This document provides an overview of the K-12 curriculum in the Philippines, including:
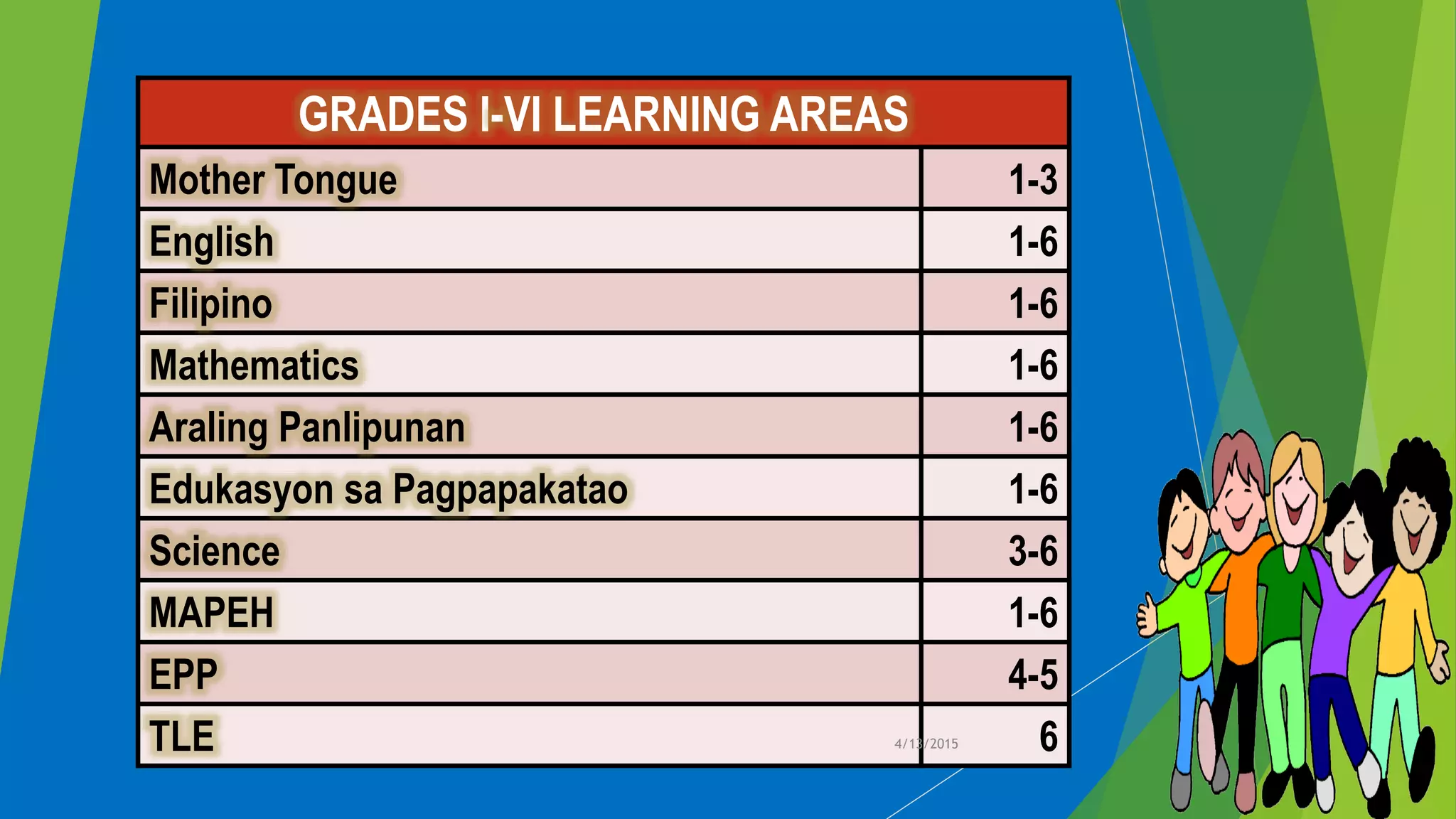
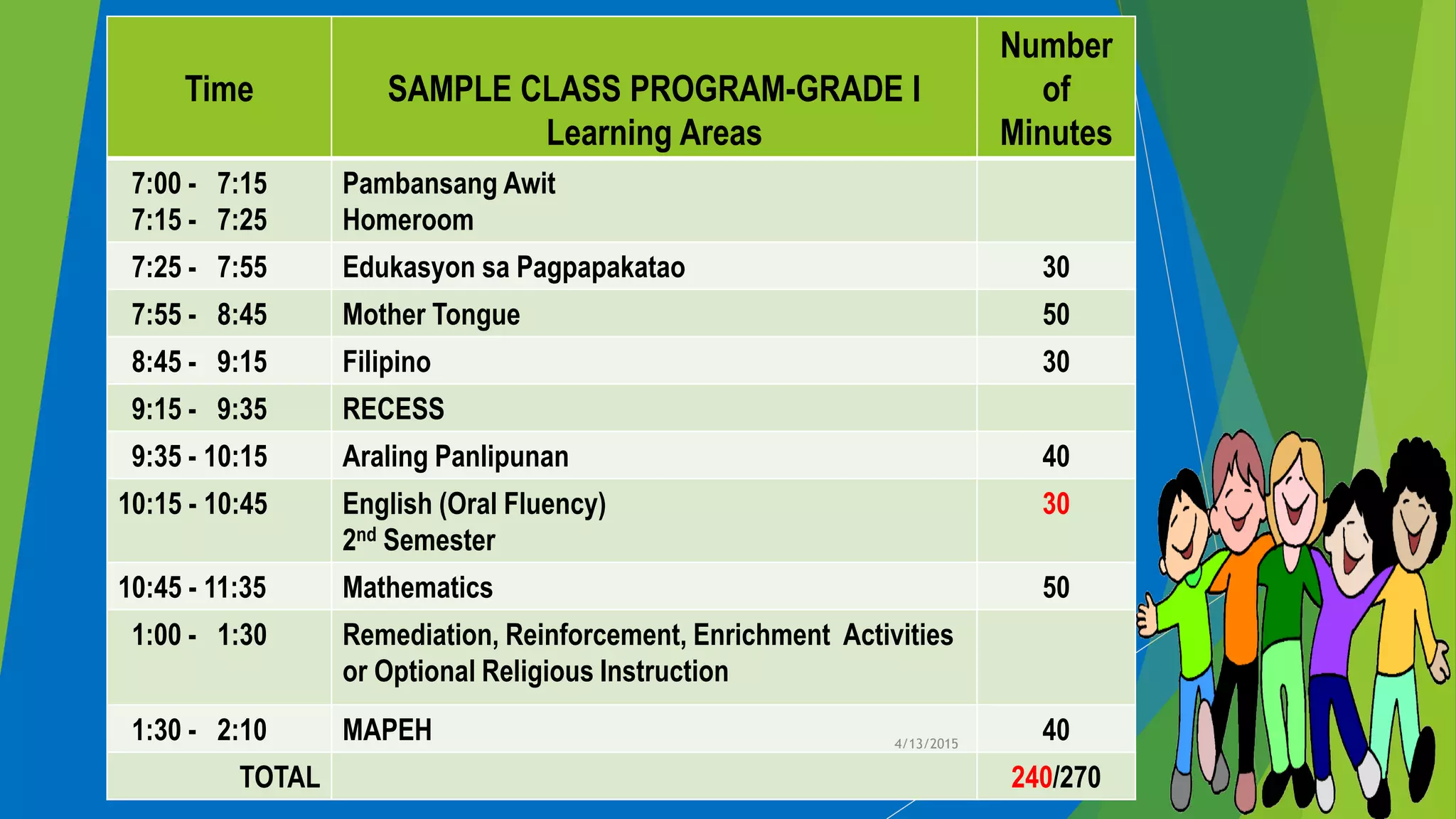
- The learning areas covered from Kindergarten to Grade 12, such as languages, arts, sciences, mathematics, and technology.
- How subjects are taught differently across grade levels, with some only starting in later elementary grades or in secondary education.
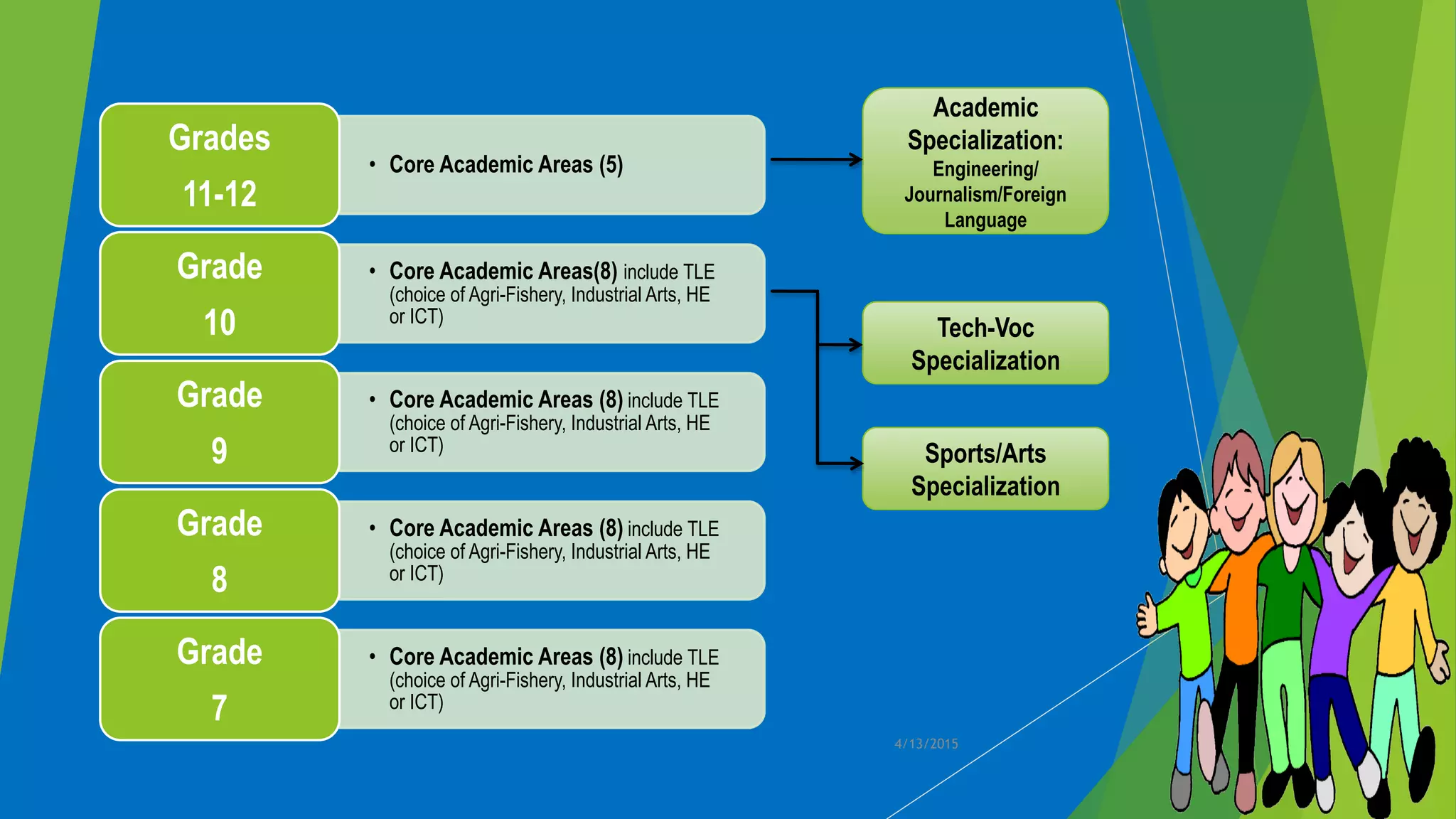
- Details on the exploratory and specialization components of Technology and Livelihood Education (TLE) in junior high school.
- An outline of the proposed core subjects and specializations available in senior high school to prepare students for career paths or further education.