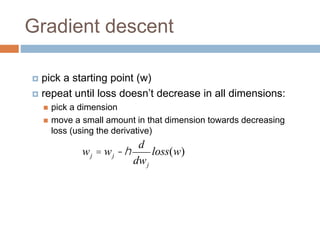
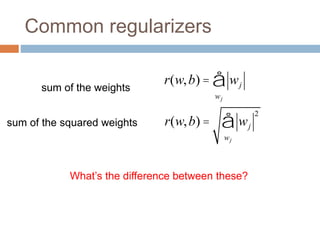
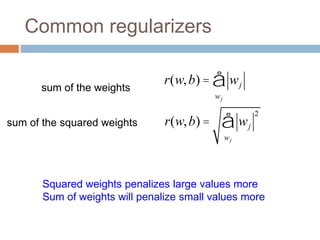
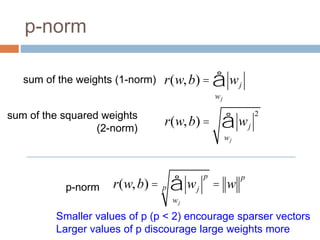
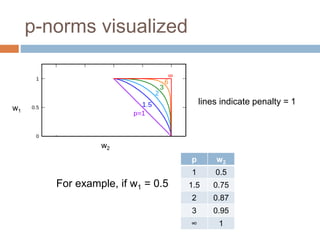
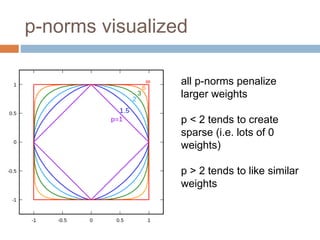
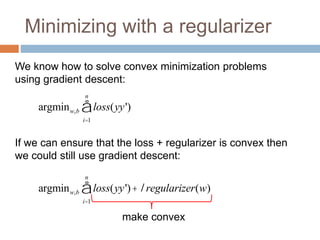
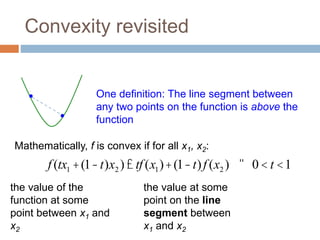
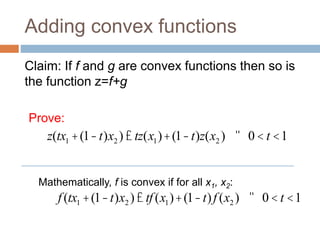
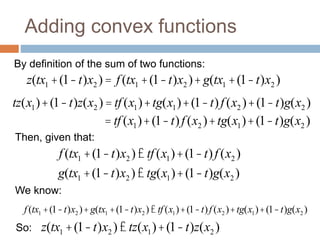
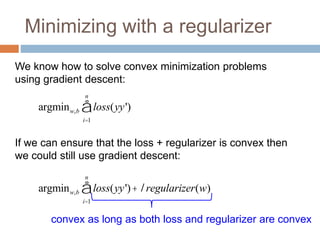
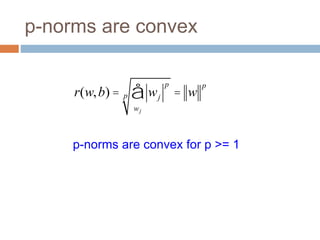
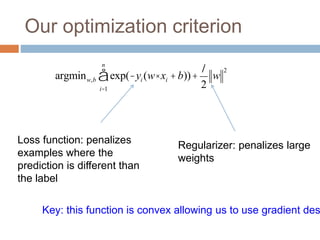
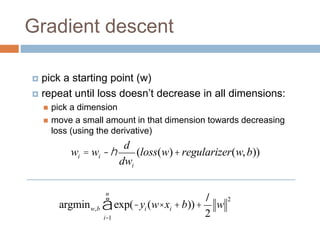
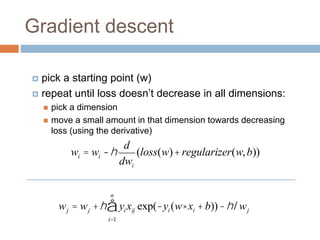
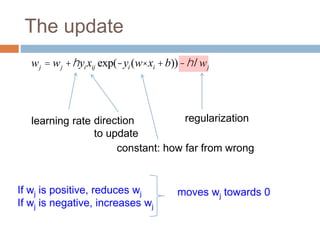
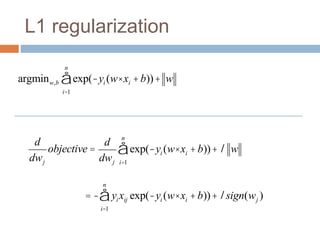
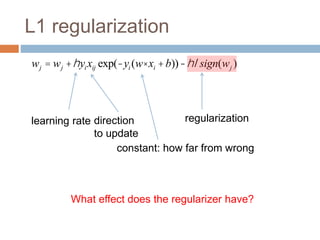
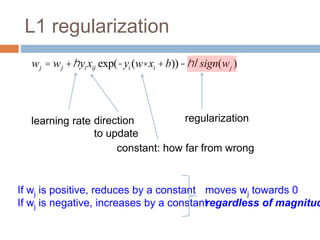
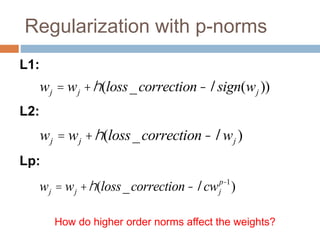
Regularization adds an additional term to the objective function being optimized in machine learning to prevent overfitting. Common regularizers include the L1 norm (sum of absolute weights), L2 norm (sum of squared weights), and Lp norms. The L1 norm encourages sparsity by driving small weights to exactly zero. Gradient descent can be used to minimize objective functions that combine a loss term and a regularizer, as long as the overall function remains convex. During gradient descent, the regularizer term pushes weights towards zero. Regularization is important for obtaining models that generalize well to new data.



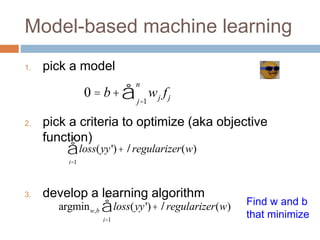
![Model-based machine learning
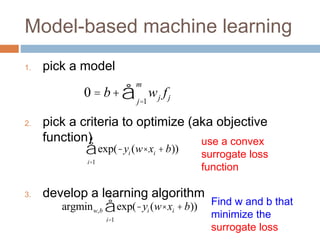
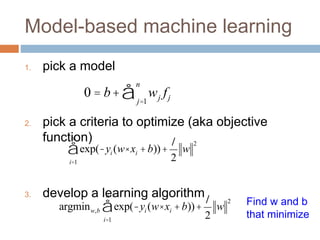
1. pick a model
2. pick a criteria to optimize (aka objective
function)
3. develop a learning algorithm
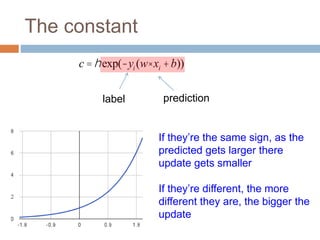
1 yi (w× xi +b) £ 0
[ ]
i=1
n
å
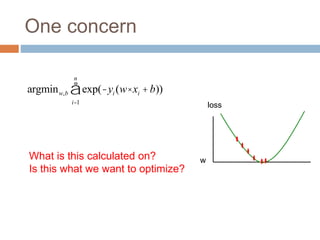
argminw,b 1 yi (w× xi +b) £ 0
[ ]
i=1
n
å Find w and b that
minimize the 0/1
loss
0 = b+ wj fj
j=1
m
å](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15-regularization-240131152926-96e65071/85/lecture15-regularization-pptx-4-320.jpg)









![The other loss functions
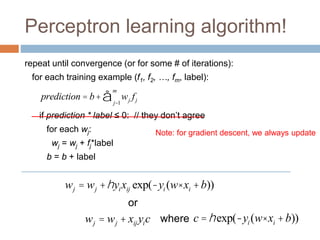
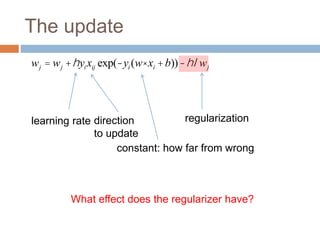
wj = wj +hyixijc
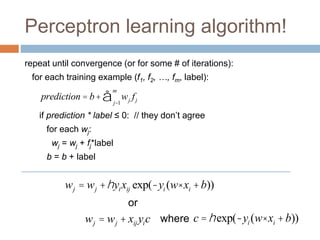
Without regularization, the generic update is:
where
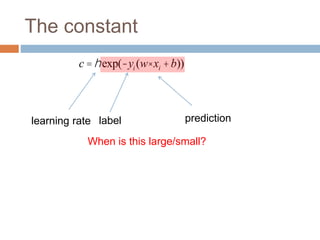
c = exp(-yi (w× xi +b))
c =1[yy' <1]
exponential
hinge loss
squared error
wj = wj +h(yi -(w× xi +b)xij )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture15-regularization-240131152926-96e65071/85/lecture15-regularization-pptx-44-320.jpg)


