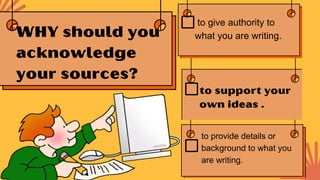
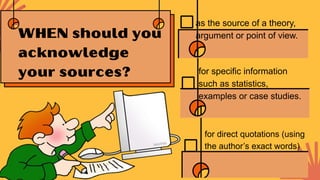
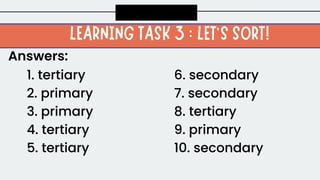
This document discusses primary, secondary, and tertiary sources of information. It provides examples of each type of source and directions for students to practice identifying primary, secondary, and tertiary sources. Students are asked to find examples of each source type and to consider the importance of citing sources in their own work to avoid plagiarism and give credit where credit is due.