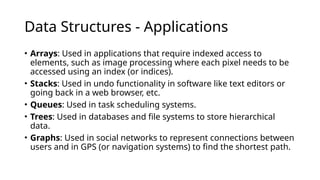
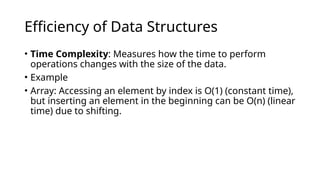
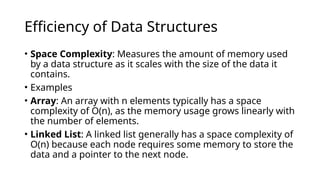
Data structures are methods for organizing and storing data in computer memory for efficient access and modification, including arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Their efficiency is assessed through time and space complexity, which measures how performance and memory usage scale with data size. Common operations on data structures include insertion, access, search, deletion, updating, traversal, and sorting.