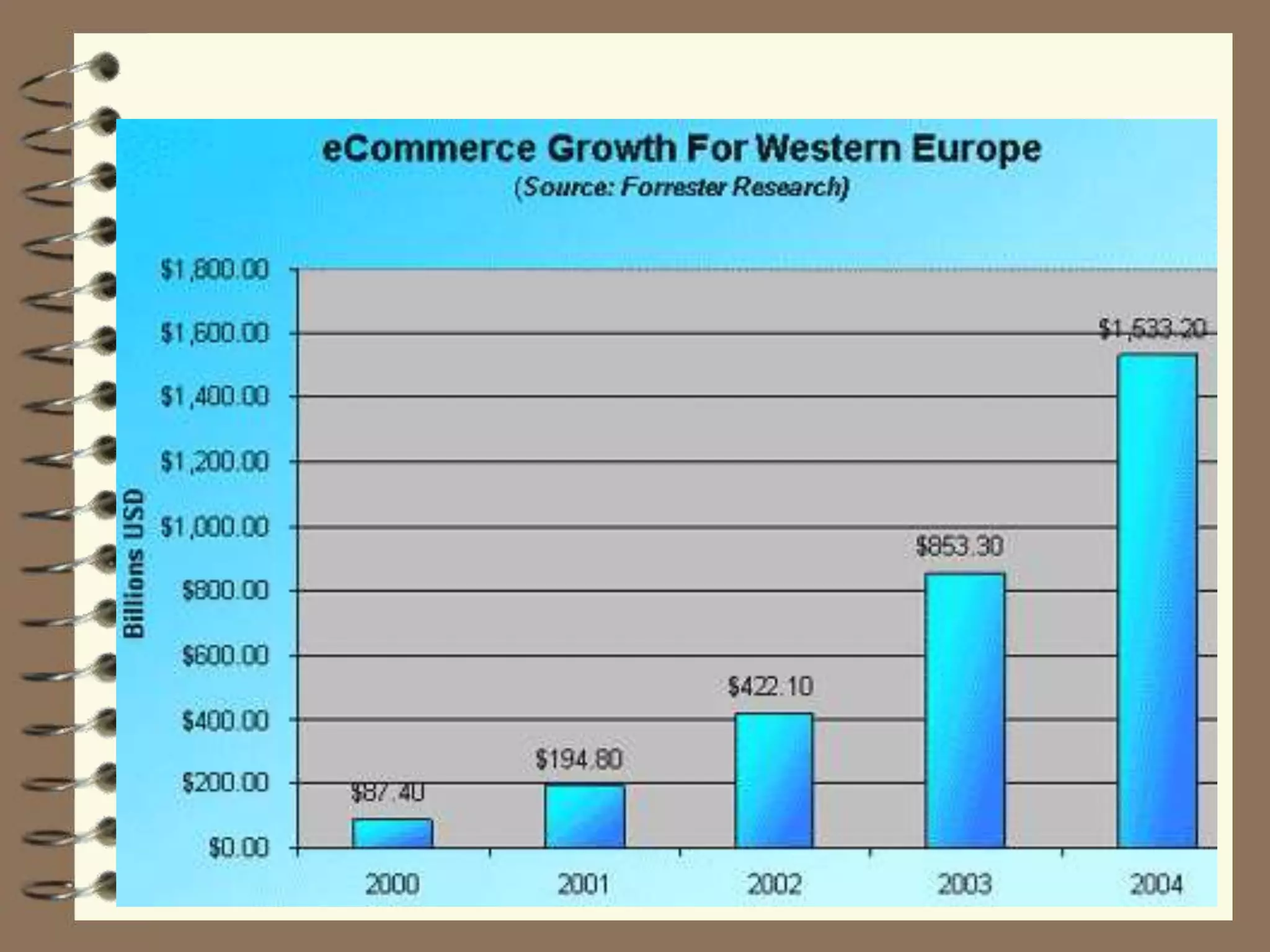
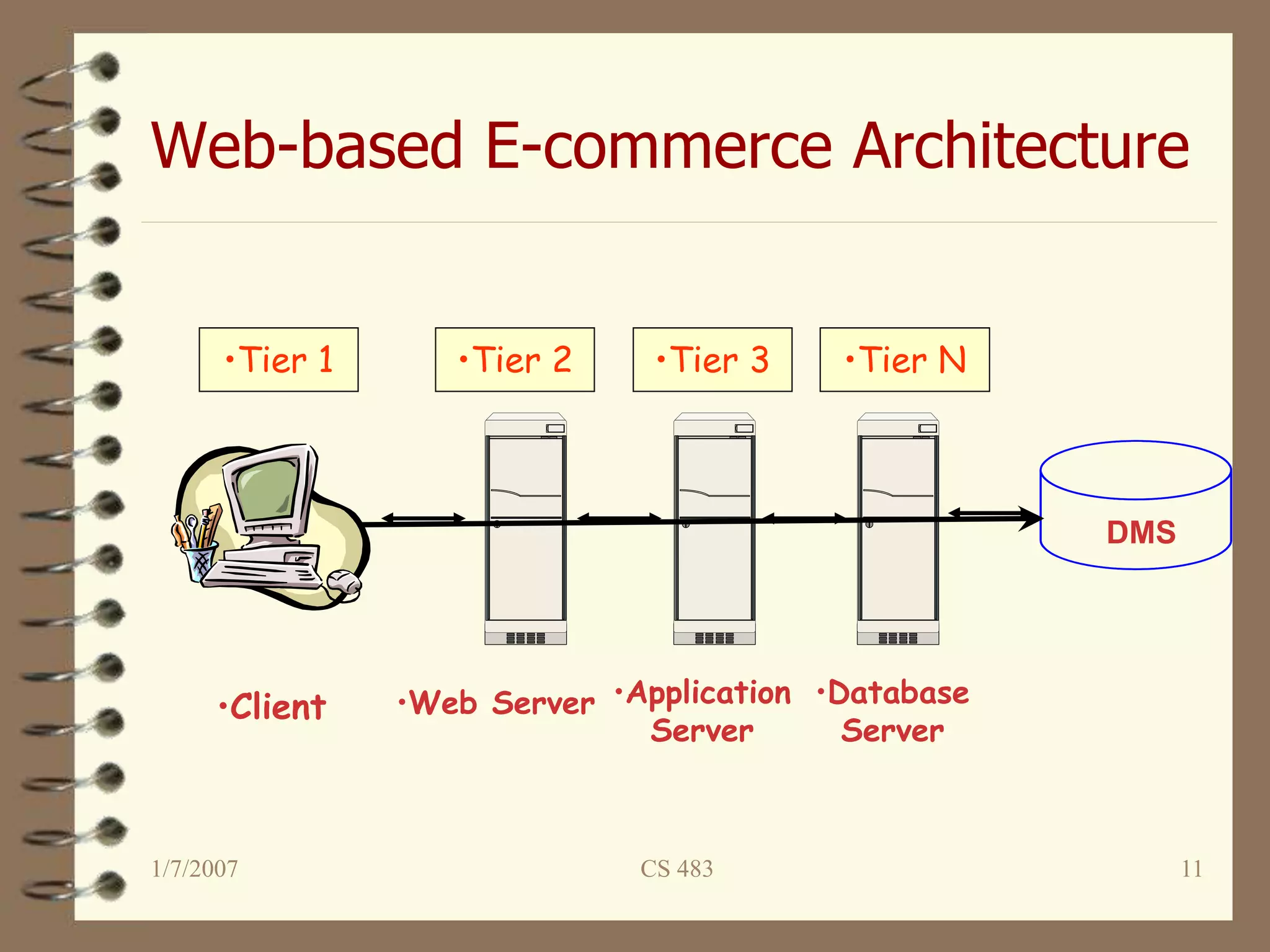
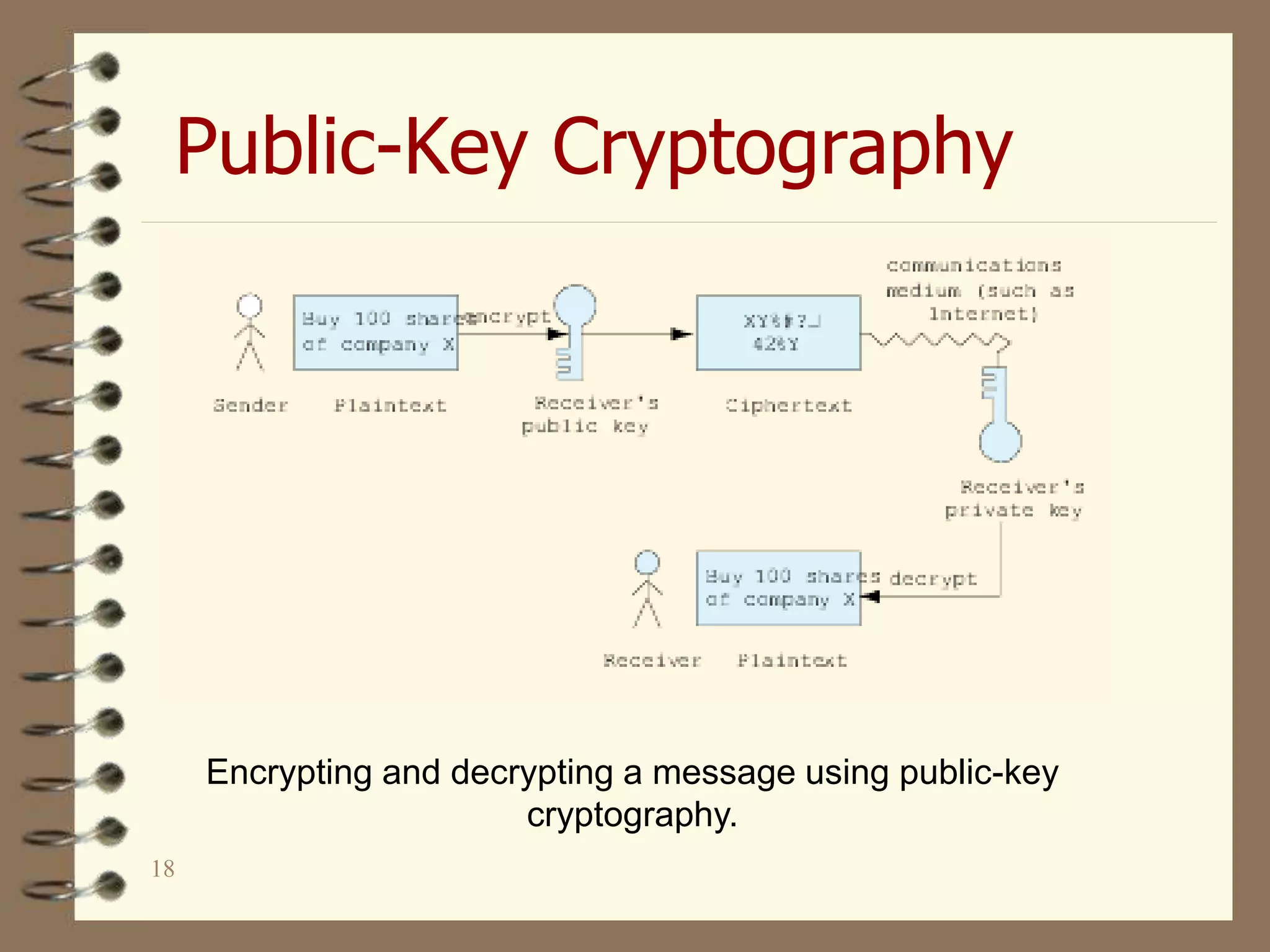
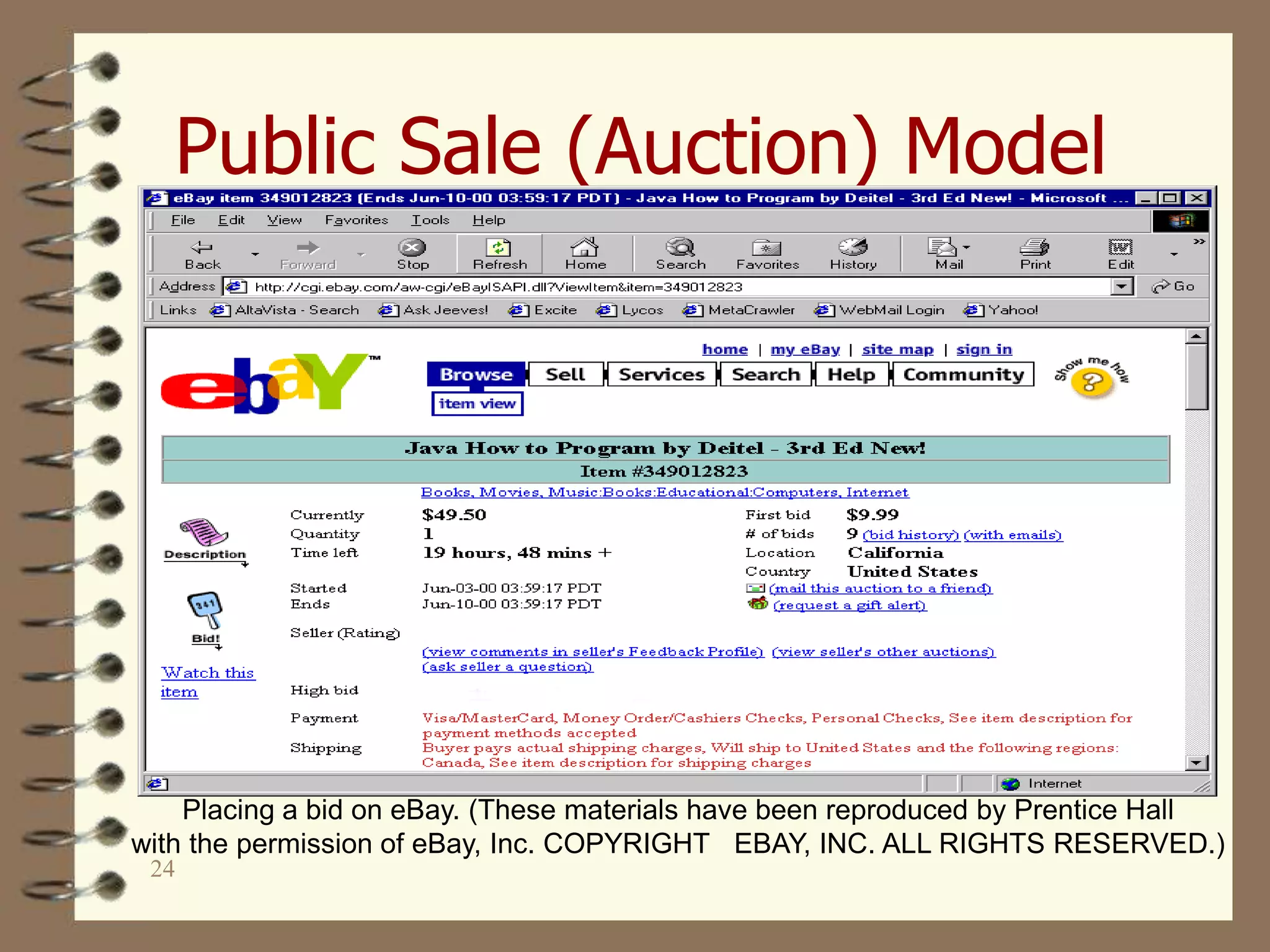
This document provides an overview of e-commerce and e-learning models. It discusses the history of e-commerce beginning in the 1970s with electronic funds transfer and electronic data interchange. The development of the World Wide Web in the 1990s enabled easier online business activities. E-commerce applications include supply chain management, online marketing, home shopping, and auctions. The main elements of e-commerce are business-to-consumer and business-to-business transactions conducted online. Advantages include increased sales and decreased costs, while disadvantages include inability to inspect products and difficulties calculating return on investment.