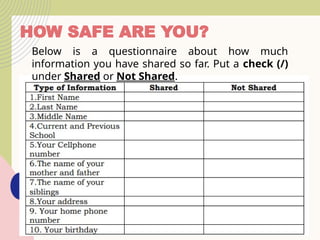
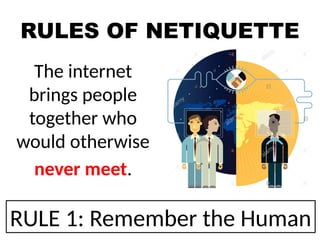
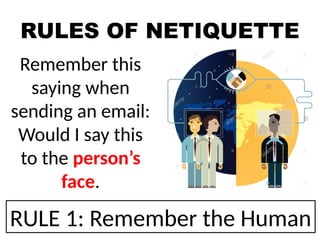
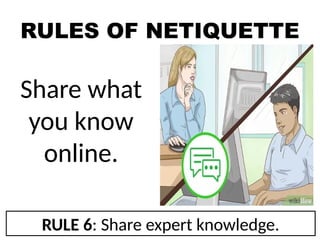
The document outlines essential internet safety concepts, focusing on safe information sharing, understanding internet threats, and responsible online behavior. It emphasizes the need for awareness about personal information risks, the importance of strong passwords, and adhering to netiquette for respectful online interactions. Additionally, it provides tips for avoiding spyware and scams while online, ensuring users can protect their privacy and security.