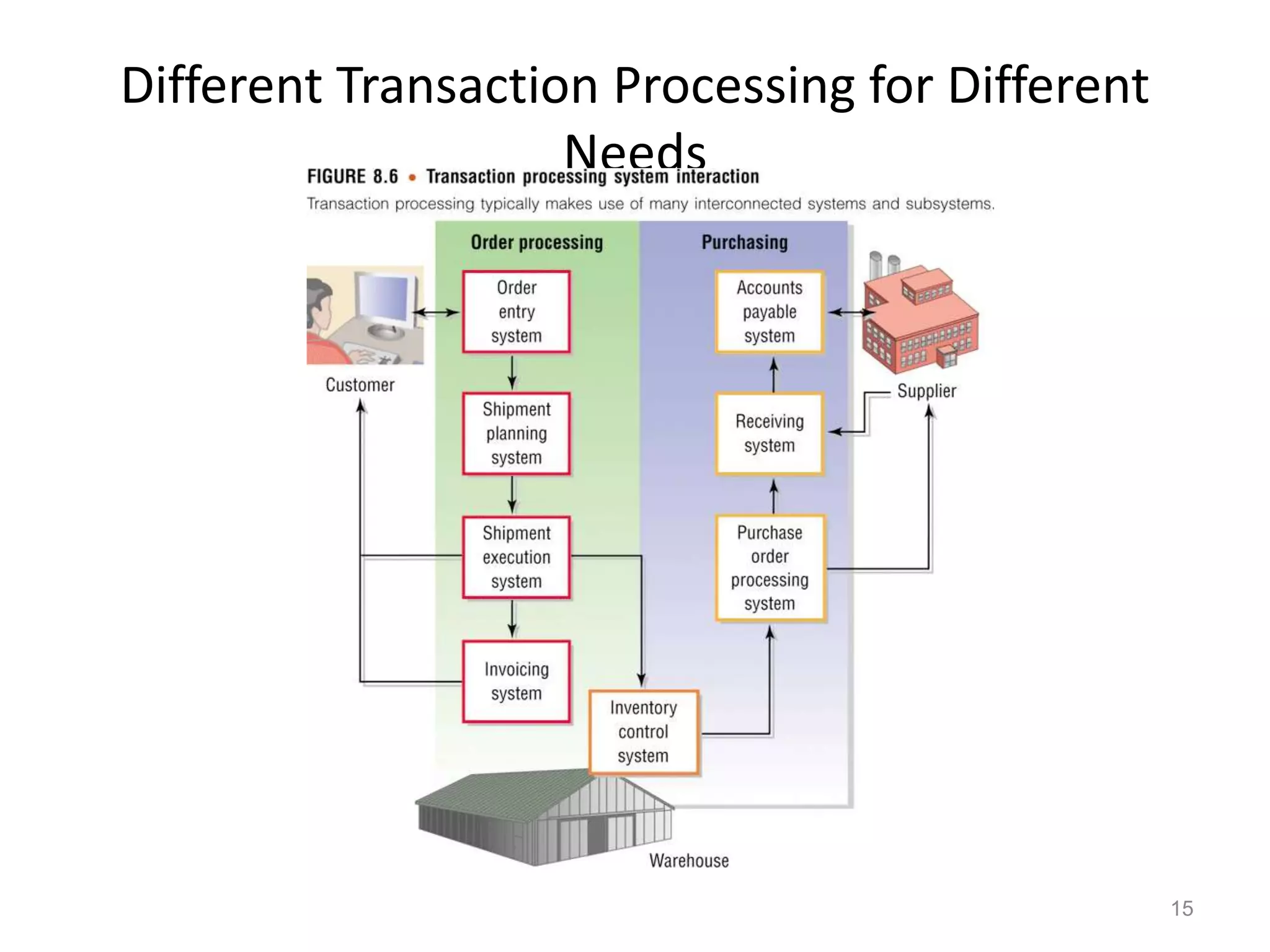
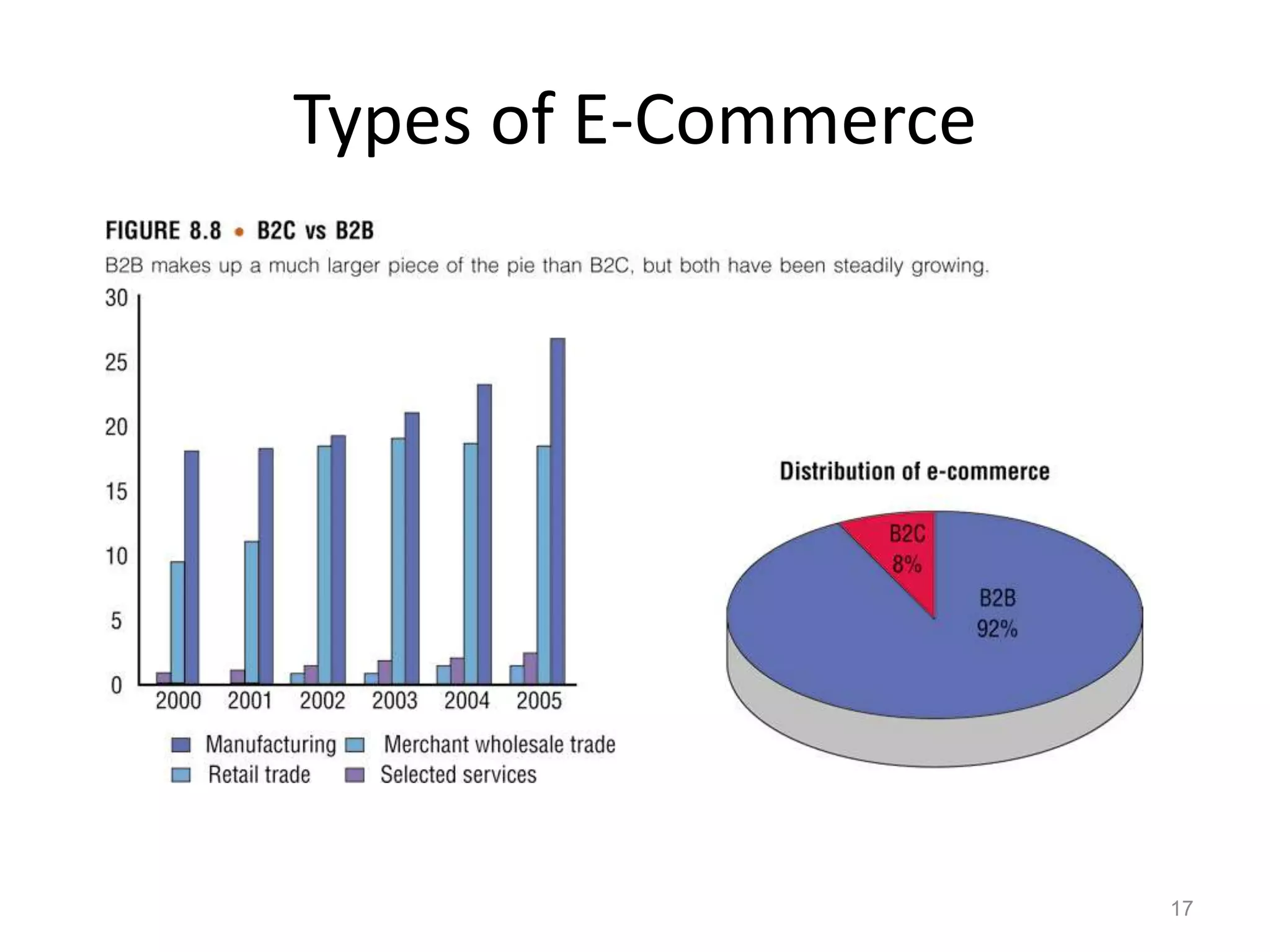
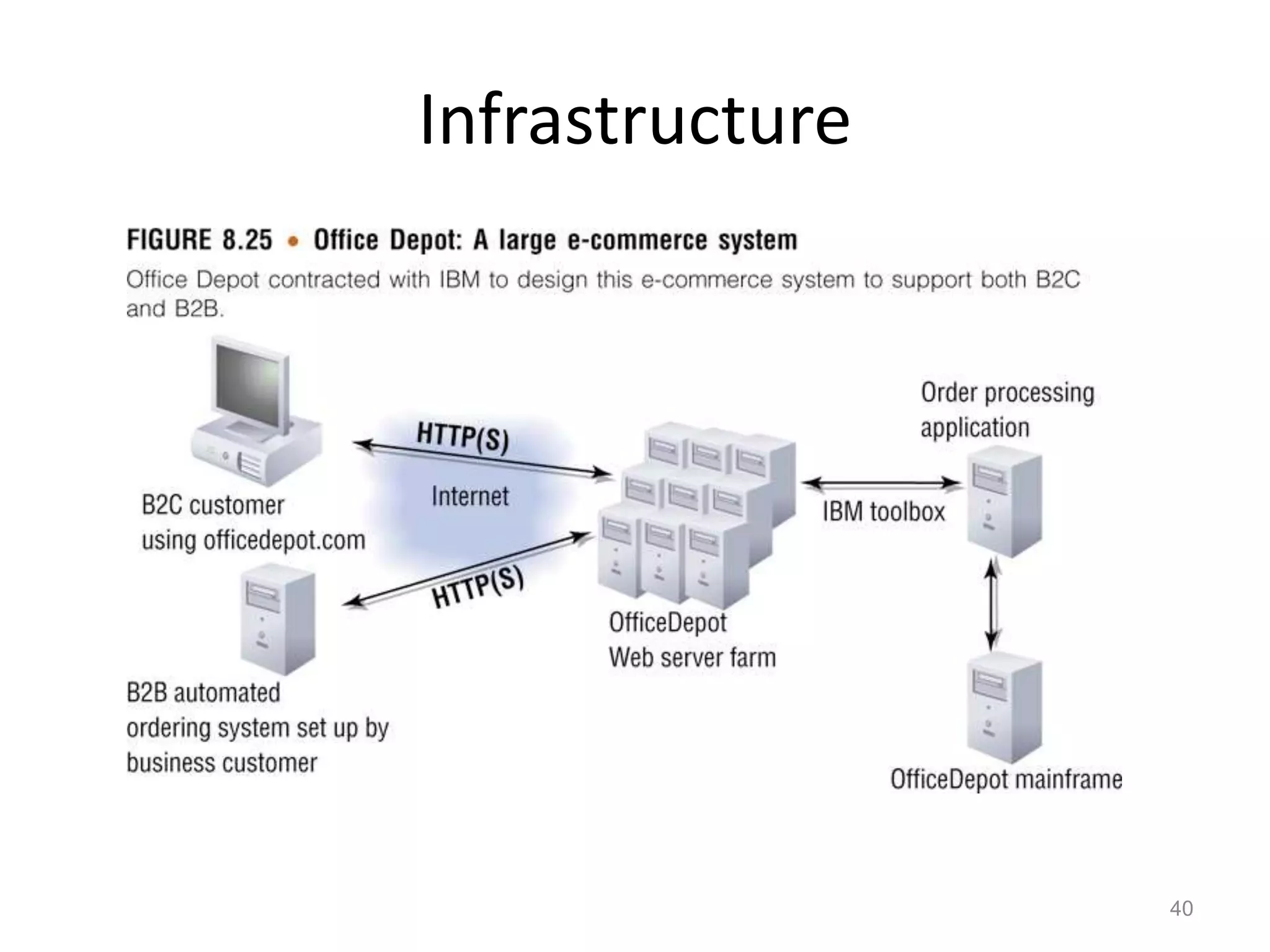
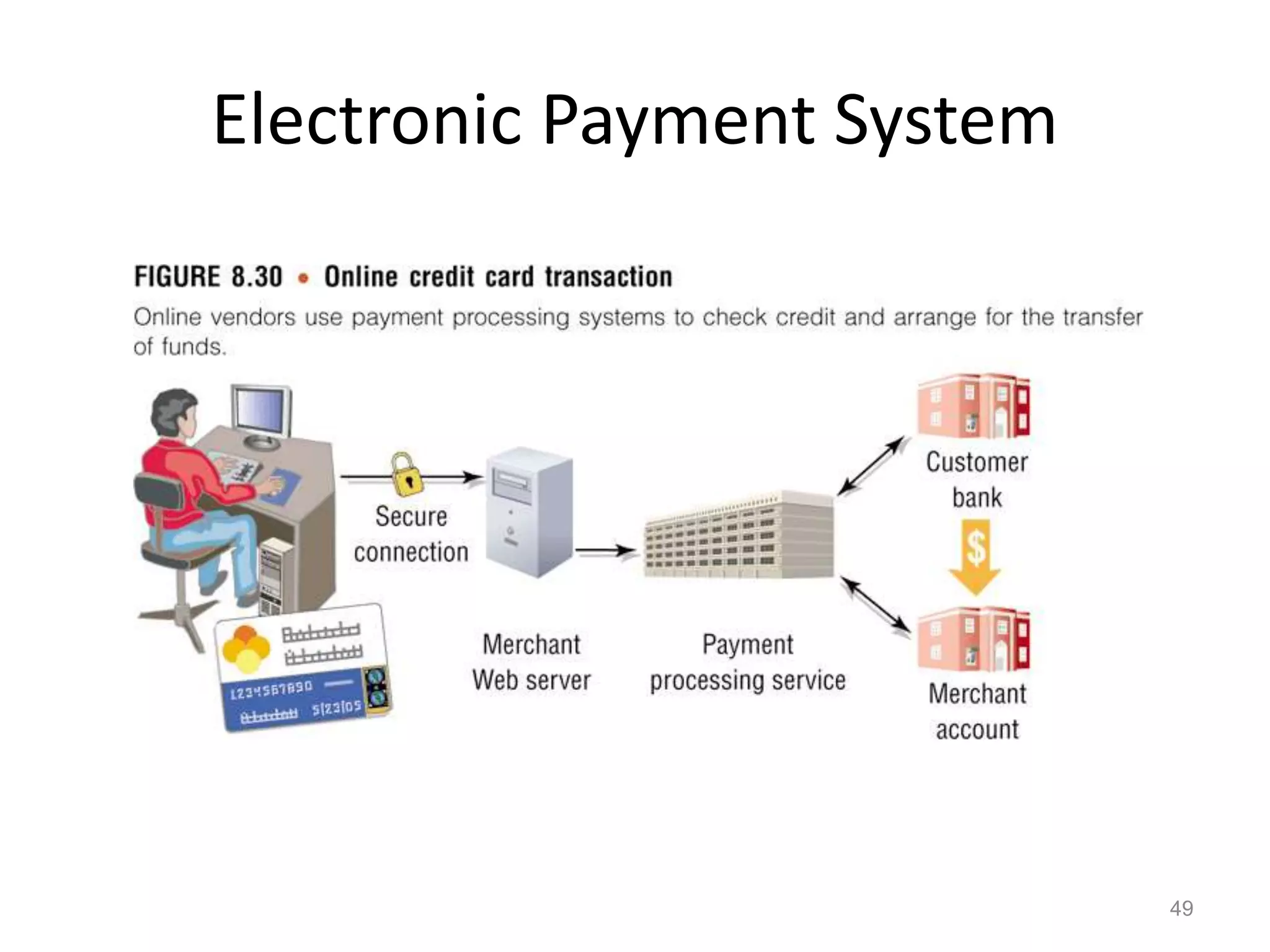
The document provides a comprehensive overview of e-commerce, covering its definition, types (B2C, B2B, C2C), and the transaction processing systems that support it. It discusses the benefits and challenges of e-commerce, the implications for buyers and sellers, mobile commerce (m-commerce), and the technological infrastructure required to implement e-commerce systems. Additionally, it highlights security issues, electronic payment systems, and considerations for international markets.