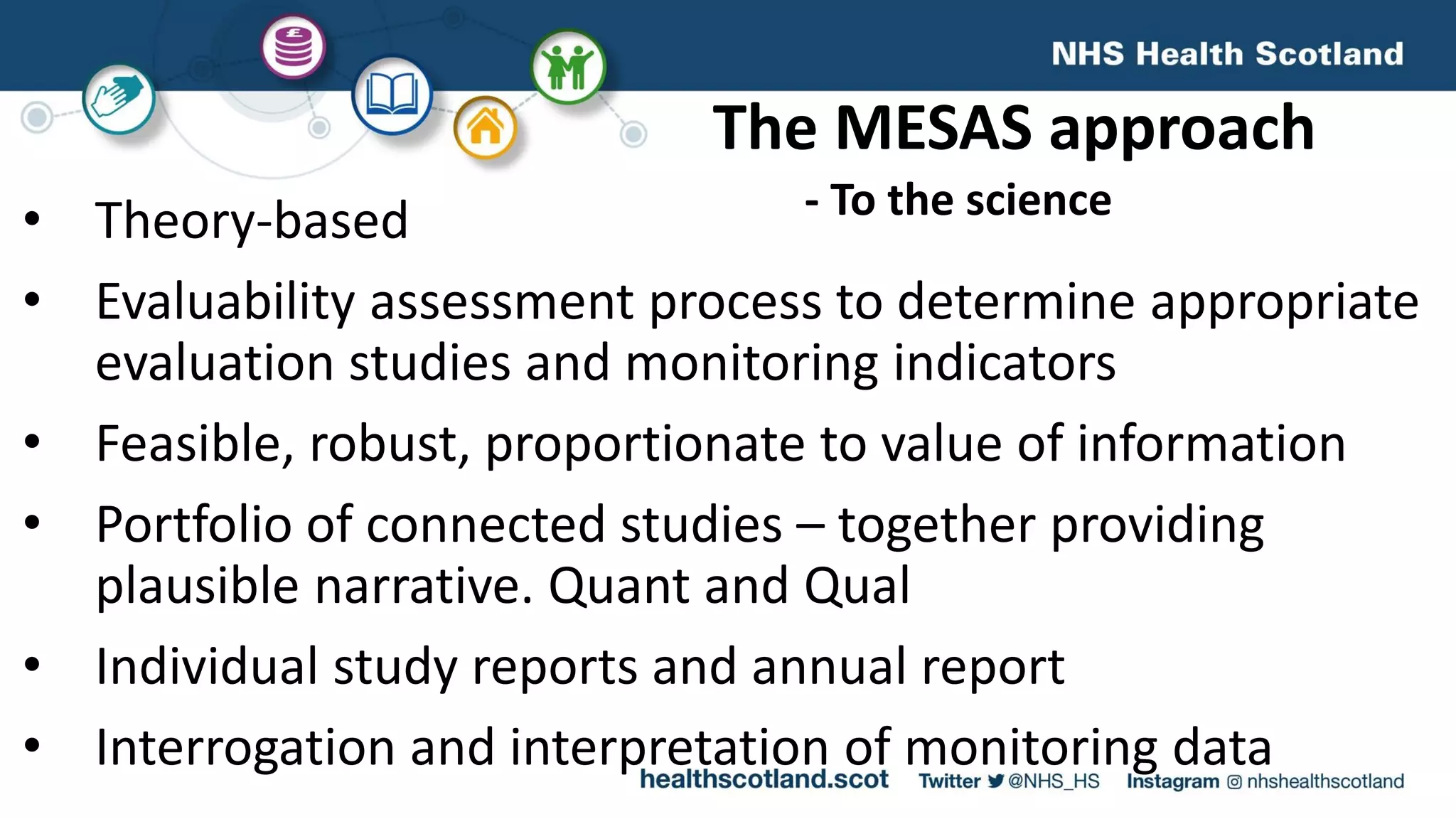
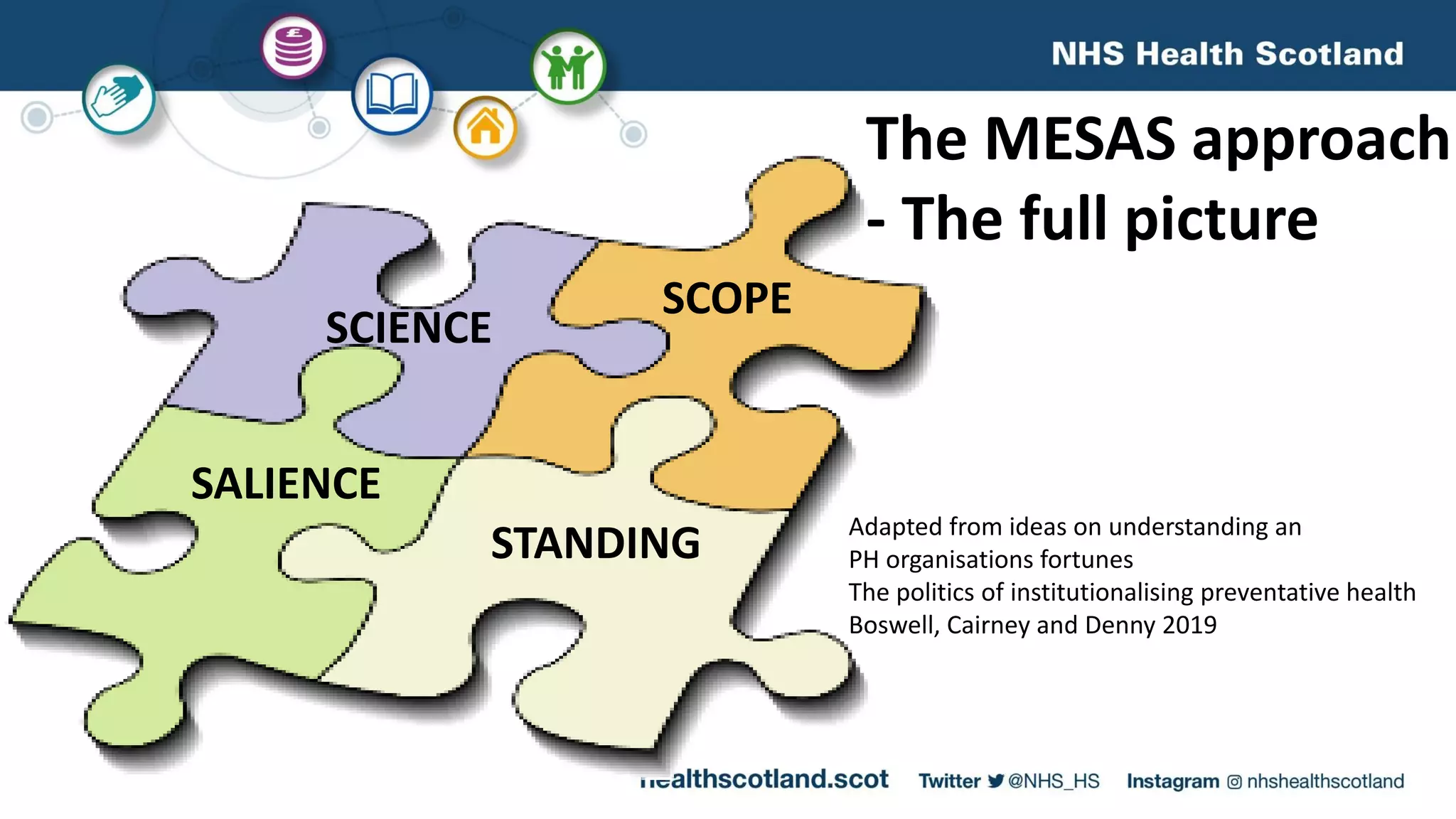
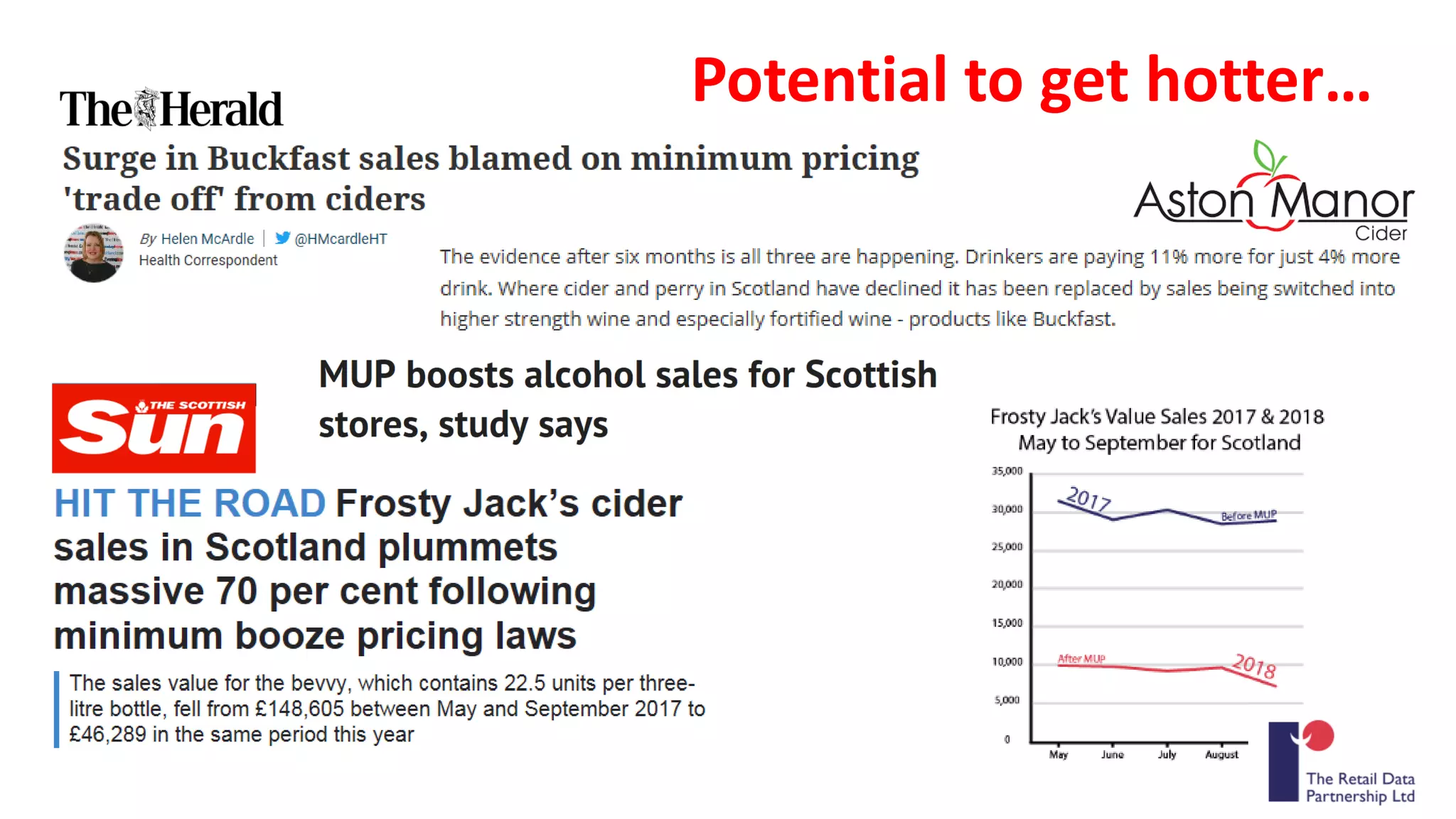
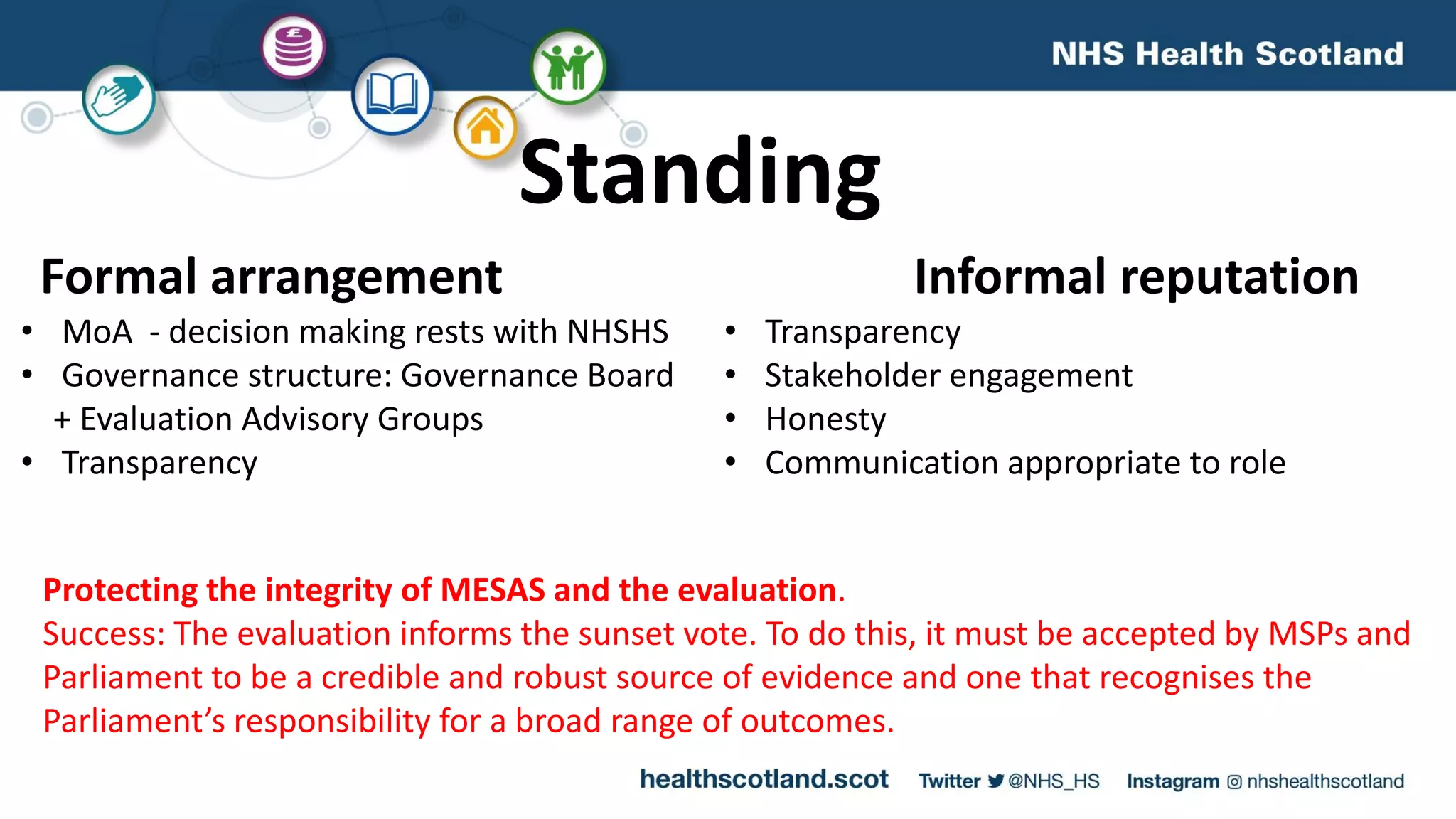
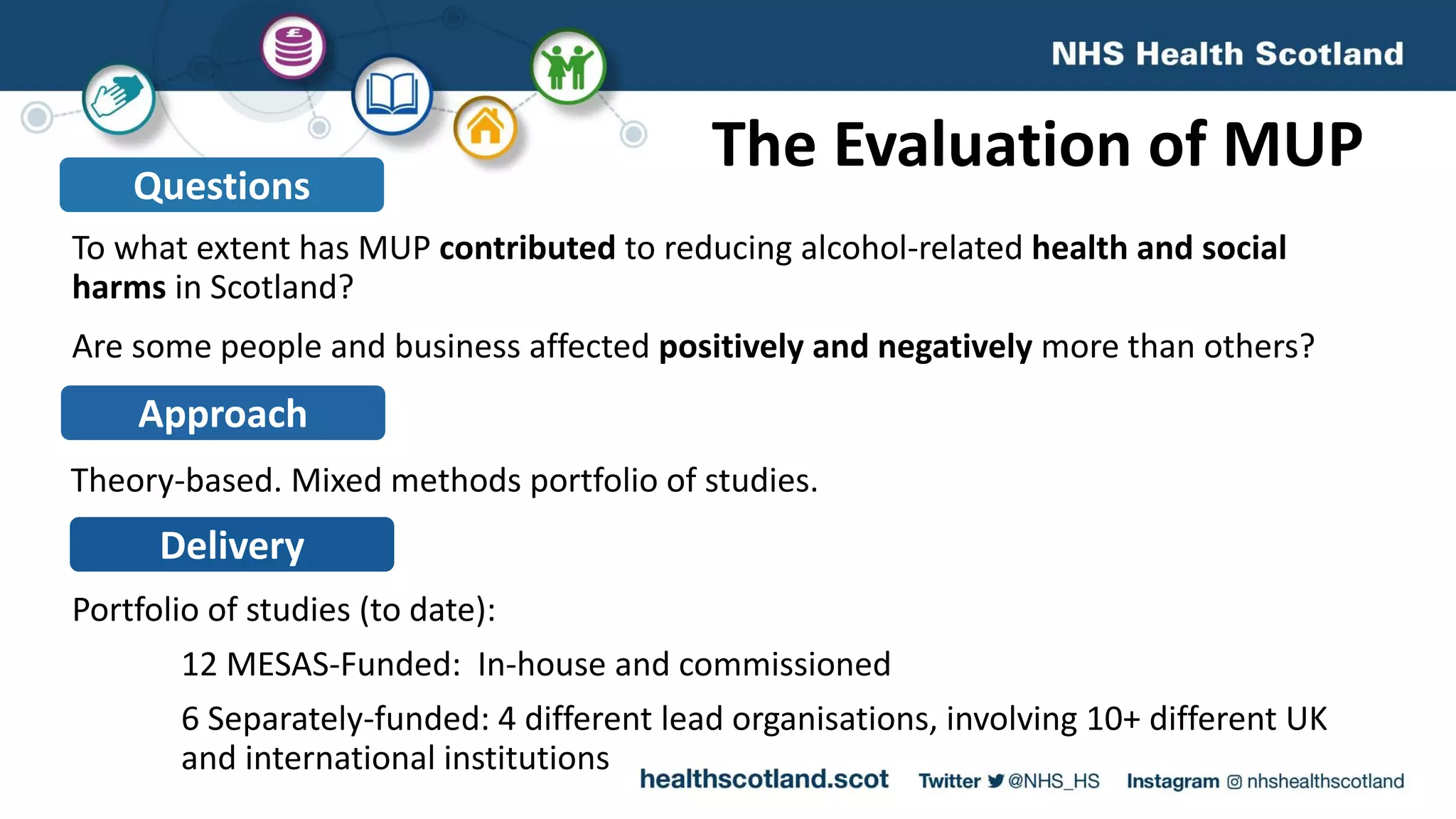
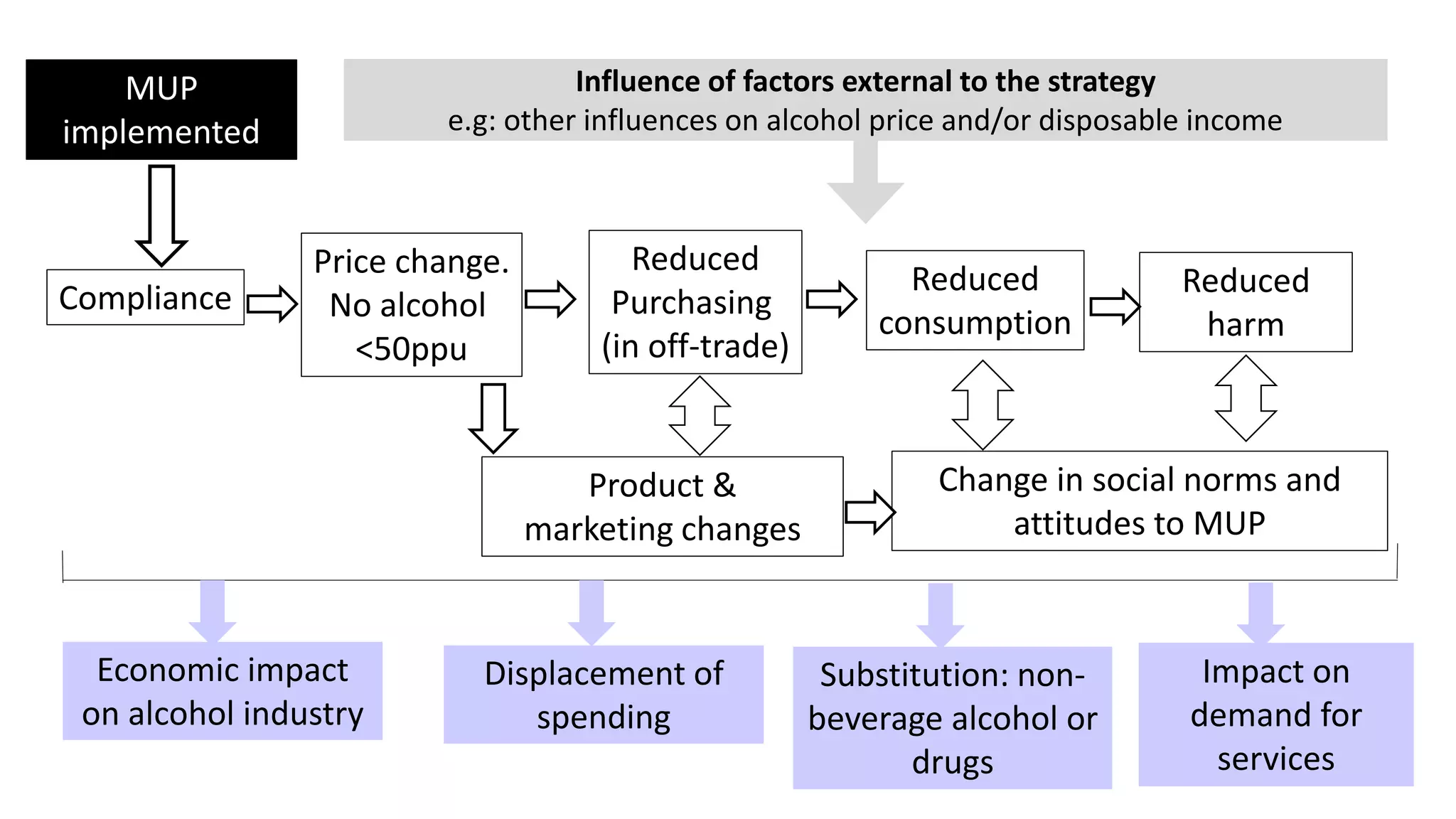
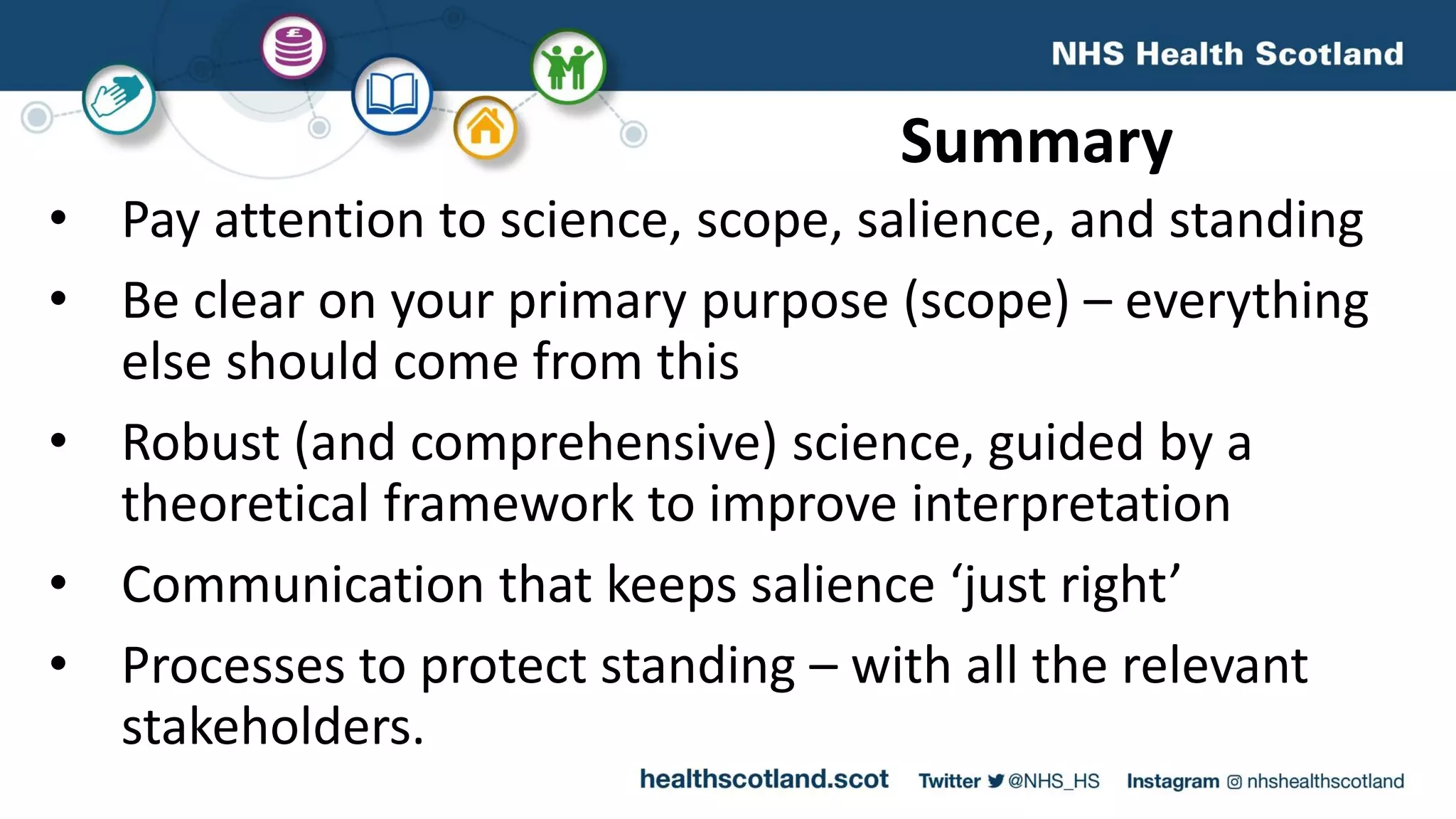
The MESAS approach to evaluating Scotland's alcohol strategy and minimum unit pricing policy focuses on building a robust evidence base through a portfolio of quantitative and qualitative studies. It aims to determine the policy's impact on alcohol consumption and harms while considering external factors, and to communicate findings in a way that informs the upcoming parliamentary vote without becoming too politicized. The evaluation emphasizes theoretical frameworks, mixed methods, transparency, stakeholder engagement, and maintaining its credibility and independence to ensure its findings can guide the future of the policy.