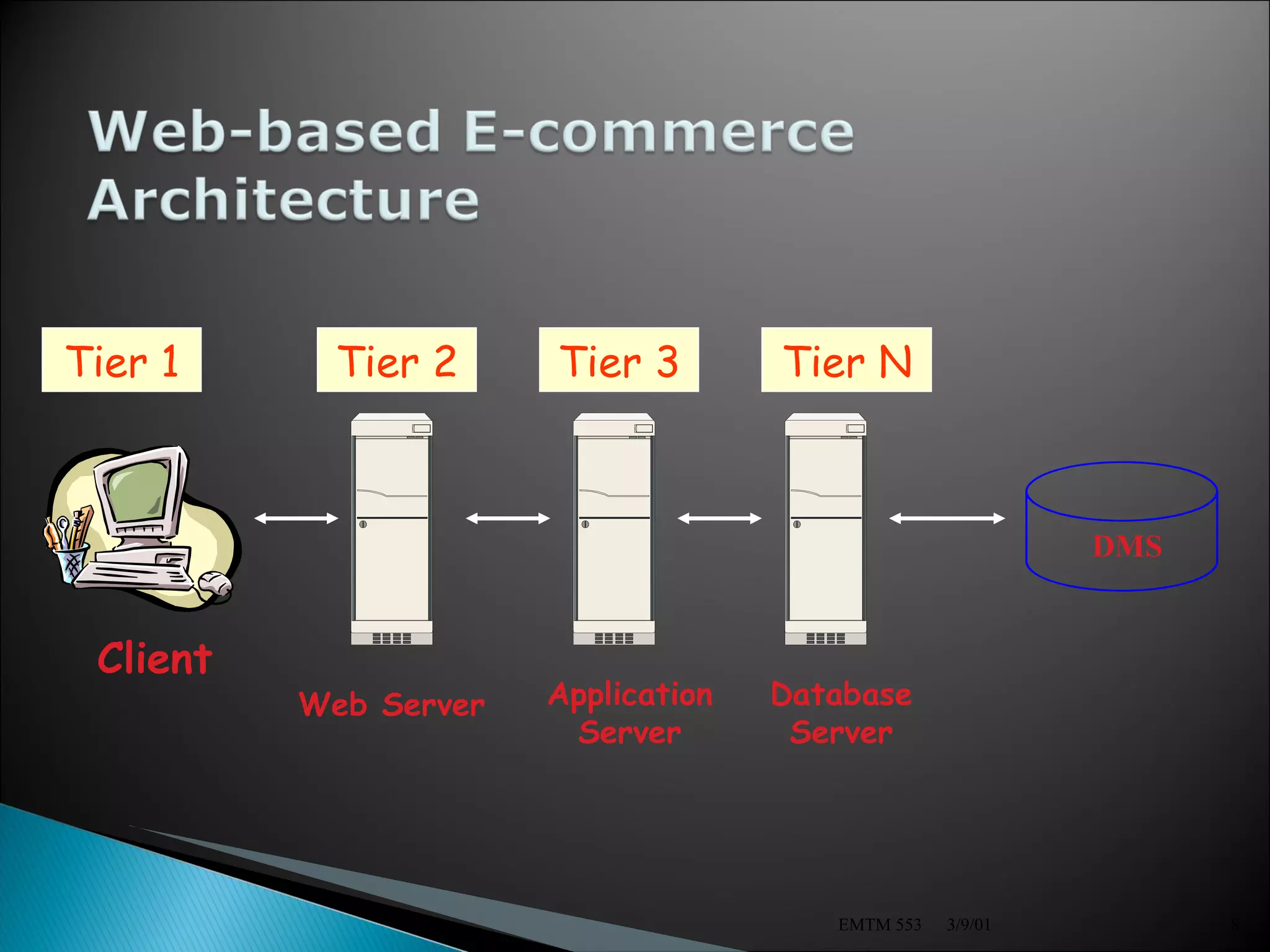
The document discusses the history and evolution of electronic commerce from the 1970s to present day. It describes how electronic commerce has developed from early electronic funds transfer and data interchange between businesses to the rise of the World Wide Web and e-commerce. The document also outlines key components of electronic commerce systems including infrastructure, business models, functions, technologies, security issues, and potential benefits and challenges.