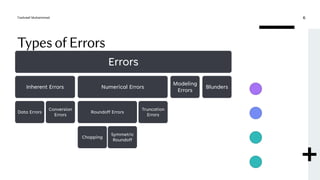
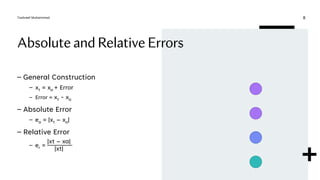
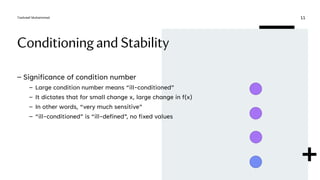
This document discusses numerical errors and concepts related to error analysis. It defines significant digits and describes different types of errors like inherent errors, data errors, and numerical errors. It then explains absolute and relative errors, defining absolute error as the difference between the true and approximate values, and relative error as the absolute error divided by the true value. Finally, it introduces conditioning and stability, defining the condition number as the ratio of relative errors in the function and input. A large condition number means the problem is ill-conditioned and small changes in the input can lead to large changes in the output.