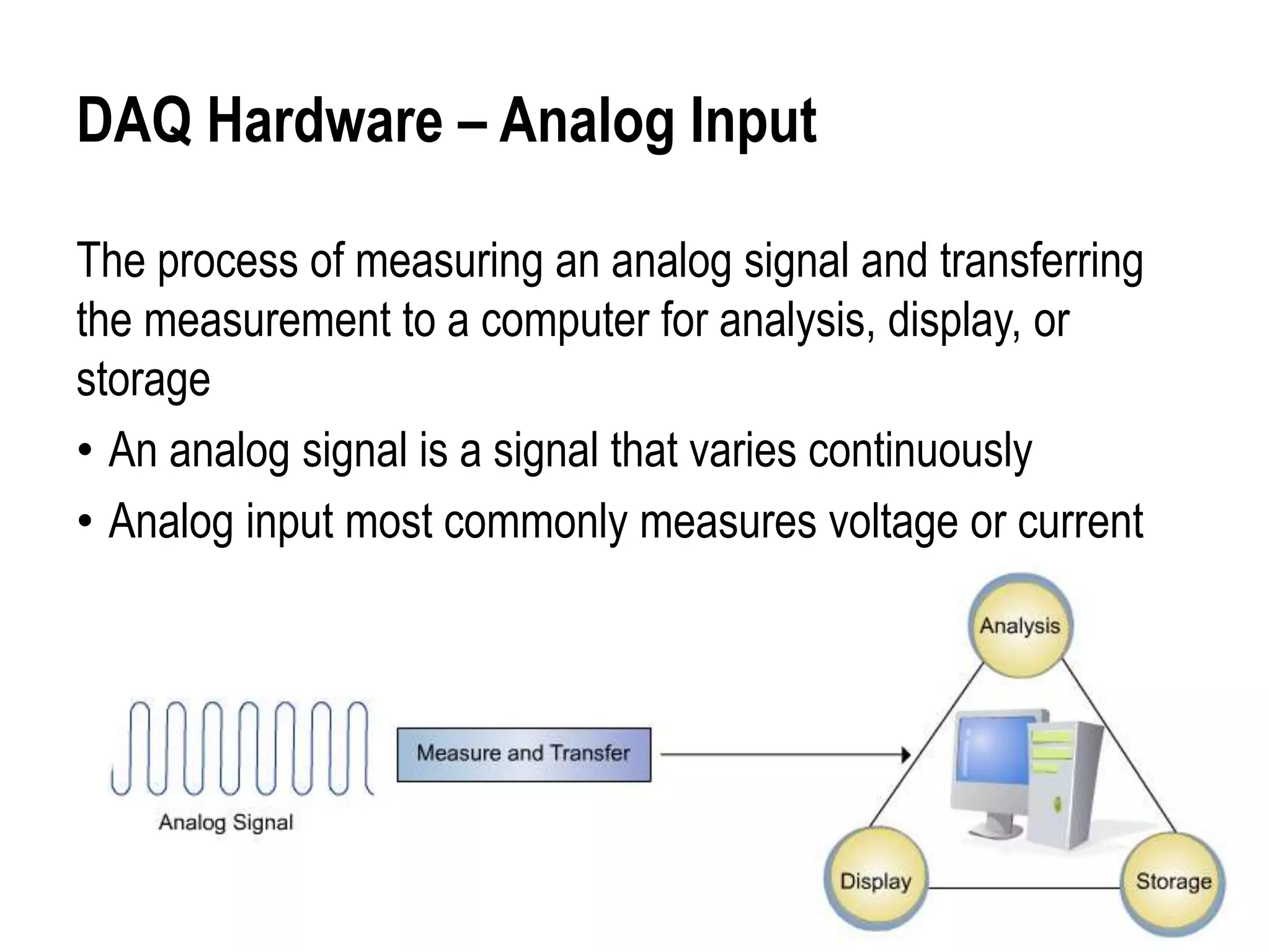
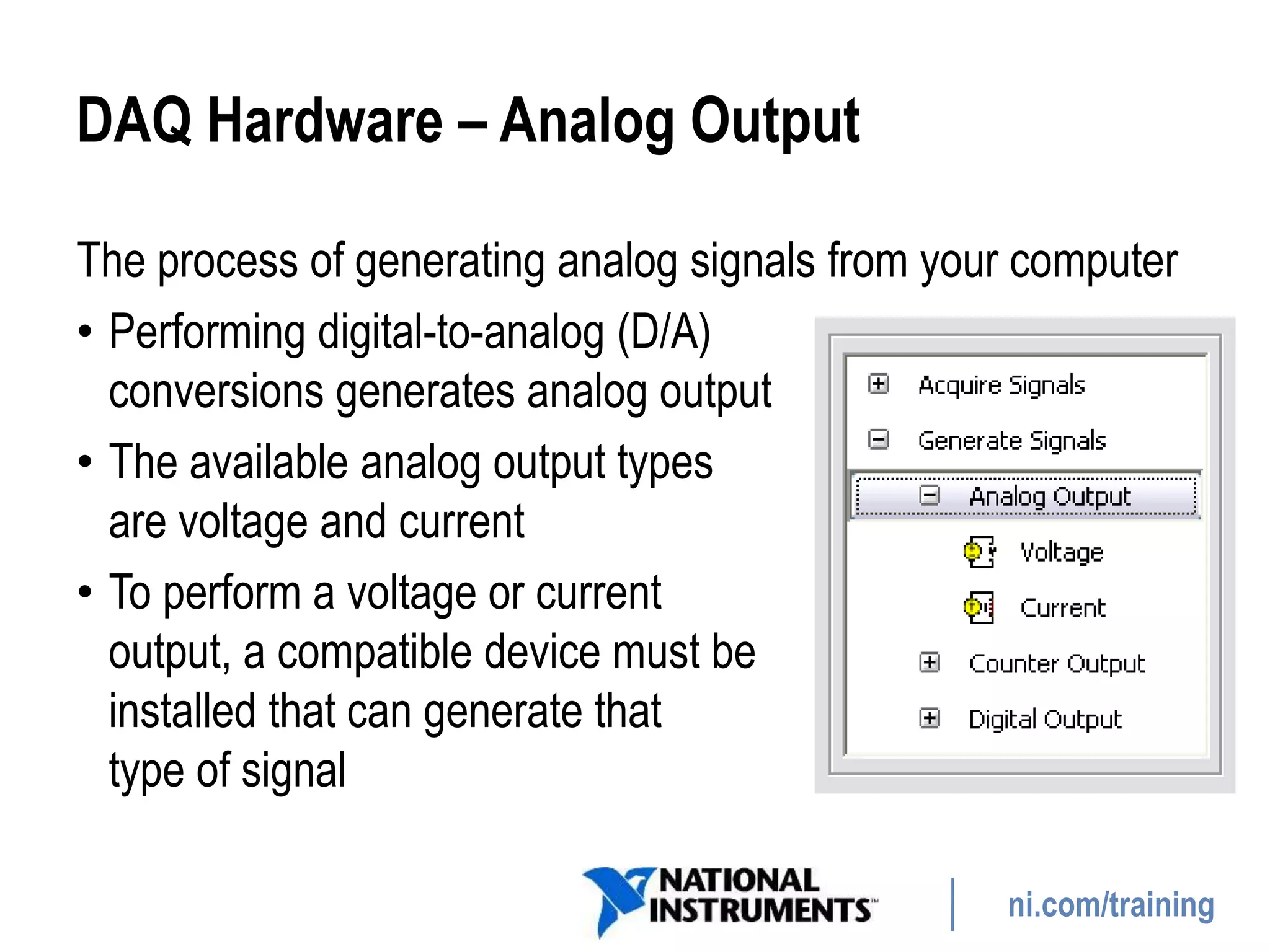
This document discusses a hands-on training session for NI LabView Core 1. It covers setting up DAQ hardware, including terminal blocks, cables, DAQ devices, and computer connections. It also discusses using the Measurement & Automation Explorer software to configure and test DAQ devices and GPIB instruments. Additional topics include instrument control using GPIB and serial communication, and how to automate processes and integrate multiple instrument types using a single computer platform.