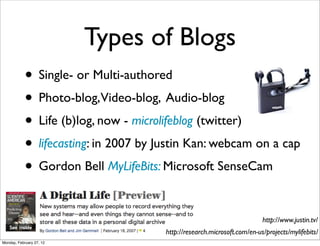
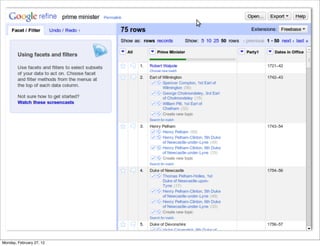
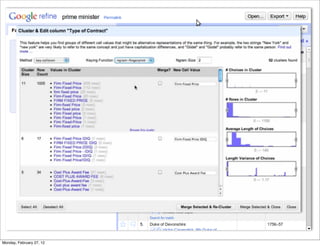
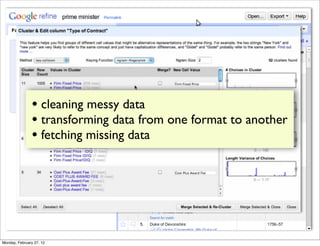
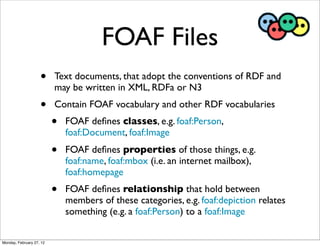
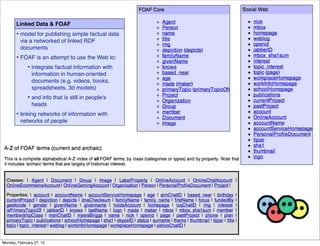
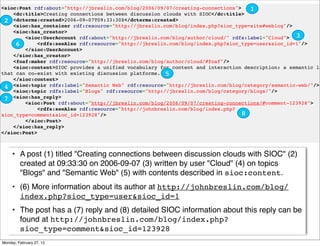
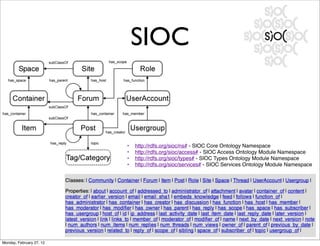
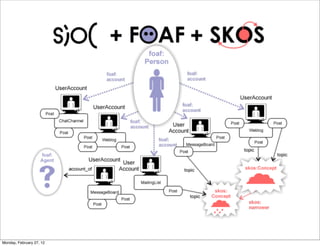
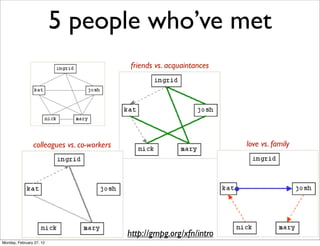
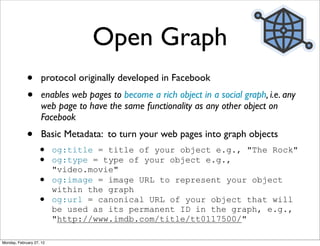
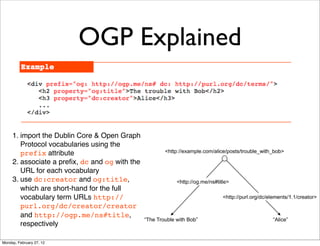
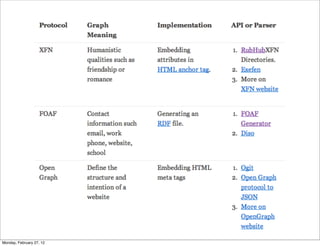
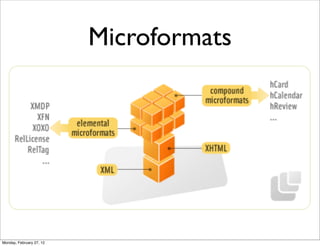
The lecture discusses various forms of content contribution on the social web, including blogs and wikis, highlighting their evolution and functionality. It covers concepts such as microblogging, crowdsourcing, folksonomies, and the semantic web, emphasizing the collaborative nature of these platforms and their impact on user-generated content. Additionally, it introduces vocabularies like FOAF and SIOC to represent social relationships and activities within these data formats.