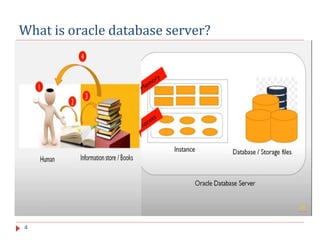
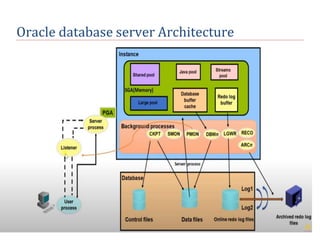
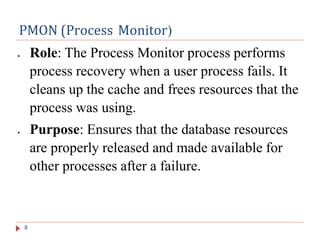
The document outlines the architecture of the Oracle Database, including its definition and key processes like checkpoint, system monitor, process monitor, database writer, log writer, recoverer, and archiver. Each process plays a critical role in maintaining data integrity, facilitating recovery, and managing resources effectively within the database. The document serves as an introductory lecture on these fundamental concepts within Oracle Database architecture.