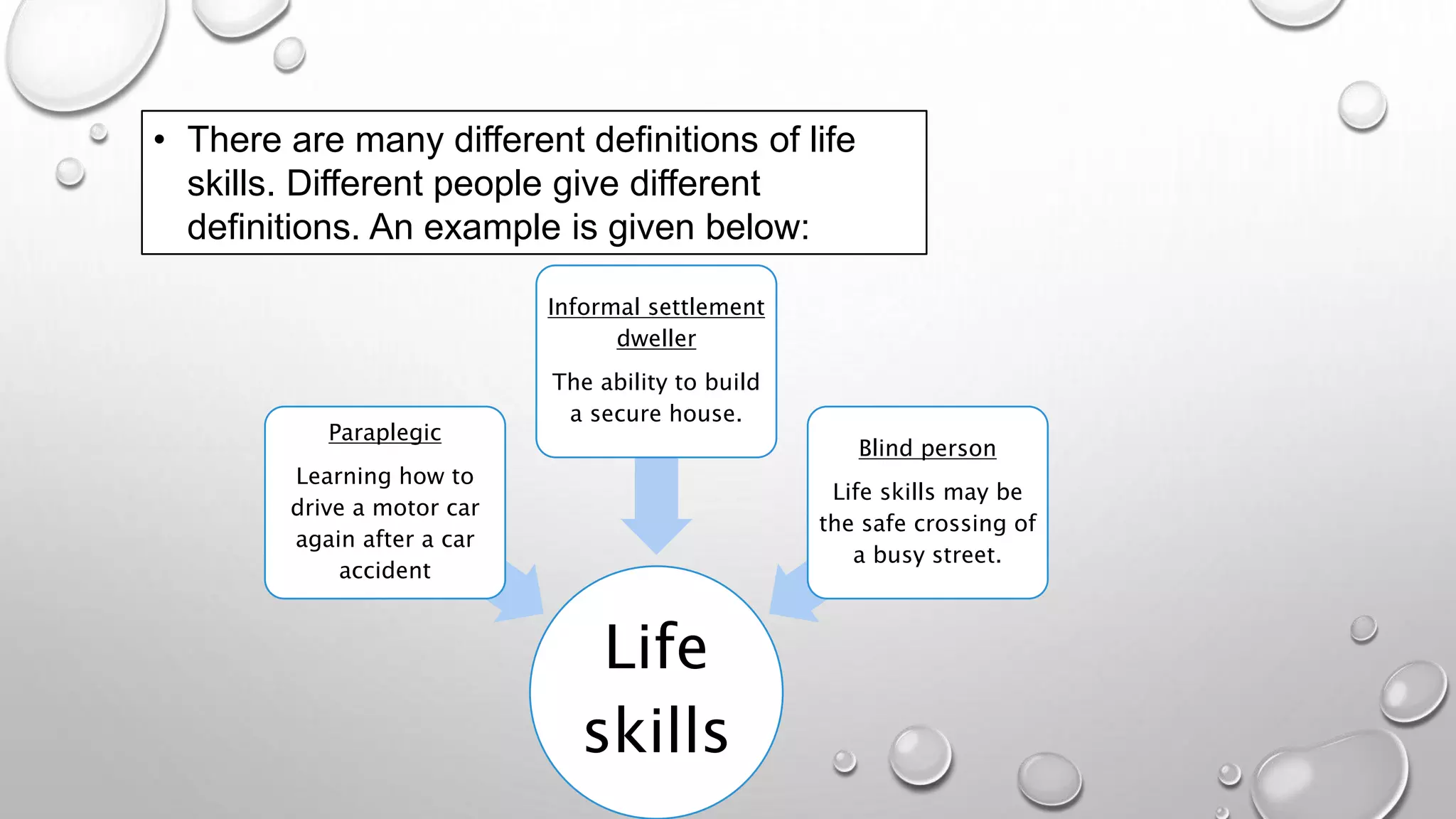
Life skills are essential skills for full participation in everyday life, enabling individuals to cope with challenges in personal, educational, and social contexts. Learners lacking life skills may struggle with respect, cultural understanding, creativity, and motivation, often due to inadequate supportive environments. Addressing life skills as a learning barrier can involve mentoring, integrating life skills into curricula, and fostering cooperative learning.