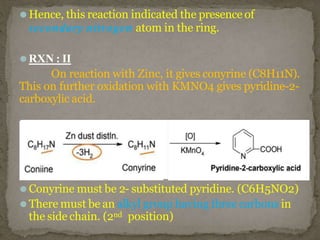
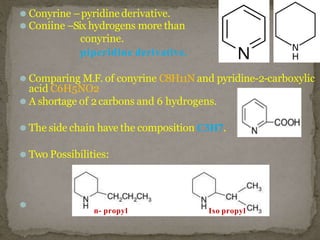
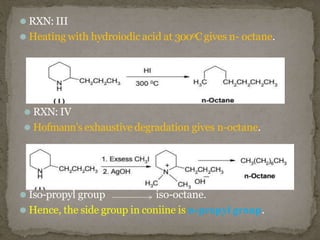
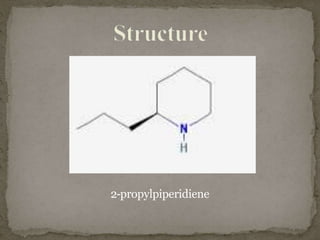
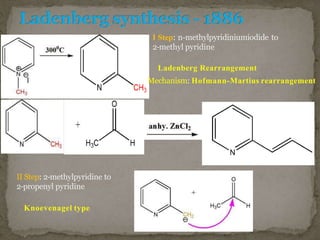
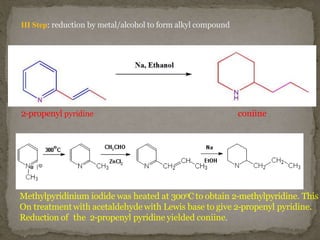
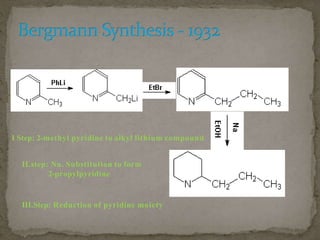
Coniine is a toxic alkaloid obtained from poisonous hemlock plants. It is a secondary amine and its molecular structure was determined to be 2-propylpiperidine. A series of chemical reactions on coniine and its derivatives such as conyrine revealed that the side chain is a propyl group. Historically, coniine was used to execute prisoners in ancient Greece by poisoning. Two major syntheses of coniine are the Ladenberg and Bergmann syntheses which involve rearrangement and substitution reactions to construct the 2-propylpiperidine core structure.