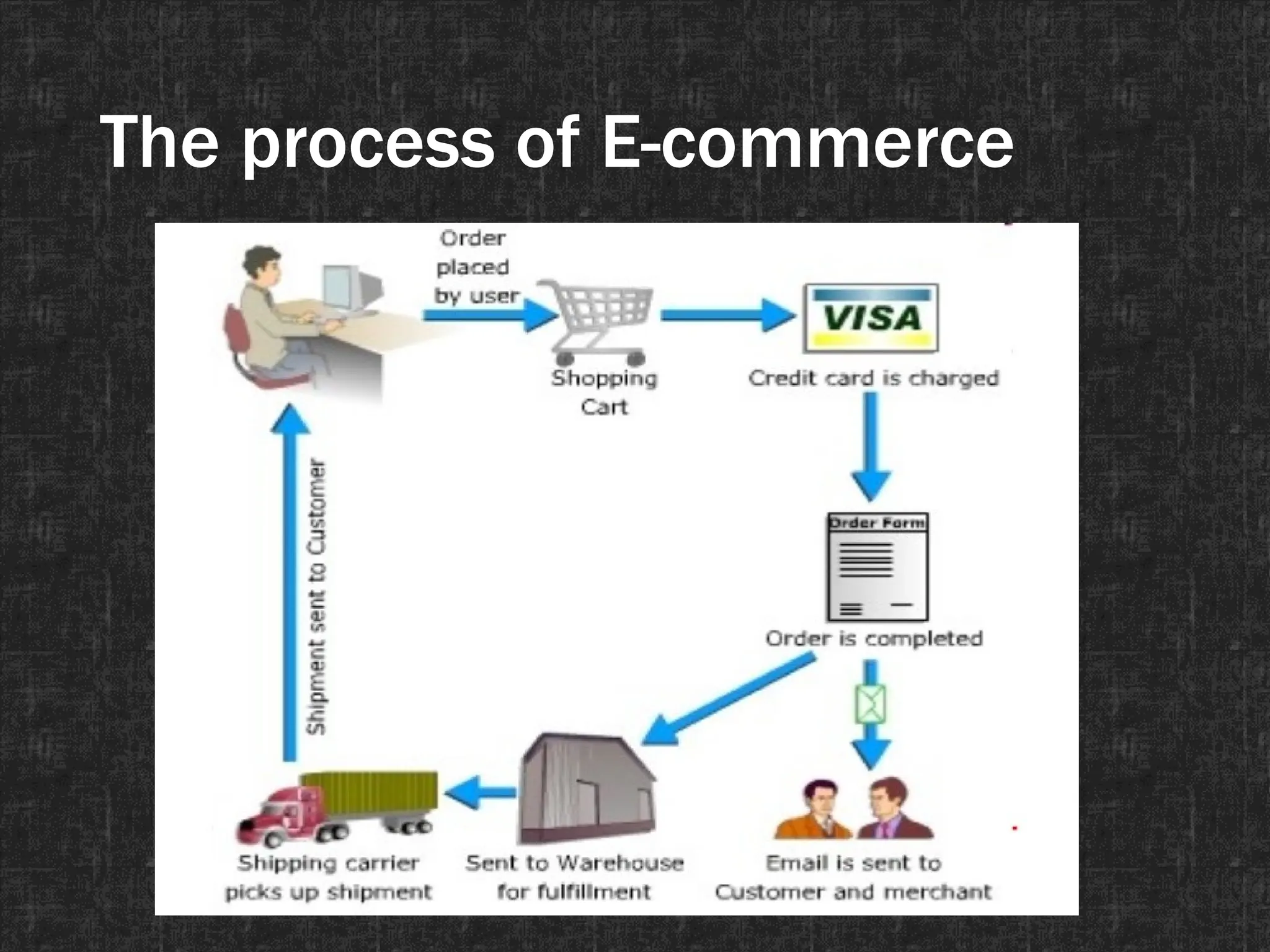
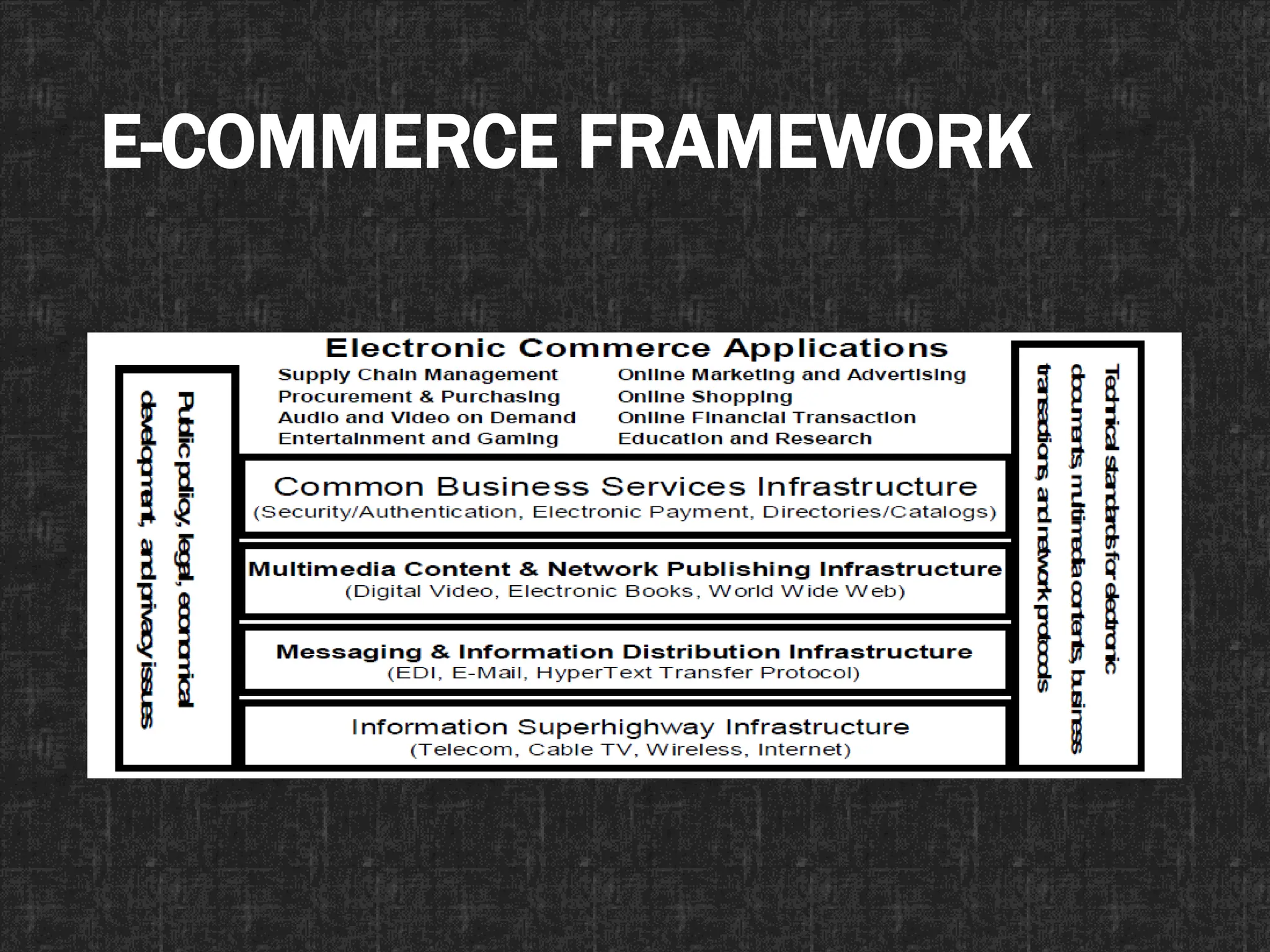
The document provides an introduction to e-commerce, defining it as the exchange of goods and services over the internet, highlighting its advantages such as operational efficiency, 24/7 access, and global reach. It points out differences from traditional commerce, including the role of technology and customer expectations, while addressing the challenges such as security concerns and lack of personal interaction. Additionally, it outlines the infrastructure necessary for e-commerce, including network infrastructure, content creation, and public policy considerations.