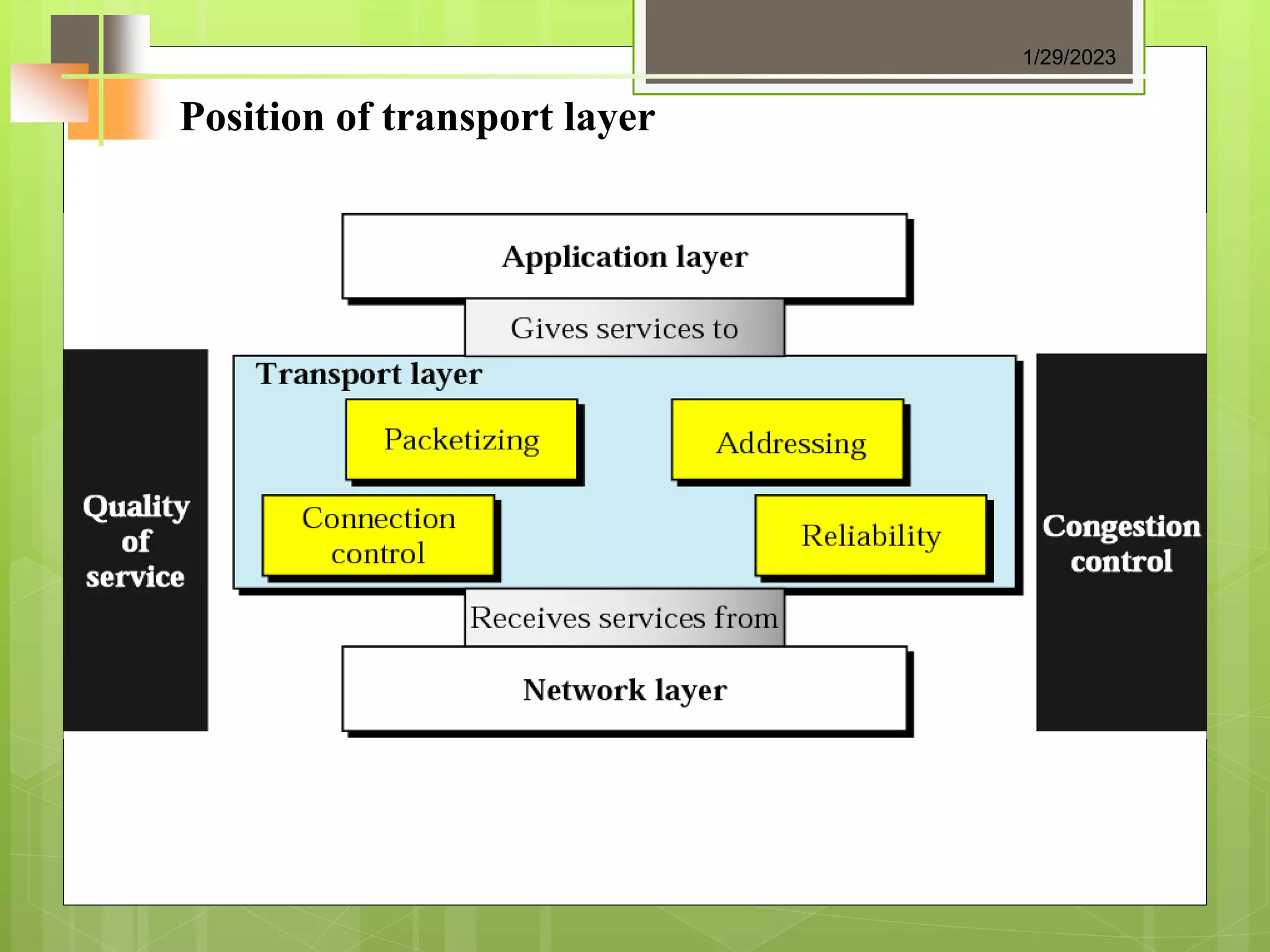
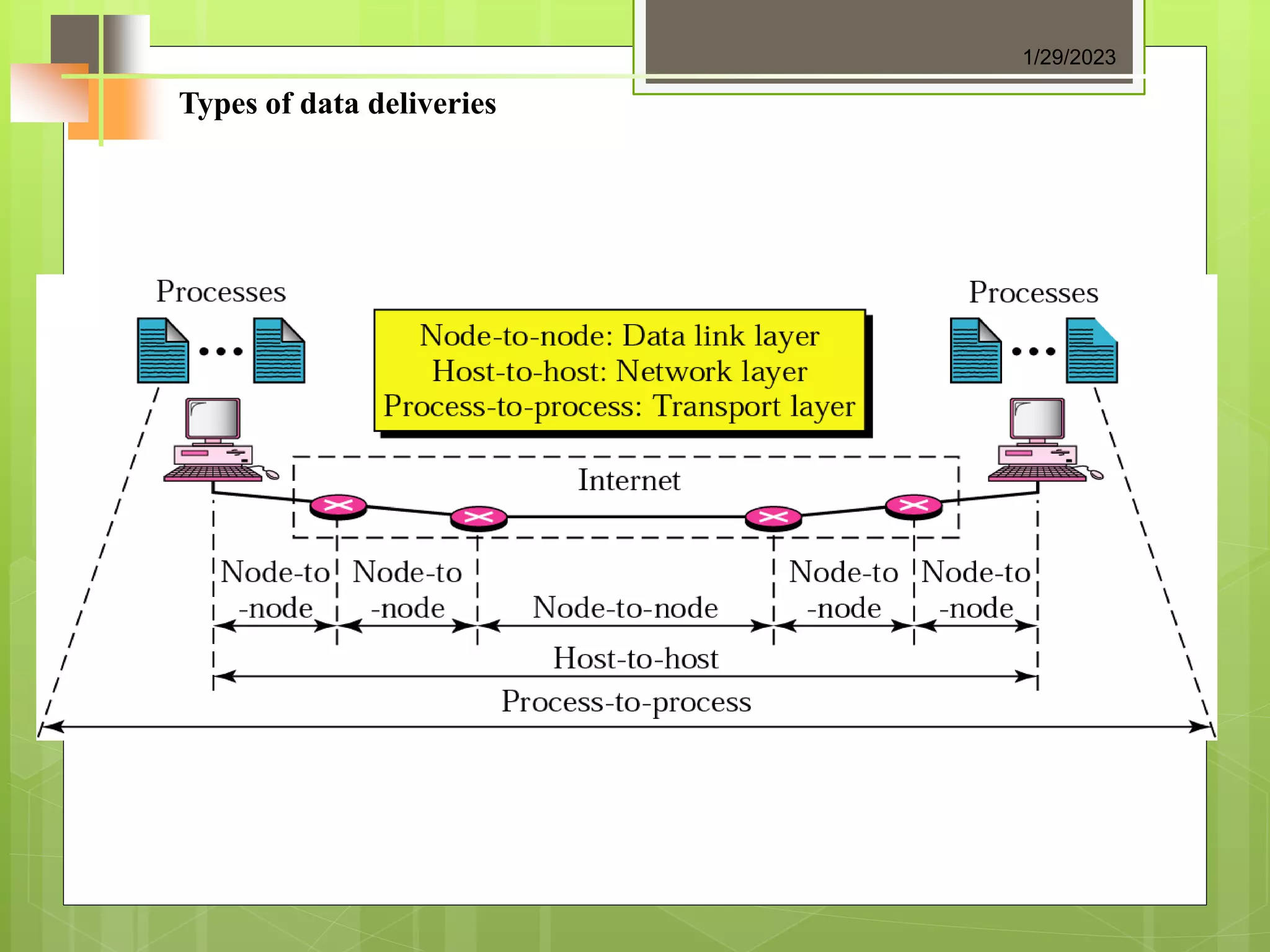
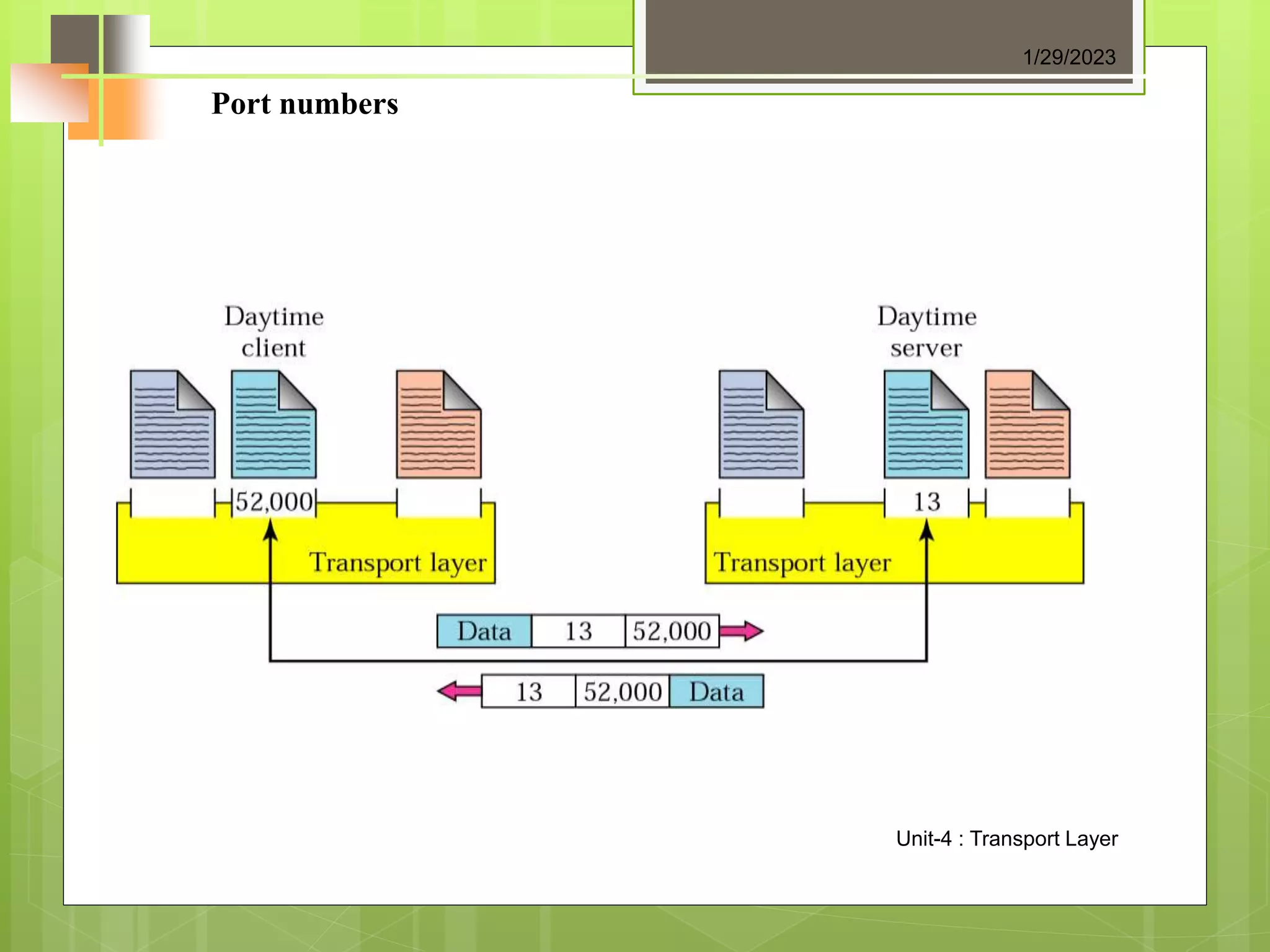
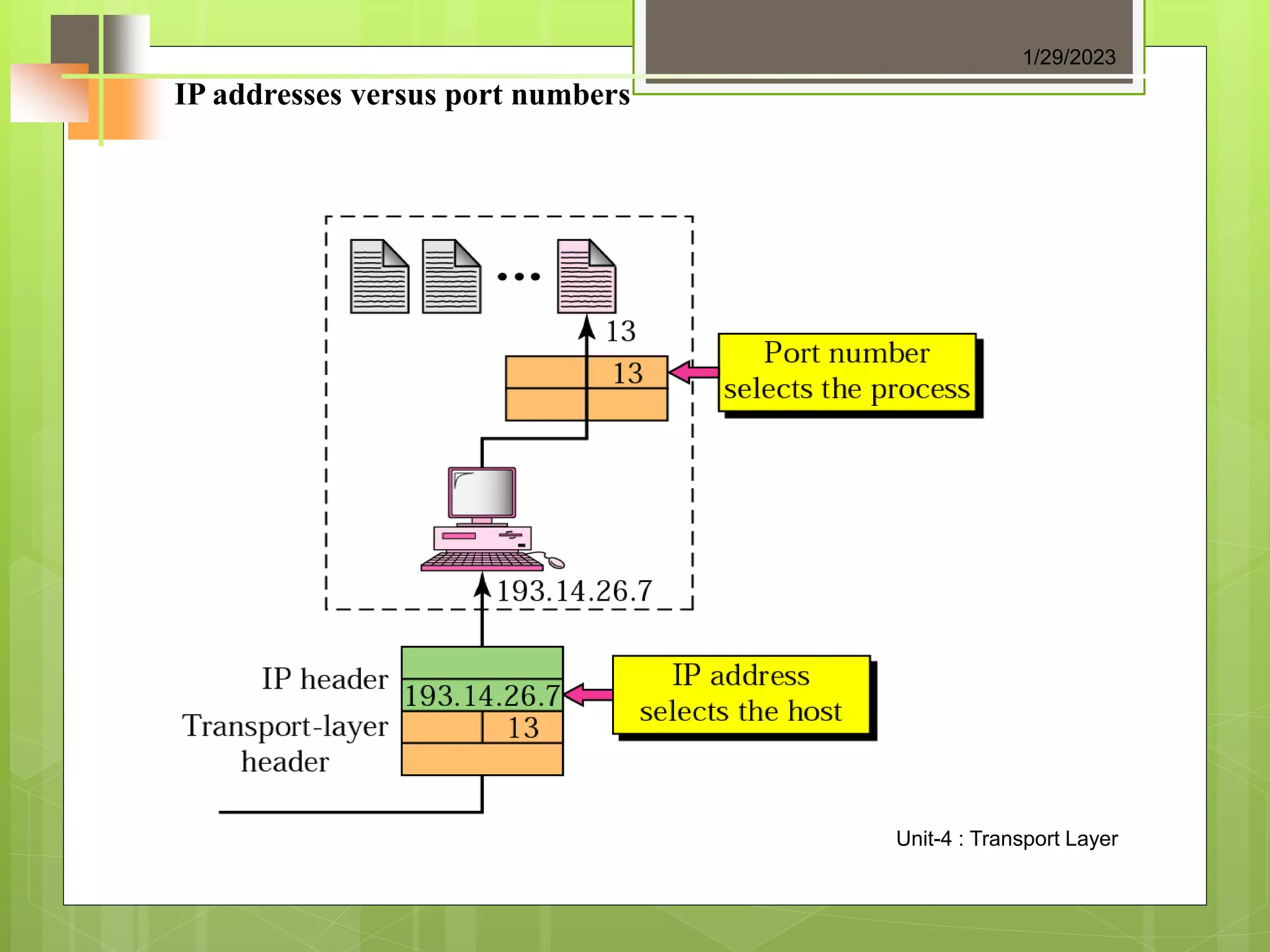
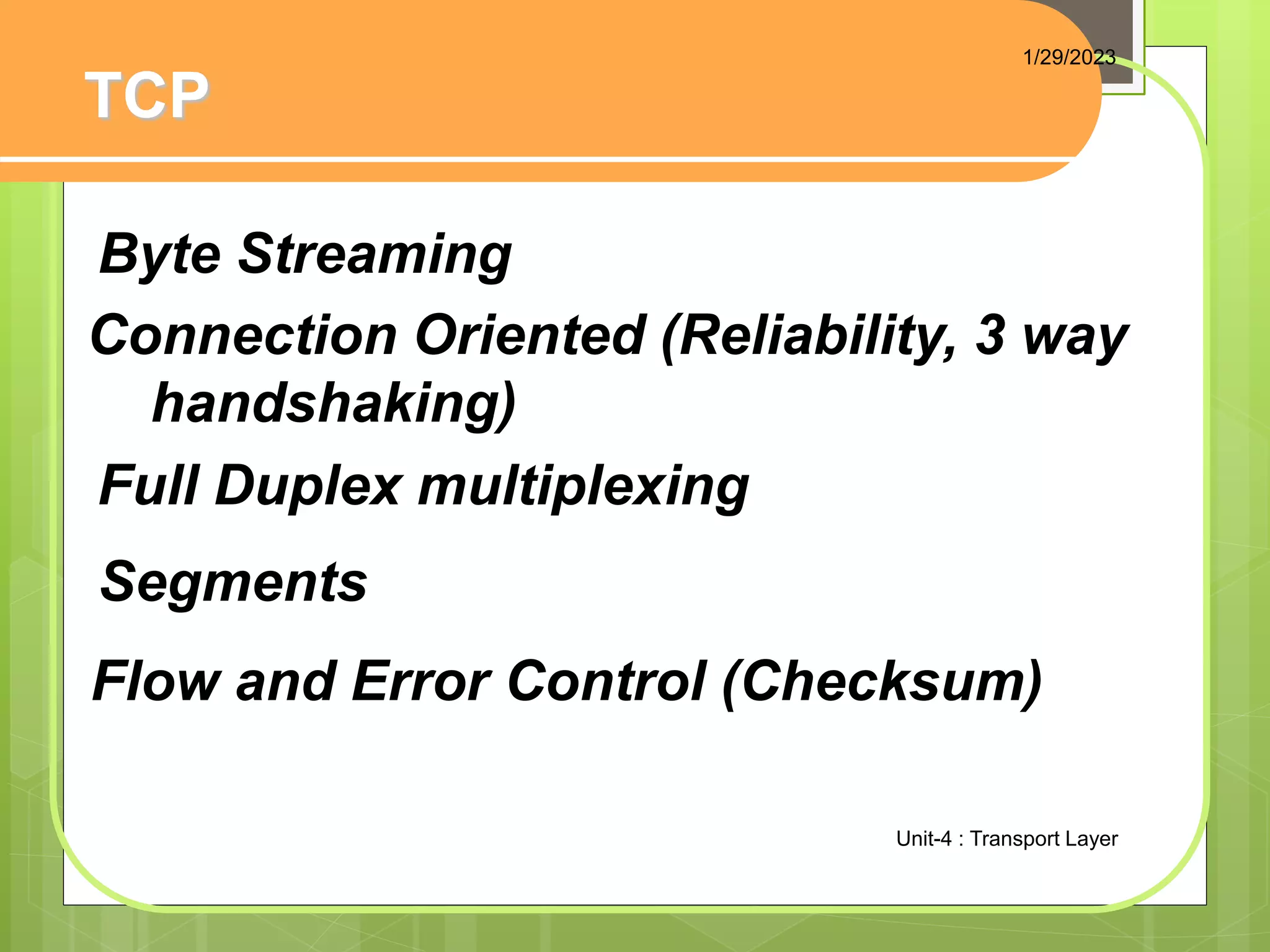
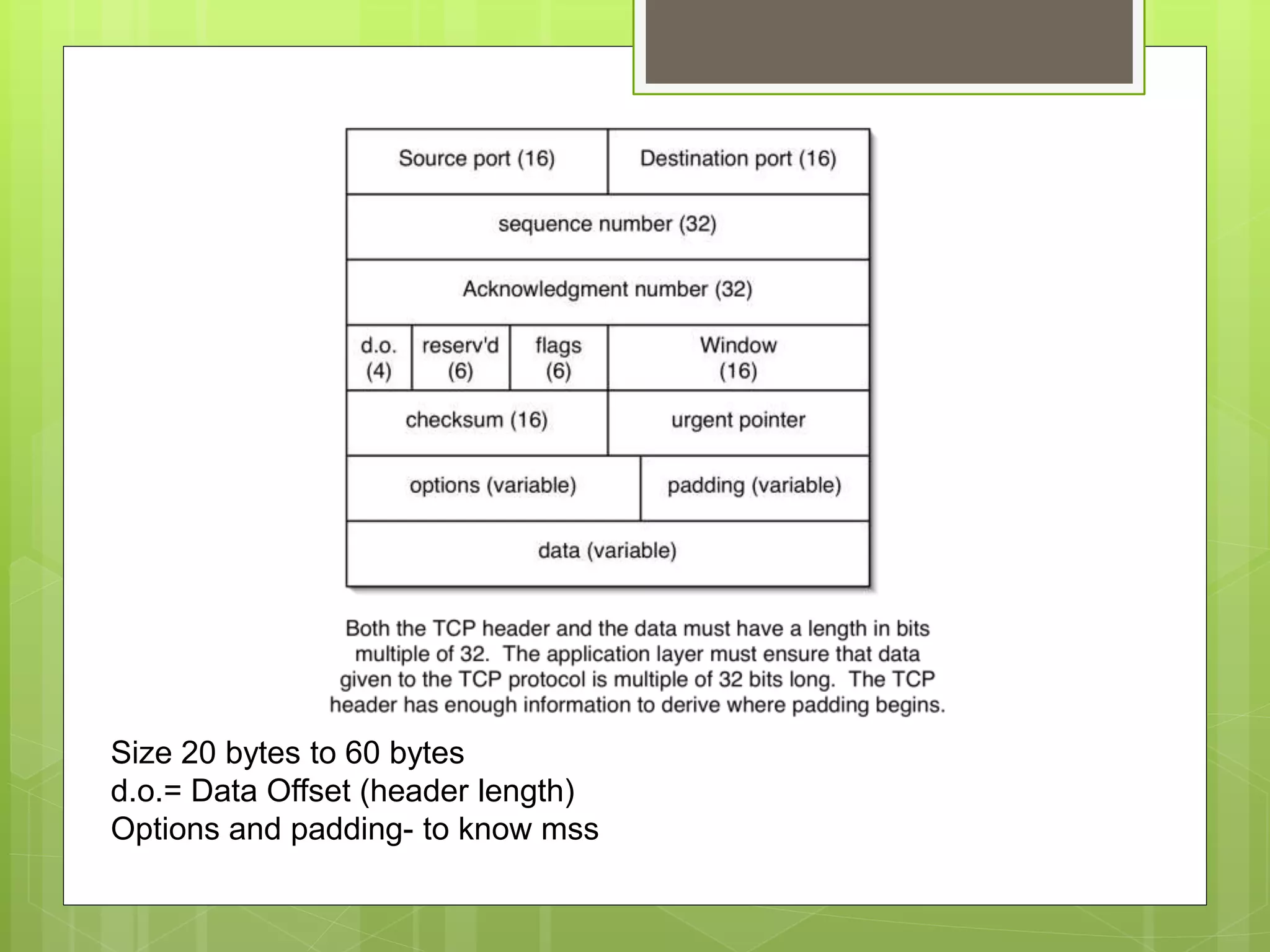
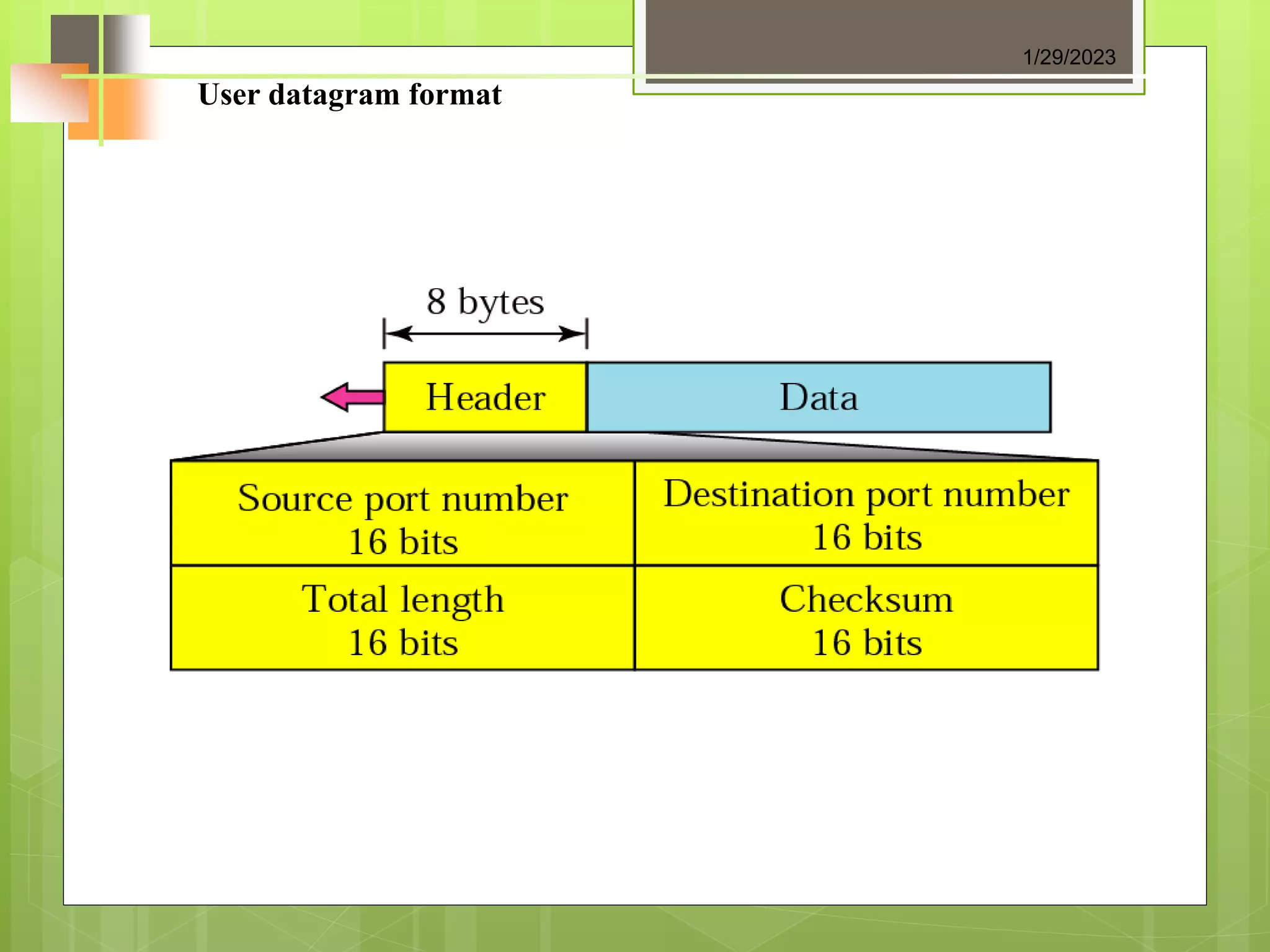
The document discusses the transport layer and its role in process-to-process delivery using UDP and TCP. It describes TCP as a connection-oriented protocol that provides reliability, flow control, and error checking using three-way handshaking and checksums. UDP is described as a connectionless and unreliable protocol that uses port numbers for multiplexing but does not provide flow or error control like TCP.