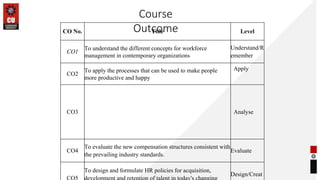
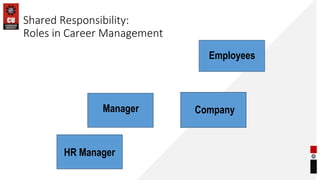
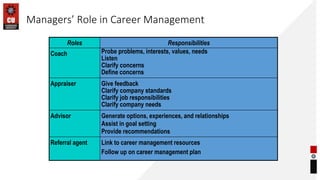
This document provides information about career planning and succession planning. It discusses what constitutes a career, models of career development, and the career management process. It outlines the components of self-assessment, reality check, goal setting, and action planning. It also discusses design factors of effective career management systems and the shared responsibilities of employees, managers, HR managers, and the company in career management. Finally, it discusses evaluating career management systems by examining customer reactions and results.