The document discusses the key components of e-commerce infrastructure and applications. It describes the main elements that enable e-commerce such as the internet, web servers, application servers and databases. It also outlines important aspects of e-commerce including business to consumer and business to business transactions, advantages like increased sales and decreased costs, and considerations around security, payment systems and transaction processing.







![3/9/01 EMTM 553 10
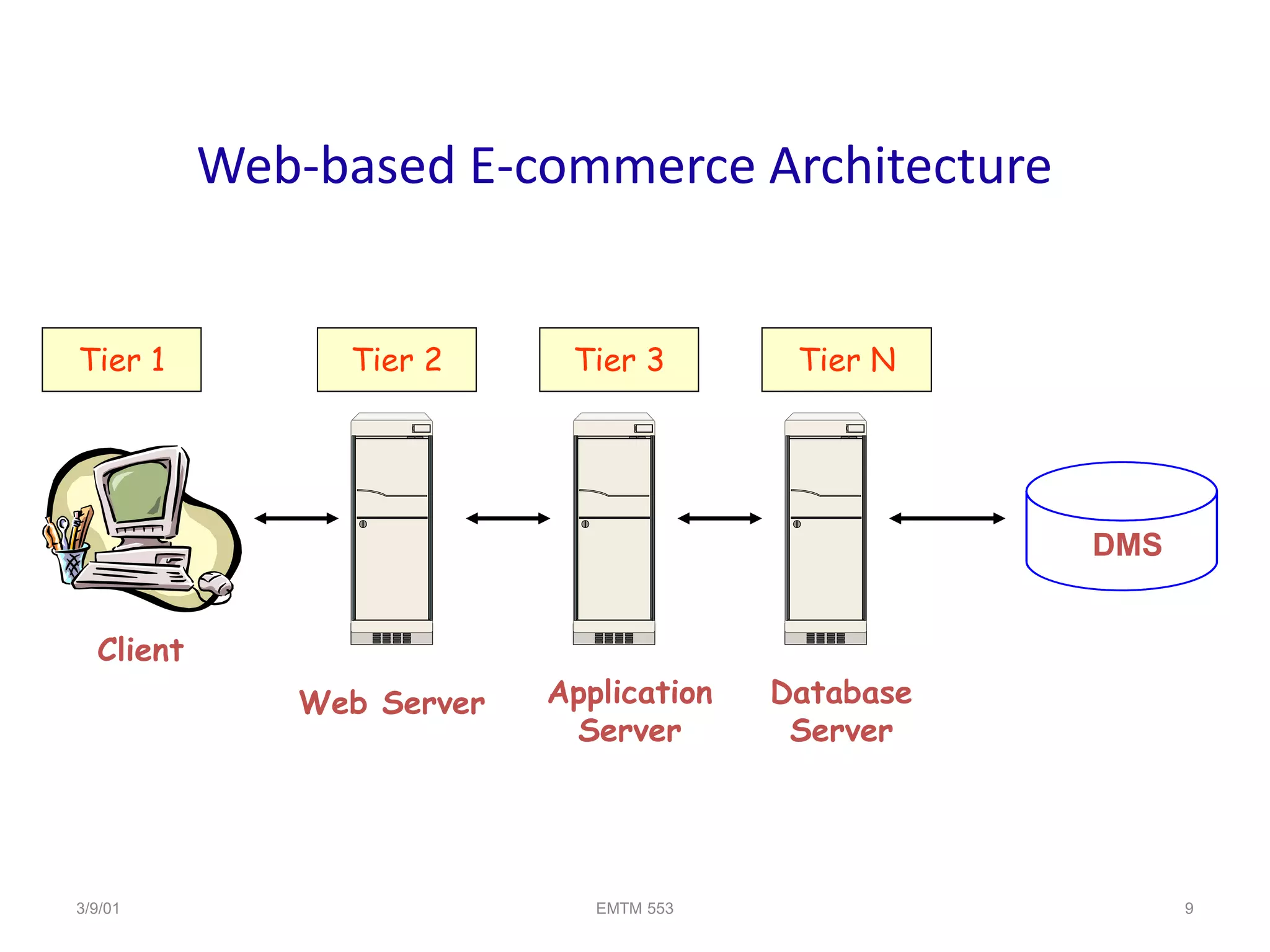
Web-based E-commerce Architecture
Web server: a software and hardware that uses HTTP (Hypertext
Transfer Protocol) and other protocols to respond to client requests
made over the World Wide Web.
Its role is to display website content through storing, processing and
delivering webpages to users
Application server: It is system software that resides between the
operating system (OS) on one side, the external resources (such as a
database management system [DBMS], communications and Internet
services) on another side and the users’ applications on the third side
Database server: is a server which uses a database application that
provides database services to other computer programs or to
computers, as defined by the client–server model.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture6e-commerceinfrastructure-230712173906-bb27600d/75/Lecture_6_E-commerce_Infrastructure-pptx-10-2048.jpg)