Left heart failure is caused by dysfunction of the left ventricle, resulting in insufficient blood flow to vital organs. It has three stages:
Stage I involves redistribution of blood flow from the lower to upper lung lobes due to increased pulmonary capillary pressure. Radiology shows cephalization and cardiomegaly.
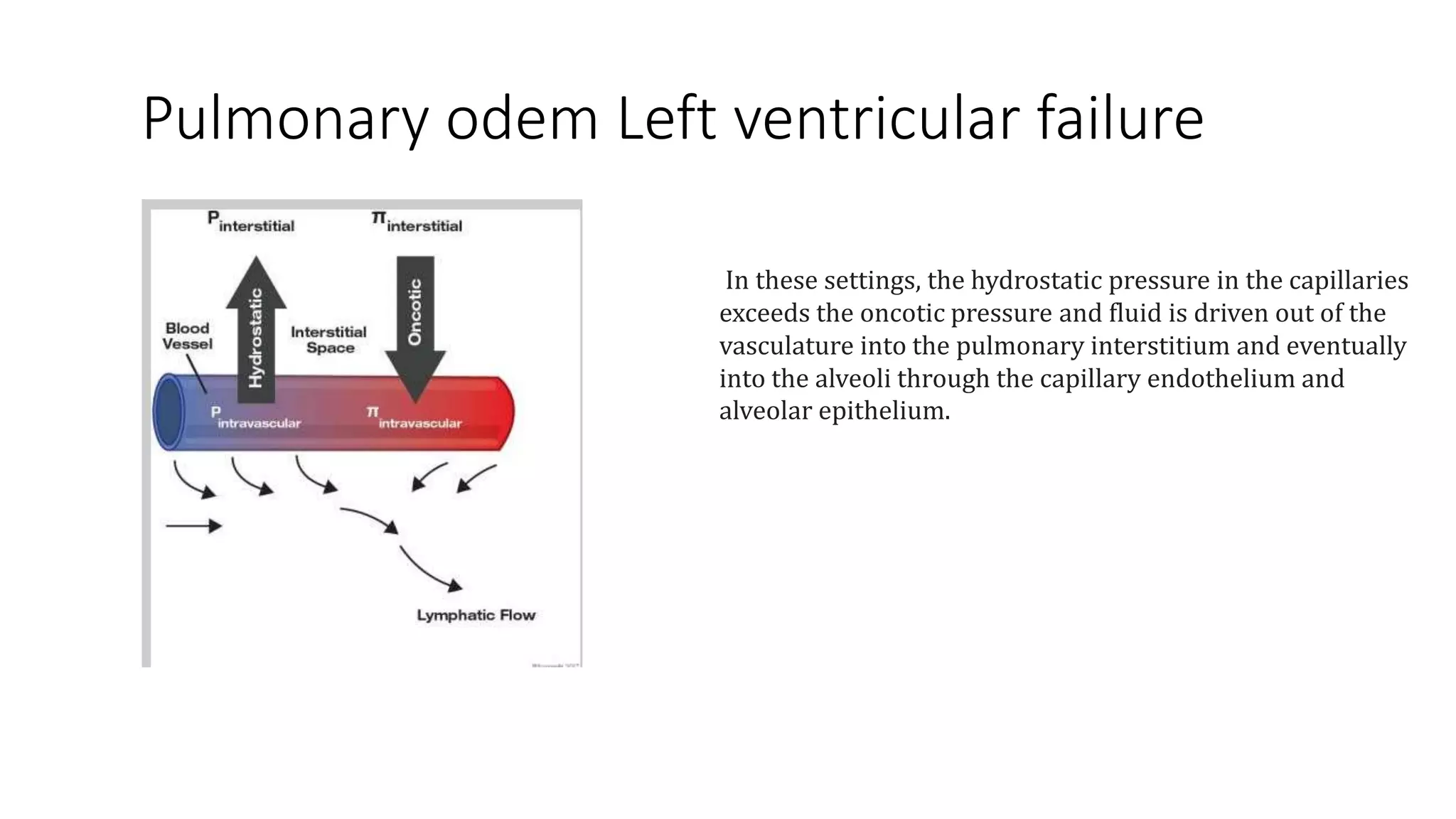
Stage II involves fluid leakage into the interstitial spaces seen as thickened septal lines, ground glass opacities, and bilateral pleural effusions.
Stage III is severe with fluid in the alveoli seen as consolidations, air bronchograms, and pleural effusions. Pulmonary edema can be cardiogenic or non-cardiogenic like ARDS.