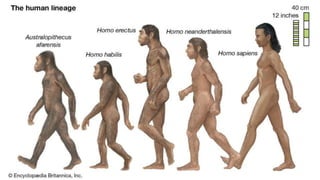
The document discusses the four major branches of science: mathematics and logic, biological science, physical science, and social science. It focuses on social science, defining it as the study of society and human relationships. Social science has several components, including anthropology, sociology, political science, history, geography, economics, and psychology. Anthropology is explained in depth, with its areas being social anthropology, cultural anthropology, linguistic anthropology, biological/physical anthropology, and archaeology. Sociology is introduced as the study of human social life, groups, and society. Physical and cultural anthropology are contrasted, with cultural anthropology studying all aspects of human society.