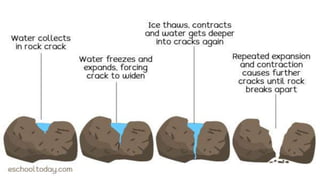
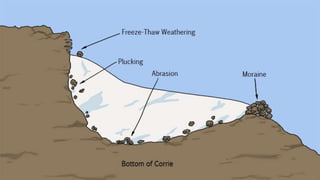
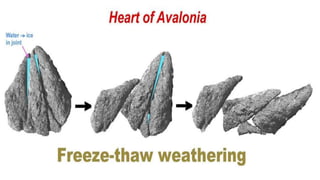
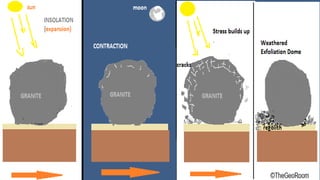
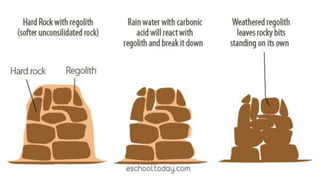
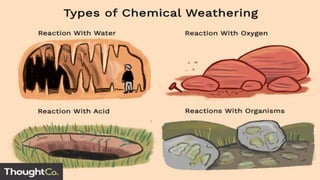
Weathering is the breakdown of rocks at the Earth's surface by various physical, chemical, and biological processes. Physical weathering breaks rocks apart through temperature changes or the abrasive action of water, ice, and gravity. Chemical weathering occurs as rainwater reacts with minerals in rocks to form new minerals and salts. Biological weathering weakens rocks through the growth of plant roots and burrowing of animals.