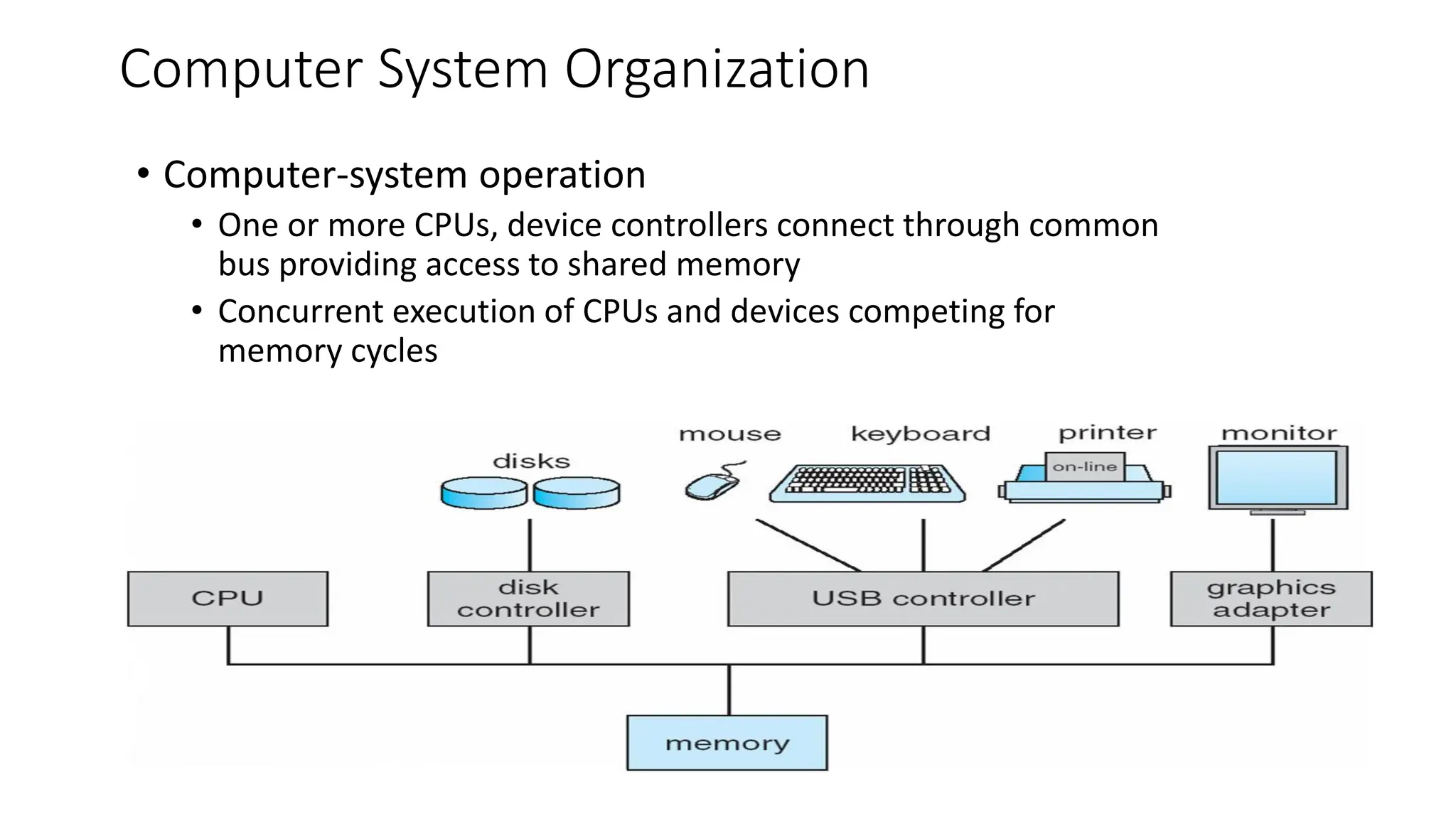
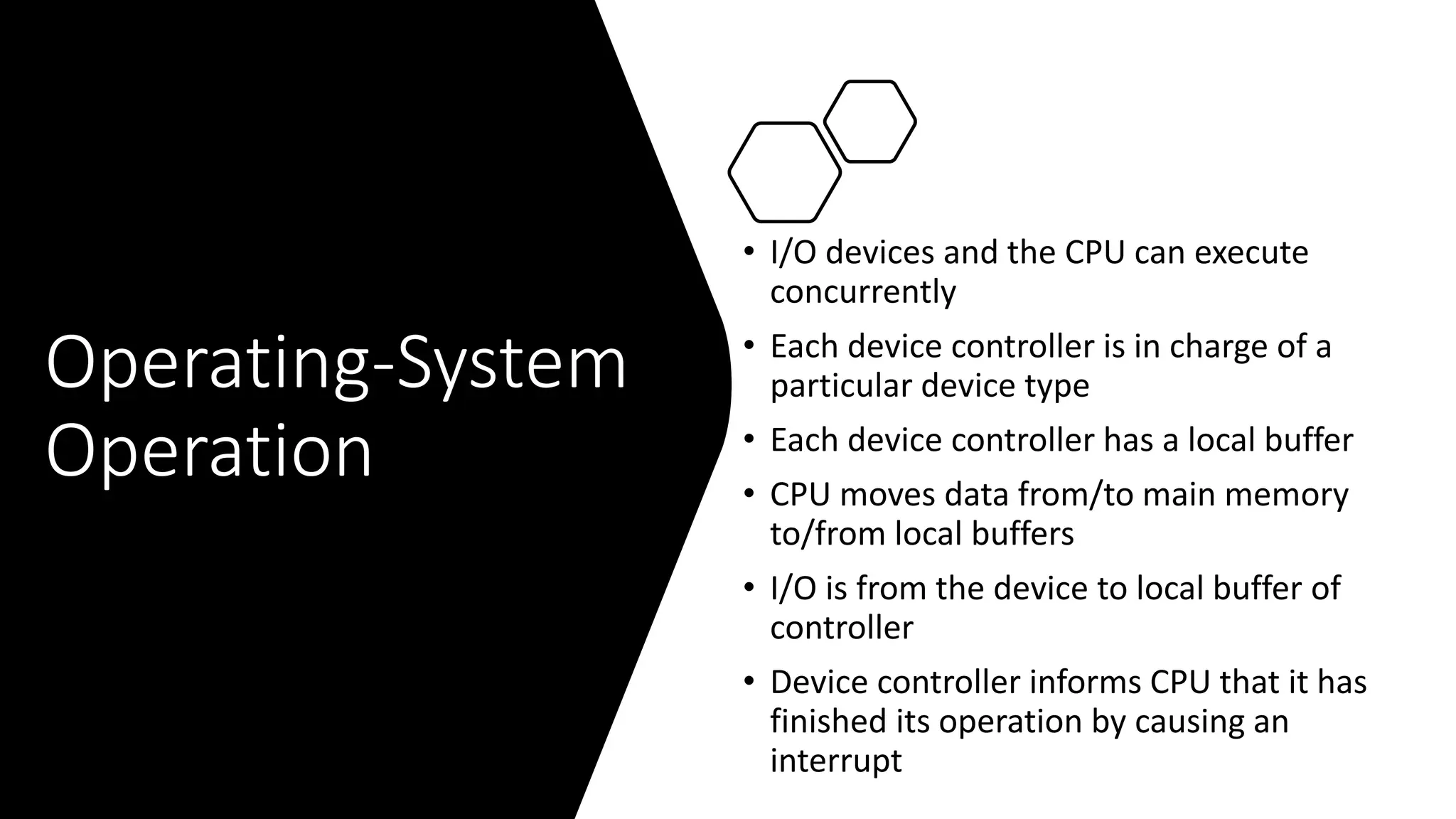
The document defines an operating system as a program that acts as an intermediary between the user and computer hardware. It manages computer resources and executes user programs. Key functions of an operating system include memory management, processor management, device management, file management, and security. The document also discusses different computing environments like time sharing, client-server, and real-time systems that operating systems can support.